![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the title for chapter 4? |
"Selection, Scale Up, and Scale Down" |
|
|
Describe chemical reactor. |
(1) It is a vessel designed to contain chemical reactions. (2) Aka reaction vessel. |
|
|
Describe Bioreactor. |
(1) It is a vessel where chemical reactions occur involving organism and biologically active substance derived from organism. (2) Usually handles liquid. (3) Process can be aerobic or anaerobic. (4) Support and control biological entities. (5) It is designed to provide higher control over process to prevent contaminations because otganism are more sensitive and less stable than chemical reaction. |
|
|
Describe bioreactor vs chemical reaction. |
(1) The difference between the 2 are selectivity and rate. Bioreactor has higher selectivity. (2) Selectivity is the measure of system capability to produce preferred product. (3) Selectivity is important in production of relatively complex molecules such as antibiotics, steroids, vitamins, proteins, certain sugars, and organic acids. |
|
|
What are the examples bioreaction ? |
(1) Wastewater Treatment. (2) Immobilized enzymes. (3) Cell and tissue culture. (4) Biomass. (5) Pharmaceutical. (6) Food industry. |
|
|
List types of bioreactor. |
(1) Continuous Stirred Tank Bioreactor. (2) Bubble Column Bioreactor. (3) Airlift Bioreactor. (4) Fluidized Bed Bioreactor. (5) Packed Bed Bioreactor. (6) Photo Bioreactor. |
|
|
Describe Continous Stirred Tank Bioreactor. |
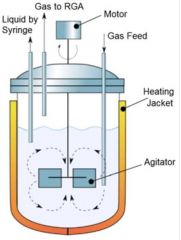
(1) Continuous Stirred Tank Bioreactor (CSTR) aka Stirred Tank Bioreactor (STR). (2) It is a cylindrical vessel with a motor driving shaft at centre that supports one or more agitators (impellers). (3) The height to diameter ratio is between 3-5. For animal cell culture, the ratio is <2. (4) The agitator diameter usually 1/3 of vessel diameter. The distance between 2 agitators approximately 1.2 agitator diameter. , concave bladed, and marine propeller. (5) Different types of agitator are used such as rustom disc, concave bladed, and marine propeller.(6) Sparger adds air into vessel. The air produced is distributed throughout vessel by agitators to create uniform and homogenous environment, and better air diffusion system. , concave bladed, and marine propeller.(6) Sparger adds air into vessel. The air produced is distributed throughout vessel by agitators to create uniform and homogenous environment, and better air diffusion system. (6) Sparger adds air into vessel. The air produced is distributed throughout vessel by agitators to create uniform and homogenous environment, and better air diffusion system. to create uniform and homogenous environment, and better air diffusion system. |
|
|
What are the objectives of liquid mixing in Stirred Tank ? |
(1) To produce uniform liquid concentration. (2) To suspend particles in liquid. (3) To disperse gas for liquid aeration. (4) To transfer heat from or to liquid through coiled tube installed in tank. |
|
|
What are the advantages of CSTR ? |
(1) Efficient gas diffusion to grow cells. (2) Good mixing. (3) Flexible operating conditions. (4) Commercially available. (5) Continous operation. (6) Good temperature control. (7) Simple. (8) Low operating cost. (9) Easy to clean. |
|
|
Describe Bubble Column Bioreactors . |
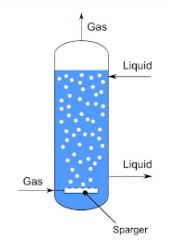
(1) The air is introduced at the base through metal micro porous sparger, or perforated pipes or plates - The air flow rate affects peformance.
(2) The vessel usually cylindrical shaped with 4-6 height to diameter ratio. |
|
|
What are the advantages Bubble Column Bioreactor? |
(1) Low capital cost.
(2) Simple.
(3) Low operational cost.
(4) Low energy requirements.
(5) Low shear rate when supplying oxygen.
(6) Combine high load of solid particles.
(7) Good mass transfer. |
|
|
What is the disadvantage of Bubble Column Bioreactor ? |
Unsuitable for high viscosity liquid and high density plant culture. |
|
|
Describe Airlift Bioreactor. |
(1) The vessel medium is divided into 2 interconnected zones.
(2) One zone referred as riser where the air is pumped. The other zone referred as down comer where no gas is pumped.
(3) This bioreactor commonly for aerobic process.
(4) It use recycle liquid flow system by pumping - The performance depends on pumping, and liquid circulation.
(5) It is more efficient than Bubble Column Biorector in term of mixing because it can handles denser microbes suspensions. |
|
|
What are the types of airlift bioreactor ? |
(1) Airlift bioreactor : - Internal loop airlift - External loop airlift (2) Two-stage airlift bioreactor. (3) Tower bioreactor. |
|
|
Describe internal loop and external loop airlift bioreactor. |
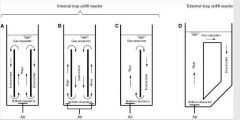
(1) Internal loop airlift bioreactor : - Has draft tube at centre that creates interior liquid circulation channels.
(2) External loop airlift bioreactor : - Has external loop that creates separate liquid independent channels. |
|
|
Describe Two-stage Airlift Bioreactor. |
(1) It is use for temperature dependent process. (2) It is necessary because to raise temperature quickly from 30 to 42°C in a same vessel is very difficult. |
|
|
Describe tower bioreactor. |
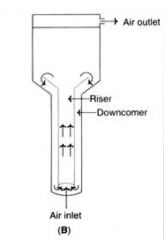
(1) It is a pressure-cycle fermenter with large dimensions. (2) A high hydrostatic pressure generated at the reactor bottom to increase oxygen solubility. (3) Going to top the pressure reduces, and facilitates the expulsion of carbon dioxide. (4) The medium flows back in down comer and completes the cycle. (5) Advantage : Has high aeration capacities without having moving component. |
|
|
What are the advantages of airlift bioreactors ? |
(1) Simple design. (2) Less maintenance. (3) Less risk of defects. (4) Easy sterilization. (5) Lowe energy requirements - do not need energy for moving components. (6) Great heat-removal - do not need heat plate to control temperature, instead has Draught-Tube inside serve as internal heat exchanger. (7) Very low cost. |
|
|
Describe Fluidized Bed Bioreactors. |
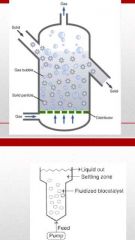
(1) Similar to Bubble Column except the top is expanded to reduce fluid velocity. (2) The design is to let solids retained in vessel while the liquid flows out. (3) This bioreactors are suitable for reactions involving fluid suspended biocatalysts such as immobilized enzymes, cells, and microbial flocs. (4) Aeration installed to create suitable gas-liquid-solid fluid bed for efficient operation. (5) The suspended solids should not be too light or to dense. (6) Recycling of liquid is important to maintain continuous contact between reactants and biocatalysts. |
|
|
What are the advantages of Fluidized Bed Bioreactor ? |
(1) Uniform mixing. (2) Uniform temperature. (3) Continuous operation. |
|
|
Describe Packed Bed Bioreactors. |
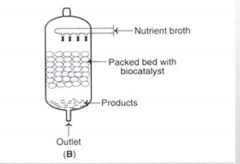
(1) A vessel with a bed of solid particles, with immobilized biocatalysts on or within the solid matrix.
(2) The solid particles used may be porous, or non-porous gels, compressible or rigid.
(3) Nutrient broth flows continuously through the solid bed containing immobilized biocatalyst. (4) The products form can be increased by increase nutrient concentration by increase its flow rate. (5) It is difficult to control the pH by addition of acid or alkali due to poor mixing. (6) This bioreactor is preferred for product-inhibited reactions. |
|
|
Describe photo bioreactor. |

(1) It is specialised for fermentation which can be carried out either by sunlight exposure, or artificial illumination which expensives. (2) Certain important compunds are produced via photo bioreactor such as p-carotene and asthaxanthin. (3) The tube is made up of glass or transparent plastic. (4) The fermenting culture can be circulated by using centrifugal or airlift pumps. The continuous circulation should not producing sediments. (5) The tubes should be cooled to prevent temperature rise. (6) The bioractor usually operated at 25-40° C. (7) Microalgae and cyanobacteria commonly used - The organisms grow during day while products produced during night. - The organisms grow during day while products produced during night. |
|
|
What are the advantages of photobioreactor ? |
(1) High potential for high productivity due to controlled algae cultivation. (2) High productivity due to large surface-to-volume ratio which offers maximum light usage efficiency. (3) Better control of gas transfer. (4) Low evaporation of growth medium. (5) Uniform temperature. (6) Better protection from outside contaminants. (7) Save space - can be mounted vertically, horizontally, or any angle indoors or outdoors. (8) Reduce fouling due to availability of tube self-cleaning mechanisms. |
|
|
What are the strategies for choosing a bioreactor ? |
(1) Microorganism. (2) Growth and oxygen requirements. (3) Shear and rheology effect. (4) Cleaning and sterility. (5) Light. (6) Foam. (7) Heating and cooling. (8) Construction materials. |
|
|
Describe scale up. |
(1) Scale up is migration of lab-scale process to pilot-scale or commercial-scale. (2) Increase scale means increase volume. Performance change with scale. Scale up leads to problems due to affected process parameters by the size of unit. (3) The homogeneity is difficult to control in large-scale due to : - Changes in surface-to-volume ratio. - Changes in culture due to increased culture time. |
|
|
What are the factors involved in scalling up ? |
(1) Inoculum development : - Extra stages may have to be incorporated. (2) Sterilization : - The numbers of contaminants in fermenter must be reduced to the same absolute number. (3) Environmental parameters : - They are affected by agitation and aeration. - Parameters which changed : a) Nutrient availability. b) pH c) Temperature d) DO e) Shear condition f) DCO g) Foam production |
|
|
Describe scale-down. |
(1) A situation where lab or pilot scale are conducted under conditions mimic industrial scale. (2) This approach is important for development of new product, and improvement of existing full-scale fermentation. |
|
|
What are the aspects to consider during scale down? |
(1) Medium design. (2) Medium sterilization. (3) Inoculation procedure. (4) Number of strain generations. (5) Mixing. (6) Oxygen transfer rate. |

