![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Organic Compounds |
Compounds that are made up of carbon atoms and other elements. |
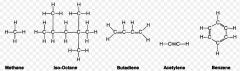
A compound that was once thought to have been formed only by living cells. |
|
|
Macromolecules |
A molecule that contains a very large number of atoms. |
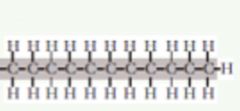
A type of molecule that forms a carbon skeleton in large complex molecules. |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
A group of organic compounds occurring in food, living tissue, and sugar. |

A compound of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen that make CH2O. |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
The simplest form of a carbohydrate. |
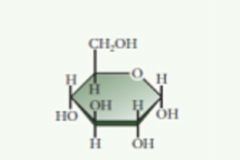
A single sugar molecule that is a type of carbohydrate. |
|
|
Disaccharides |
A sugar composed of two monosaccharides. |
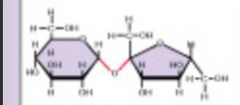
Another type of carbohydrate that joins two sugar molecules. |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Monosaccharides joined together by glycosidic bonds. |
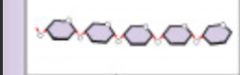
A type of carbohydrate that joins many sugar subunits. |
|
|
Lipids |
Naturally occurring hydrophobic molecules. |

Basically a fat or oil that does not dissolve in water. |
|
|
Fatty acids & glycerd |
A chain of hydrocarbon derived from the breakdown of fats. |
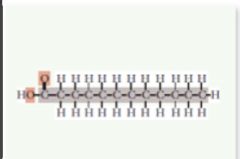
Building blocks of lipids that are most commonly found in diets. |
|
|
Saturated & unsaturated fats |
Unsaturated fats are sometimes oils at room temp. Saturated fats are sometimes solids at room temp. |
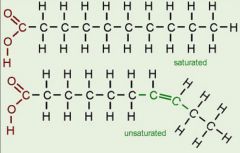
A hard or soft triglyceride at room temperature and are a form of energy storage. |
|
|
Proteins |
Thousand different macromolecules in living cells that help a cells structural component. |

An important enzyme that fights diseases, and is part of the skeleton. |
|
|
Amino acids |
Cells make proteins that are linked by amino acids. |
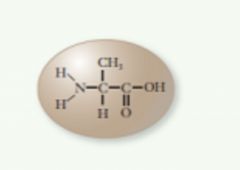
An acid that has a central carbon atom that connects to three other groups and a hydrogen atom. |
|
|
Peptide bond |
A dehydration synthesis reaction that usually occurs between amino acids. |
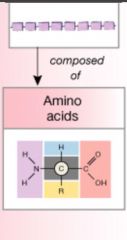
A covalent bond that is formed between amino acids. |
|
|
Polypeptide |
Long polypeptide chains form proteins. |
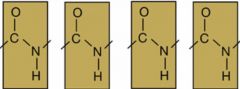
Chains of amino acids that use peptide bonds. |
|
|
Primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary structures |
The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. |
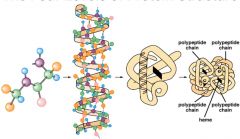
Steps to creating a protein by making a chain, then it folds, twists, then creates folding spherical chains. |
|
|
Enzymes |
A catalyst to bring about a specific biochemical reaction. |
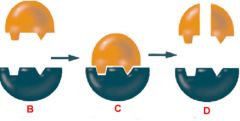
Molecules that help complex reactions occur. |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Macromolecules that decide the amino acid sequence of proteins. |
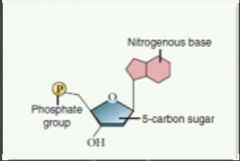
An acid that controls the basic life process and is the source of genetic information. |
|
|
Nucleotides |
A simple unit of nucleic acids. |
Ribose and deoxyribose are two sugars found in this nucleic acid. |
|
|
Deoxyribose |
Deoxyribose is like ribose, but is missing one oxygen. |
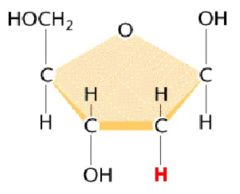
Almost like ribose, but a part in the name means "minus oxygen". |
|
|
Double helix |
A two long chain of nucleotides that run next to each other. |

a model that was constructed by James Watson and Francis Crick. |
|
|
Single helix |
Adenine, guanine, thymine, and cytosine are attached to a phosphate and a deoxyribose to form a backbone. |
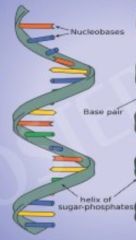
What a normal helix is. |
|
|
DNA |
Nucleotides containing deoxyribose that form DNA. |
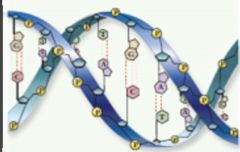
Another name for this is deoxyribonucleic acids. |
|
|
RNA |
Nucleic acids that contain ribose in their nucleotides are RNA. |
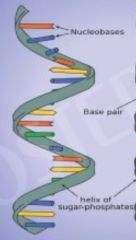
Another name for this is ribonucleic acids. |
|
|
Ribose |
One of the two sugars found in nucleotides that has OH connected to it.
|
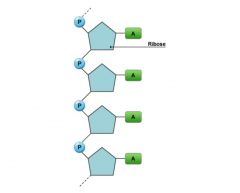
Organic compound with a fomula of C5H10O5. |
|
|
Nitrogen bases |
Symbols used to represent the four different nucleotides. |
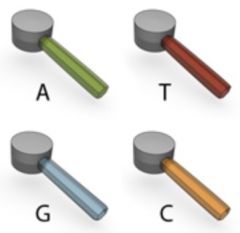
The four ________ bases that occur in nucleotides. |
|
|
Gene |
Units of genetic information. |
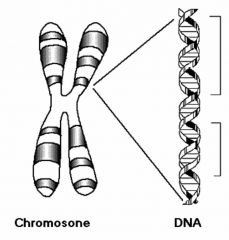
What DNA forms that pass from parent to off spring. |

