![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
list the biological functions of lipids |
1) components of cell membranes (phospholipids & cholesterol) 2) precursors of hormones (cholesterol--> steriod hormones) (arachidonic acid--> prostaglandins) 3) long term fuels (triglycerides)- fat is another source for ATP production |
|
|
list some features of triglycerdies as fuels |
-fat is a storage molecule (compact storage)- triglycerides are stored as fat droplets in the fat cells of adipose tissue -large body stores. Rougly a 70kg adult has 11Kg of fat (as TG), 120g of glycogen in the liver and 10g of glucose. -more energy is released from oxidising fat- 1g of fat yields 38KJ of energy (1g of protein releases 21KJ and 1g of carbohydrate 17KJ) |
|
|
what does a triglyceride fat consist of? |
1 glycerol molecule and 3 fatty acid tails |
|
|
what is the name of a common 16C saturated fatty acid? |
palmitic acid 16:0 |
|
|
what is the name of a common 18C saturated fatty acid? |
stearic acid 18:0 |
|
|
name a common monounsatuated fatty acid... |
oleic acid 18:1 |
|
|
name a common unsaturated fatty acid (with 2 double bonds)... |
linoleic acid 18:2 |
|
|
name a common unsaturated fatty acid (with 3 double bonds) |
linolenic acid 18:3 |
|
|
what is the first step in the energy release from fat? |
the breakdown of stored triglyceride fat in adipose tissue the first step is to separate the fatty acids from the glycerol using lipase enzymes (hydrolyse the fatty acid from the glycerol one by one). |
|
|
what is the lipase enzyme activated by? |
adrenaline and glucagon |
|
|
what happens to the free fatty acids? |
fatty acids are bound to a protein called albumin and transported into the blood |
|
|
how is glycerol metabolised? |
Glycerol is water soluble and is taken up by all tissues. In most tissues, glycerol enters the glycolysis pathway (gets made into dihydroxyacetone and then into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate) for conversion to pyruvate, then into TCA cycle for oxidation to C02 In the liver (in starvation) glycerol enters the glycolysis pathway and is converted to glucose by gluconeogenesis. |
|
|
how are fatty acids metabolised? |
1) activation of fatty acids by formation of fatty acyl-coA derivatives 2) transport of fatty acyl-CoA derivatives into the mitochondria
3) conversion of fatty acyl-CoA into acetyl-CoA molecules inside the mitochondrion by B-oxidation pathway |
|
|
list some features of fatty acid metabolism... |
-all reactions occur in the mitochondrial matrix -intermediates present as CoA thioesters -the biological energy of fatty acid molecules are conserved as the transfer of 2 H atoms to the cofactors NAD+ and FAD to form NADH & FADH2 (no direct ATP synthesis)- reduced carrier molecules store the energy from fatty acid breakdown -a series of 4 enzyme reactions results in the removal of two carbon units as acetyl CoA |
|
|
step 1, the activation of long chain fatty acids... |
-Acetyl-CoA formation from fatty acids (occurs in the cytosol) -Add a Co-ASH to the fatty acid, ATP is phosphorlyated to AMP + PPi (ATP is used only for energy not for phosphorlylation) -creates an activated fatty acid- Fatty acyl-CoA catalysed by fatty acyl-CoA synthetase |
|
|
the Coenzyme A forms a thioester bond with the carboxylic acid ( of the fatty acid) |
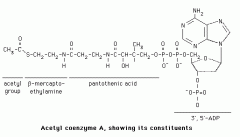
|
|
|
diagram of activation of long chain fatty acids... |
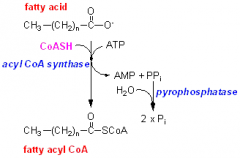
|
|
|
the next step is the transport of fatty acyl CoA into the mitochondria. This creates a problem because... |
the outer mitochondrial membrane is permeable to most metabolities thus the fatty acyl-CoA crosses it to enter the intermembrane space but cannot cross the inner mitochondrial membrane to reach the site of conversion into acetyl-CoA (mitochondrial matrix) |
|
|
Step 2-Transport of fatty acyl-CoA deriviatives into the mitochondria Stage 1 of fatty acid transport into the mitchondria... |
When the fatty acyl-CoA crosses the outer mitchondrial membrane, the acyl group splits off from the CoA and gets attached to carnitine- Acyl group forms a ester linkage with carnitine. |
|
|
what is the enzyme that catalyses the transfer of acyl from CoA to carnitine? |
Carnitine palmitoyl-transferase 1 (or carnitine acyltransferase 1, located in the outer mitochondrial membrane) |
|
|
at the end of stage 1 of transport into the mitochondria we have... |
the fatty acyl group attached to carnitine in the intermembrane space |
|
|
Transport of fatty acids into mitochondria stage 2- crossing the inner mitochondrial membrane |
-the acyl-carnitine complex is transferred across the inner mitchondrial membrane by a translocase -Carnitine is exchanged for co-enzyme A to make actyl-CoA - catalysed by carnitine palmitoyl-transferase II (or acyltransferase II, located in the inner mitochondrial membrane) |
|
|
at the end of stage 2 of transport into the mitchondria we have... |
a fatty-acyl CoA molecule in the mitchondrial matirx |
|
|
Step 3- Conversion of the fatty acyl-CoA into acetyl-CoA molecules inside the mitchondrion by B-oxidation pathway... |
consists of 4 reactions removal of 2 carbons at a time from fatty acid |
|
|
reaction 1 is a... |
oxidation reaction- removal of 2 H atoms (creates a c=c) FAD becomes reduced to FADH2 catalysed by acyl-CoA dehydorgenase |
|
|
diagram of reaction 1 |
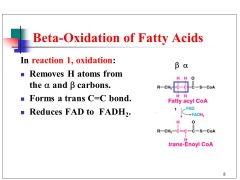
|
|
|
reaction 2 is a... |
hydration reaction (addition of H20) across the c=c bond catalysed by Enoyl-CoA hydratase results in a hydroxyacyl-CoA |
|
|
reaction 3 is another oxidation reaction... |
it involves the removal of 2 H atoms- NAD becomes reduced to NADH catalysed by Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (the hydroxyl group is oxidised to a ketone)- produces B-ketoacyl-CoA |
|
|
reaction 4 involves... |
the removal of 2C units by the addition of Coenzyme A molecule 2 carbons are split off as aceyl-CoA forming a shorter fatty acetyl CoA derivative. catalysed by a thiolase enzyme- the molecule is split by the -SH group |
|
|
overall B oxidation |
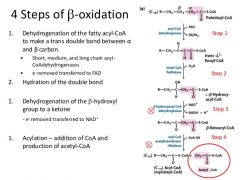
|
|
|
the acetyl CoA formed enters the TCA cycle and the fatty acyl-CoA (2 carbons shorter) ... |
... goes through the same 4 reactions again (oxidation, hydration, oxidation, removal of 2C by addition of actyl-CoA) |
|
|
each 4 reactions produces... |
1 FADH2 1 NADH + H+ |
|
|
a fatty acid with 16 C atoms will pass through 7 repeats of the B oxidation pathway producing 7 NADH and 7 FADH2 |
the same fatty acid (16C) will also give rise to 8 acetyl CoA which enter the TCA cycle. |
|
|
the energy yield from fatty acid oxidation... |
16 carbon fatty acid ATP = (2.5 x 7) + (1.5 x 7) = 28 fatty acid with 16C atoms produces 8 acetyl CoA, ATP yield from complete oxidation of acetyl CoA by TCA cycle= 8 x 10 ATP= 80 Total= 80+28= 108 -1 = 107 |
|
|
107 ATP are yielded, from which it can be concluded that... |
fat is a much more energy efficient storage molecule |
|
|
regulation of fat metabolism... |
-release of fatty acids from adipose tissue is regulated by adrenaline and glucagon ( which activate the lipase enzyme) -regulation of rate of entry into mitochondria via carnitine shuttle -regulation of rate of reoxidation of cofactors NADH & FADH2 by cytochrome chain (feedback via ETC) |
|
|
the metabolism of odd numbered fats involves an extra step... |
-add CO2 to add an extra carbon -this makes the 3C molecule to 4 carbons -this 4C molecule undergoes isomerisation t make succinyl-CoA which can enter the TCA cycle. |
|
|
ketone body formation (ketogenesis) occurs when... |
fat metabolism is the main source of energy (in starvation and in Type 1 diabetes) |
|
|
how are ketone bodies formed? |
fatty acid oxidation in hepatocytes leads to high concentrations of Acetyl-CoA but not enough oxaloacetate to react with it. - acetyl CoA exceeds the capacity of the TCA cycle The liver then takes the acetyl CoA and concerts it into ketone bodies i.e Acetoacetate and B-Hydroxybutyrate |
|
|
if ketone bodies are present in the blood in high concentrations it can... |
alter the pH of the blood due to the presence of more COO- ----> ketoacidosis. |
|
|
ketone bodies can be utilised for energy by most (but not all) tissues... |
-the liver cannot utilise ketone bodies -the brain cannot utilise fatty acids (fats can't pass the blood brain barrier) -red blood cells can only use glucose because they have no mitochondria- can only undergo glycolysis. |

