![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are fatty acids synthesized from?
|
Acetyl CoA
|
|
|
What is "Fat" synthesized from?
|
Fatty acids and glycerol
|
|
|
Where is fat stored?
|
In adipose cells
|
|
|
What is made from surplus carbohydrate and proteins?
|
Acetyl CoA
|
|
|
What transports acetyl CoA from the mitochondria to the cytosol?
|
The citrate shuttle:
Citrate -> malate -> pyruvate shuttle |
|
|
Where in the cell is Acetyl CoA synthesized?
|
In the mitochondrial matrix
|
|
|
What enzyme carries out fatty acid synthesis? where is this reaction carried out in the cell?
|
By fatty acid synthase in the cytosol
|
|
|
Where does the majority of fatty acid synthesis take place?
|
In the liver
|
|
|
Where is the citrate transporter located?
|
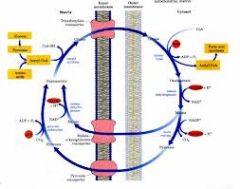
In the inner mitochondrial membrane
|
|
|
What is the citrate synthase enzyme's reaction? Where does it take place?
|
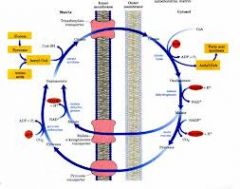
Acetyl CoA + OAA -> citrate, which takes place in the mitochondrial matrix
|
|
|
What happens to citrate once it crosses into the cytosol?
|
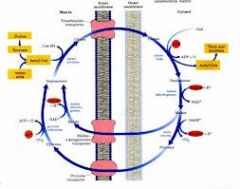
It is lysed by ATP-citrate lyase to form Acetyl Coa and OAA using ATP.
|
|
|
What happens to the OAA that is produced from the citrate shuttle?
|
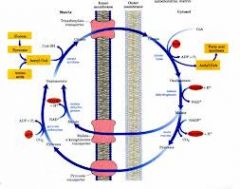
It is reduced to malate using NADH by malate dehydrogenase.
|
|
|
What happens to malate in the citrate shuttle?
|
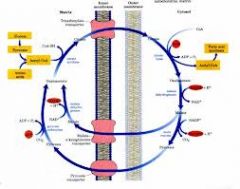
It is decarboxylated by malic enzyme using NADP+ to form pyruvate, NADPH and CO2
|
|
|
What happens to Pyruvate in the citrate shuttle?
|
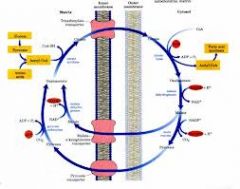
It crosses the inner mitochondrial membrane where it forms OAA using ATP and CO2 by pyruvate carboxylase.
|
|
|
What products of the citrate shuttle are used in fatty acid synthesis?
|
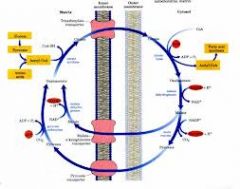
Acetyl CoA and NADPH
|
|
|
What is the first step in fatty acid synthesis?
|
Carboxylating the acetyl CoA to turn it into malonyl CoA
|
|
|
What is the reaction that forms malonyl CoA?
|
Acetyl CoA and Co2 are carboxylated to form malonyl CoA by acetyl CoA Carboxylase using ATP
|
|
|
What coenzyme is required by Acetyl CoA carboxylase?
|
Biotin
|
|
|
What is the committed step in fatty acid biosynthesis?
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase
|
|
|
What regulates acetyl CoA carboxylase?
|
1. adenylate energy charge
2. hormones 3. allosteric effectors |
|
|
What is the adenylate energy charge?
|
The fraction of the adenine nucleotides in a cell that contains a high-energy phosphoanhydride bonds (~P).
*It is a quantitative description of the cell's ~P energy state. |
|
|
How do you calculate the energy charge of a cell?
|
E.C. = ([ATP] + .5[ADP])/([ATP] + [ADP] + [AMP])
|
|
|
What is the energy charge of well-nourished aerobic cells?
|
~ 0.9, a high energy charge
|
|
|
What is the relationship b/e energy charge and acetyl CoA carboxylase activity?
|
The higher the energy charge the more active the acetyl CoA carboxylase will be.
|
|
|
What is Insulin's effect on acetyl CoA Carboxylase?
|
Insulin promotes dephosphorylation of acetyl CoA carboxylase via protein phosphatase 24.
*promotes formation of the active form of acetyl CoA carboxylase |
|
|
What are glucagon/epinephrine's effects on acetyl CoA Carboxylase?
|
Promote phosphorylation of acetyl CoA carboxylase to its inactive form via cAMP-dependent protein kinase.
|
|
|
What effect does a low cell energy charge have on acetyl coa carboxylase?
|
Stimulates phosphorylation of acetyl coa carboxylase to its inactive form via AMP-activated protein kinase.
|
|
|
What is the inactive form of acetyl coa carboxylase?
|
It exists as a inactive dimer and as active filaments
|
|
|
What effect does citrate have on acetyl coa carboxylase?
|
Citrate facilitates the formation of active filaments, so it activates acetyl coa carboxylase formation by causing the inactive dimers to come together and form a polymer which is the active enzyme.
|
|
|
What effect do long-chain fatty acyl CoAs such as palmitoyl CoA have on acetyl CoA carboxylase?
|
causes the disassembly of the acetyl coa carboxylase polymer to its inactive dimer form.
*so it is a negative feedback loop |
|
|
What is fatty acid synthase?
|
A multi-subunit complex on which fatty acid synthesis is carried out. It contains two sulphhydril groups.
|
|
|
What is attached to the ACP-pantetheinyl sulfhydril group?
|
A malonyl group
|
|
|
What is attached to the cysteinyl sulfhydril group?
|
An acetyl group
|
|
|
What are the two components of fatty acid synthase?
|
A cysteinyl SH and a ACP-pantetheinyl SH
|
|
|
What happens to the acetyl and malonyl groups after they are attached to their SH groups?
|
They condense to form a acetoacetyl group that is attached to the ACP-pantetheinyl sulfhydryl.
|
|
|
What drives the fatty acid synthase reactions to keep going in the forward direction?
|
The fact that CO2 is produced in the final step of the reaction which is then exhaled, the removal of the product drives the reaction via le chatelier's principle.
|
|
|
How many cycles does the Fatty acid synthase reaction go through to generate palmitate?
|
7 total cycles
|
|
|
What is the sequence of reactions that occurs during reduction of the ketone sequence after the synthesis of acetoacetyl-enzyme?
|
Two NADPH linked reductions w/ a dehydration in between.
|
|
|
Where does beta-oxidation occur?
|
In the mitochondria
|
|
|
Where does fatty acid synthesis occur?
|
in the cytosol
|
|
|
What is the importance of the compartmentalization of fatty acid synthesis and beta-oxidation?
|
That both processes can proceed in their forward direction w/o substrate cycling.
|
|
|
How can fatty acids be modified?
|
By chain lengthening and by introducing double bonds (desaturation)
|
|
|
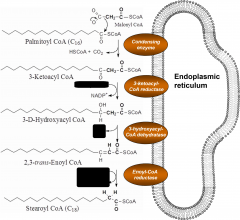
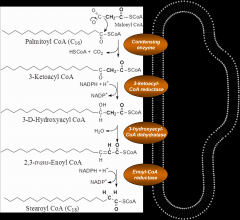
Where do fatty acid elongation reactions take place?
|
In the ER
|
|
|
How is FA elongation carried out in the ER?
|
By condensation of palmitoyl CoA w/ malonyl CoA
|
|
|
What is the function of unsaturated fatty acids?
|
Important for regulating the fluidity of TAGs and membrane phospholipids as well as forming cholesterol esters and waxy skin secretions.
|
|
|
What is the furthest down the FA chain that double bonds can be introduced?
|
Carbon 9
|
|
|
What is used to synthesize eicosanoids?
|
polyunsaturated fatty acids
|
|
|
What are the essential fatty acids?
|
Linoleic acid or alpha-linolenic acid
|
|
|
What does Steaoryl CoA desaturase do? where is it located?
|
Located in the ER it introduces a C9 double bond forming oleic acid
|
|
|
What are triacylglycoerols (TGs/fat) made from?
|
Phosphatidic acid
|
|
|
What is phosphatidic acid made from?
|
Actyl CoA and glycerol phosphate or dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
|
|
where else do you find dihydroxyacetone phosphate besides TG synthesis?
|
Glycolysis
|
|
|
What are the sources of glycerol phosphate for fat synthesis?
|
Glucose and glycerol
|
|
|
Where is glycerol-P-dehydrogenase located?
|
In adipose tissue and in the liver
|
|
|
Where is glycerol kinase located?
|
In the liver
|
|
|
What does glycerol kinase do?
|
Converts glycerol to glycerol-3-phosphate using ATP
|
|
|
What does glycerol-P-dehydrogenase do?
|
Converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate to glycerol-3-phosphate using NADH
|
|
|
What is phosphatidic acid synthesized from?
|
Glycerol phosphate and acyl CoA OR from dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
|
|
What is triacylglycerol synthesized from?
|
Phosphatidate
|
|
|
What is the process of phosphatidate synthesis from triacylglycerol?
|
Phosphatidic acid is converted to diacylglycerol using water and the enzyme phosphatase
Then triacylglycerol is synthesized from diacylglycerol using SCoA and the enzyme acyltransferase |
|
|
Why store fat and not glycogen?
|
Glycogen takes more space and is more polar, so you can store way more TAG than glycogen.
|
|
|
What do membrane lipid complexes contain?
|
1. phosphatidates
2. ether lipids 3. sphingolipids 4. cholesterol |
|
|
What does phosphatidate synthesis begin with?
|
Diacylglycerol and phosphatidate
|
|
|
How are phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine synthesized?
|
By transferring activated bases to DAG.
|
|
|
What provides the activated bases in phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine synthesis?
|
CDP derivatives
|
|
|
How is phosphatidylserine synthesized?
|
By exchanging serine for ethanolamine on PE
|
|
|
How are cardiolipid and phosphatidylinositol synthesized?
|
1. DAG is activated to CDP-diacylglycerol
2. Phosphatidylglycerol displaces CMP to yield cardiolipin. 3. Inositol displaces CMP to yield phosphatidylinositol |
|
|
Do sphingolipids contain a glycerol moiety? what is their moiety?
|
Nope, their alcohol moiety is sphingosine
|
|
|
What is the reactive nucleotide in making phosphatidylcholine?
|
Cytidine (CTP); which makes the reactive amine which reacts w/ DAG to make phosphatidylcholine (lecithin)
|
|
|
What is the reactive nucleotide in making glycogen?
|
UDP-glucose
|
|
|
How are CDP-ethanolamine and CDP-choline synthesized?
|
By taking ethanolamine or choline => reacting them w/ ATP using ethanolamine kinase or choline kinase, then taking the phosphoethanolamine/phosphocholine and reacting them w/ the reactive nucleotide CTP to yield CDP-ethanolamine or CDP-choline
|
|
|
How do you make phosphatidylethanolamine or phosphatidylcholine (PC, or lecithin)?
|
By taking CDP-choline or CDP-ethanolamine and reacting them w/ DAG, CMP is a byproduct.
|
|
|
How do you make phosphatidylserine?
|
By reacting phosphatidylethanolamine w/ serine, this yields phosphatidylserine and gives off ethanolamine as a byproduct.
|
|
|
How do you make diacylgylcerol? (DAG)
|
1. By taking a long chain fatty acid, reactive it w/ CoA using acyl CoA synthase to give long chain fatty acyl CoA.
2. Then taking long-chain fatty acyl CoA and react it w/ glycerol using glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase to give a monoglycerol. 3. The monoglycerol is reacted w/ another long-chain fatty acyl CoA using acyl glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase to yield a DAG w/ a phosphate 4. The DAG w/ phosphate is dephosphorylated using phosphatidic acid phosphatase to DAG. |
|
|
What are the "cephalins"?
|
1. phosphatidylethanolamine
2. phosphatidylserine |
|
|
What is the difference b/e cardiolipin/phosphatidylinositol synthesis and phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylethanolamine/phosphatidylserine synthesis?
|
In cardiolipin and phosphatidylinositol instead of activating the group (i.e. choline) they activate glycerol instead.
|
|
|
How are cardiolipin and phosphatidylinositol synthesized?
|
1. DAG is activated as CDP-diacylglycerol
2. Phosphatidylglycerol displaces CMP to yield cardiolipin. 3. inositol displaces CMP to yield phosphatidylinositol |
|
|
What is the importance of phosphatidylinositol?
|
It can be phosphorylated to form the phosphoinositides like PIP, PIP2 and PIP3
|
|
|
How are ether lipids synthesized?
|
1. An acyl group is esterified to C1 of dihydroxyacetone phosphate
2. the acyl group is displaced by fatty alcohols to produce an ether linkage at C1 3. the keto-group at C2 is reduced by NADPH 4. A fatty acid ester is formed at C2 using Acyl CoA 5. Dephosphorylation at C3 and addition of choline follow. |
|
|
What is the starting substrate of phosphatidalcholine synthesis?
|
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
|
|
|
What is the clinical importance of phosphatidalcholine?
|
The fatty acyl group at C2 can be replaced w/ an acetyl group to yield platelet-activating factor (PAF).
|
|
|
When is PAF synthesized and released?
|
When polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) are stimulated.
|
|
|
What processes does PAF mediate?
|
1. platelet aggregation
2. hypersensitivity 3. acute inflammatory responses 4. allergic responses 5. anaphylactic shock |
|
|
What does sphingolipid synthesis start with?
|
Palmitoyl CoA and serine
|
|
|
What is produced if you add a NH2 to C2 of sphinganine?
|
A dihydroceramide
|
|
|
What is produced by reacting palmitoyl CoA and serine?
|
Sphinganine
|
|
|
What does desaturation of dihydroceramide yield?
|
ceramide
|
|
|
What does addition of phosphorylcholine to C1 of ceramide yield?
|
sphingomyelin
|
|
|
What does addition of a sugar at C1 of ceramide yield?
|
If you added galactose you get galactosylcerebroside; if you added glucose you get glucosylcerebroside
|
|
|
What does adding an oligosaccharide containing N-acetylneuraminic acid to C1 of ceramide produce?
|
Ganglioside
|
|
|
|

