![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Surface anatomy of femoral triangle |
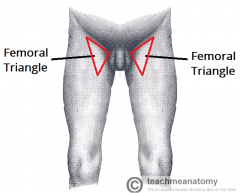
Triangular landmark Appears as depression as thigh is flexed, abducted and laterally rotated. |
|
|
Boundaries |
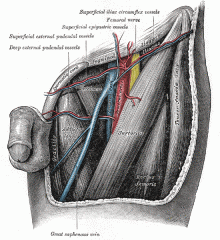
Sup : Ingiunal ligament Medial: Lateral border of adductor longus Lateral: Sartorius Floor: Iliopsoas lat, Pectineus medial Roof: Fascia lata, cribriform fascia, subcutaneous tissue and skin |
|
|
Job of the inguinal ligament |
acts as flexor retinaculum retains structures that pass anteriorly to hip joint against the joint during flexion of the thigh. |
|
|
What is the retroinguinal space |
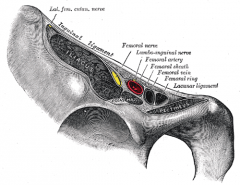
The space between the bony structures ASIS and Pubic tubercle.
Creates important passageway connecting trunk or abdominal cavity
Houses the iliacus, femoral artery, vein, femoral canal as different compartments.
2 rooms separated by thickening of iliopsoas fascia; called iliopectineal arch.
Lateral room: muscular compartment - iliopsoas and femoral nerve
medial room: vascular compartment - major vascular structures. |
|
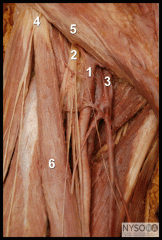
Femoral nerve: origin |
Abdomen descends posterolaterally through pelvis to midpoint of inguinal ligament |
|
|
Femoral nerve journey |
Enters femoral triangle
divides into further branches to ANTERIOR THIGH MUSCLES
Saphenous nerve descends through femoral triangle. |
|
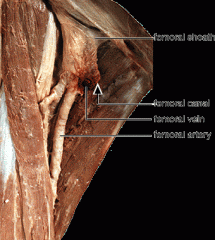
Femoral Sheath: Features |
Funnel shaped fascial tube
3-4 cms
formed by prolongation of Transversalis (ant) and Iliopsoas (post) from abdomen |
|
|
Femoral Sheath: Function |
Lines vascular compartment of retro inguinal space.
Encloses proximal parts of femoral vessels and creates femoral canal medial to them |
|
|
Femoral Sheath: Compartments |
Later: Femoral artery Intermediate: Femoral vein Medial: Femoral canal |
|
|
Femoral canal: features |
1.5 cm long
lies medially to the femoral vein and femoral sheath
contains loose connective tissue, few lymphtic vessels and sometimes a deep inguinal lymph node
allows expansion of femoral vein during venous return from lower limb increases. short canal
Femoral Ring
Femoral Septum |
|
|
Femoral Ring |
Located at superior border
Closed by connective tissue layer |
|
|
Femoral canal: Boundaries |
Lateral: Septum between canal and vein
post: Superior ramus of pubis
medial: lacunar ligament
anter: medial part of inguinal ligment |
|
|
Femoral canal: Contents |
Loose connective tissue
fat
Lymphatic vessels
Deep inguinal lymph node
Inferior epigastic vessels |
|
|
Femoral Septum |
opening is closed by extraperitoneal fatty tissue that forms femoral septum
Femoral septum is pierced my lymphatic vessels connecting inguinal and external iliac lymph nodes. |

