![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
218 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What can be used in both adults and children for up to 8 weeks as daily prophylaxis during an Influenza outbreak?
|
Amantidine
|
|
|
Treatment for a 10 cm enlarging hematoma adjacent to the episiotomy site in a baby who you delivered 6 hours ago
|
removal of the sutures and clots, and ligating the bleeding sites
|
|
|
Common cause of Retinal Detachment
|
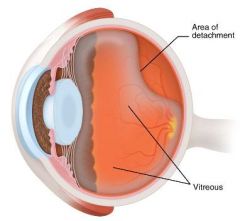
Posterior detachment of the Vitreous
Vitreous detachment is very common after age 60 and occurs frequently in younger persons with myopia.The separation of the posterior aspect of the vitreous from the retina exerts traction on the retina, with theattendant risks of a retinal tear and detachment. Symptoms of retinal detachment may include light flashes(photopsia), a sudden appearance or increase in “floaters,” or peripheral visual field loss, any of whichshould prompt an ophthalmology referral. Cataract surgery can result in premature shrinkage of the vitreousand thereby poses an increased risk, but vitreous detachment resulting from other processes is more common.Hyphema, glaucoma, and diabetic retinopathy are not specific risk factors for retinal detachment. |
|
|
Treatment of choice for a 4 year old with suspected Pertussis?
|
Erythromycin, Azithromycin, or Clarithromycin
|
|
|
What vitamin has been shown to reduce the risk of falling in the elderly?
|
Vitamin D
|
|
|
What is an effective treatment for Bulimia nervosa?
|
Fluoxetine
A number of placebo-controlled, double-blind trials have demonstrated the effectiveness of a variety of antidepressants in the treatment of bulimia nervosa. Fluoxetine has FDA approval for this indication. The other agents are not used for treating bulimia. |
|
|
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
A)sets a federal minimum on the protection of privacy B)requires that privacy notices be acknowledged and signed at eachofficevisit C)allows the patient to inspect and obtain a copy of his/her record without exception D)requires privacy notices prior to giving emergency care |
ANSWER: A
HIPAA regulations set a minimum standard for privacy protection. Privacy notices must be provided at the first delivery of health services, and written acknowledgement is encouraged but not required. Exceptions to patient inspections include psychotherapy notes and instances where disclosure is likely to cause substantial harm to the patient or another individual in the judgment of a licensed health professional. Although it is not necessary to provide patients with a privacy notice at the time of rendering emergency care,it is required that patients be provided with a privacy notice after the emergency has ended. |
|
|
What is the most common cause of visual loss in children?
|
Amblyopia = Amblyopia refers to diminished vision in either one or both eyes, for which no cause can be discovered upon examination of the eye. Amblyopia is the medical term used when the vision in one of the eyes is reduced because the eye and the brain are not working together properly. The eye itself looks normal, but it is not being used normally because the brain is favoring the other eye. This condition is also sometimes called lazy eye
Evaluation of visual symptoms in children canbe challenging, but is important for identifying correctableconditions.Amblyopia, or“lazy eye,”is the most common cause of visual loss, with a prevalence of 2% inchildhood. It isoftenrelated to strabismus, in which the image from one eye is suppressed in order toeliminate diplopia. Iritis is unusual and may have minimal symptoms; it isfrequently associated withjuvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Glaucoma does occur in children, oftenaftercataract surgery. Eye trauma isrelatively common, especially in boys. They may sustain abrasions, foreign bodiesandpenetrating injuries.Conjunctivitis will usually resolve without visual loss except when complicated by keratitis, such as inherpetic infections. |
|
|
What tumor marker is used to detect the recurrence of colon cancer?
|
CEA
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is a marker for colon, esophageal, and hepatic cancers. It is expressed innormal mucosal cells and is overexpressed in adenocarcinoma, especially colon cancer. Though not specific for colon cancer, levels above 10 ng/mL are rarely due to benign disease. CEA levels typically return tonormal within 4–6 weeks after successful surgical resection. CEA elevation occurs in nearly half of patientswith a normal preoperative CEA level that have cancer recurrence. |
|
|
Tumor marker for Ovarian Cancer?
|
CA-125
|
|
|
What levels are elevated in PCOS?
|
Testosterone
LH and FSH (usually 3:1) This patient presented with classic symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)—oligomenorrhea,infertility, hirsutism, and acne—reflecting hyperandrogenic anovulation. The underlying pathophysiologyof PCOS includes insulin resistance leading to increased ovarian androgen production. LH and FSH levelsare often elevated in PCOS, with the LH:FSH ratio often being greater than 3:1. Prolactin is usually normal,although mild elevations are possible. |
|
|
What is the most effective drug used for the treatment of Alcohol dependence?
|
Naltrexone (ReVia)
* opioid receptor antagonist |
|
|
What method most reliably detects a ureteral stone?
|
Helical CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis without contrast
An unenhanced helical CT scanof the abdomen and pelvis is the best study for confirming the diagnosis ofa urinary tract stone in a patient with acute flank pain, supplanting the former gold standard, intravenous pyelography. A CT scan may also reveal other pathology, such as appendicitis, diverticulitis, or abdominalaortic aneurysm. Although abdominal ultrasonography has a very high specificity, it is still not better than CT, and its sensitivity is much lower; thus, its use is usually confined to pregnant patients with a suspected stone. Plain abdominal radiographs may show the stone if it is radiopaque, and are useful for following patients with radiopaque stones. CT will reveal a radiopaque stone. While most patients with stones will have hematuria, its absence does not rule out a stone. |
|
|
What method has been shown to prolong survival in cases of COPD?
|
oxygen therapy
|
|
|
Radiologic evaluation of the cervical spine shows an air-fluid level in the Sphenoid sinus. What facial fracture would this be consistent with?
|
Basilar Skull Fracture
|
|
|
Facial fracture associated with double vision, fluid in the Maxillary sinus, an air-fluid level in the maxillary sinus, and diplopia?
|
Orbital floor fractures
|
|
|
Facial fractures more visible in Towne's view and have characteristic swelling and lateral orbital bruising
|
Zygomatic arch fractures
|
|
|
Facial fractures associated with dental misalignment or bleeding
|
Mandible fractures
|
|
|
Which vitamin reverses the effect of Warfarin?
|
Vitamin K
|
|
|
What class of antihypertensives may help preserve bone mineral density?
|
HCTZ
|
|
|
What drug would be used for first-line treatment of OCD with a depressive episode?
|
Fluoxetine or other SSRI's
-Escitalopram -Sertraline (Zoloft) -Paroxetine (Paxil) Clonazepam would be 2nd line |
|
|
Pain during rest and exercise and the presence of swelling and soreness behind the knee and in the calf is found in those with?
|
Baker's cysts
|
|
|
What finding would support the diagnostic impression of peripheral vascular disease?
|
Treadmill arterial flow studies showing a 20-mm HG decrease in ankle systolic blood pressure immediately following exercise
|
|
|
Read question 31 on Exam Book 1
|
-
|
|
|
What medications are most effective for Restless Leg Syndrome?
|
Carbidopa/Levodopa (Sinemet)
or Ropinirole (Requip)or Pramipexole (Mirapex) -Dopamine agonists used in Parkinson's disease |
|

-
|

Anticoagulation with Warfarin
|
|
|
What are the key factors in the diagnosis of Streptococcal pharyngitis?
|
1. fever > 100.4
2. Tonsillar exudates 3. Anterior Cervical LAD 4. absence of cough |
|

-
|

A
|
|
|
Imiquimod (Aldara) is approved by the FDA for the treatment of what?
|
External genital and perianal warts in pts 12 year and over
BUT it is also used off-label for plantar warts, flat warts, periungual warts, and mollucsum contagiosum |
|
|
What is used prophylactically after total knee or hip replacements to prevent DVT's?
|
LMW-heparin (Enoxaparin 30 mg subQ q 12h) and adjusted dose Warfarin
*these can be augmented by intermittent pneumatic compression |
|
|
What is Black Cohosh?
|
Herbal preparation widely used in the treatment of Menopausal symptoms and menstrual dysfunction
|
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
What medication class is the most appropriate for treating patients with Post-traumatic stress disorder?
|
SSRI's due to low side-effect profile
-Sertraline, Escitalopram, Paroxetine |
|
|
What drug class is contraindicated in the treatment of patients with cocaine-arrhythmias? Why?
|
Beta-blockers (Metoprolol)
b/c they have been shown to exacerbate coronary vasospasm |
|
|
A 3 yo female is brought to your office for evaluation of mild intoeing. The child's patellae face forward, and her feet point slightly inward. What is the most appropriate thing to do? What is the cause of this?
|
Reassurance
Internal Tibial Torsion is believed to be caused by sleeping in the prone position, and sitting on the feet. In 90% of cases, the condition gradually resolves w/o intervention by the age of 8. |
|
|
When is it recommended to screen women for Gestational Diabetes?
|
24-28 WGA
*pt is given 50-g oral glucose load followed by glucose determination 1 hour later |
|
|
What co-morbidity is Sleep Apnea associated with? By improving sleep apnea this condition may also be improved.
|
Hypertension
|
|
|
What medication can provide rapid relief of the symptoms of a patient in severe panic disorder?
|
Alprazolam (Xanax) - works in hours
|
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
After how many weeks is a pregnancy termed "post-date or post-term"? What is the signifigance?
|
42 weeks
b/c perinatal mortality doubles at 42 WGA |
|
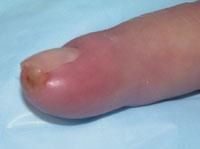
When draining a felon, what incision is recommended?
|
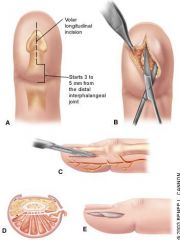
High lateral incision or volar longitudinal incision
|
|
|
Leishmaniasis
|

A 36 yo member of the National Guard who has just returned from Iraq consults you b/c of several "boils" on the back of his neck that have failed to heal over the last 6 months, despite 2 week-long courses of cephalexin. you observe 3 1-to-2-cm raised minimally tender lesions with central ulceration and crust formation. He denies any fever or systemic symptoms. What is the most likely cause?
|
|
|
What is the earliest presenting symptoms in most older patients with open-angle glaucoma?
|
Tunnel vision = gradual loss of peripheral vision
|
|
|
DOC's for Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
|
SSRI's
-Fluoxetine, Sertraline |
|
|
Why should patients with CHF avoid taking NSAID's?
|
b/c they cause Sodium and water retention, as well as increase systemic vascular resistance which may lead to cardiac decompensation
|
|
|
A pregnant patient is positive for Hepatitis B surface antigen. What is the most appropriate therapy for the infant?
|
Hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) and Hepatitis B vaccine at birth
Testing for seroconversion is recommended at 9-12 months of age |
|
|
What is the amount of RhoGam administered to an Rh negative mother if she has an ectopic pregnancy/spontaneous/therapeutic abortion at less than 12 WGA? > 12 WGA?
|
< 12 WGA = 50 g RhoGAM
> 12 WGA = 300 g |
|
|
What is the leading cause of death among women?
|
Cardiovascular disease
|
|
|
Describe "postpartum blues"
|
affect up to 85% of women and typically resolve by the 10th day postpartum
|
|
|
Describe Postpartum Depression
|
may not occur until 6 months following delivery (as opposed to postpartum blues, which resolves by 10 days postpartum)
Can be treated with SSRI's |
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
Describe GER in infants
-is it normal? -is it harmful? |
It is common & self-limited and represents a physiologic process of "spitting up"
Occurs in the absence of poor weight gain, irritability, cough, pain, or anemia...majority are thriving Usually resolves by 1 year of age |
|
|
What is the most frequent etiologic agent of occult bacteremia in children?
|
S. pneumo
|
|
|
What is the cause of Kaposi's Sarcoma?
|
HHV-8
|
|
|
How long is the Nuvaring kept in place before removing it?
|
3 weeks and then removed for 1 wk so that withdrawal bleeding occurs
-new ring is then inserted If for some reason the ring is out of the vagina for more than 3 hours, back-up contraception should be used until the device has been in place for 7 days |
|
|
What is the prophylactic treatment for an outbreak of Menigococcal disease in a day care center?
|
Rifampin
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of chronic, unilateral nasal obstruction in adults?
|
Nasal septal deviation
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of nasal obstruction in all age groups?
|
Common cold
-usually bilateral and intermittent |
|
|
What is the most common tumor or growth to cause nasal obstruction?
|
Adenoidal hypertrophy followed by nasal polyps
|
|
|
List the 4 diagnostic criteria for Delerium
|
1. disturbances of consciousness with reduced ability to focus, sustain, or shift awareness
2. A change in cognition (memory, disorientation, language disturbance) or development of a perceptual disturbance that is not better accounted for by a preexisting, established, or evolving dementia 3. Development over a short period of time with a tendency to fluctuate during the course of a day 4. Evidence from the history, PE, or lab findings that indicated the disturbance is caused by direct physiologic consequences of a general medical condition |
|
|
What treatment is recommended for intravaginal genital warts in pregnant women?
|
Cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen
|
|
|
A 25-year-old white truck driver complains of 1 day of throbbing rectal pain. Your examination shows a large, thrombosed external hemorrhoid. What is your treatment?
|
Elliptical excision of the thrombosed hemorrhoid
|
|
|
How long should a pharmacologic treatment of depression last?
|
minimum of 6 months
|
|
|
What is the best definition of Specificity?
|
true-negative rate, or how well the test correctly identifies patients without disease
|
|
|
What is the best definition of Sensitivity?
|
True-positive rate, or how well the test correctly identifies patients with disease
|
|
|
What is most bleeding in Meckel's diverticulum secondary to?
|
heterotrophic gastric mucosa causing acid-induced ileal ulceration
|
|
|
What is the most common cause of proteinuria in children? Describe...
|
Orthostatic Proteinuria
|
|
|
What is the most appropriate treatment for asymptomatic chlamydial infection during the 2nd trimester of pregnancy?
|
Azithromycin
|
|
|
What is the general notion regarding the use of automated external defibrillators by lay persons in out-of-hospital settings?
|
It has been shown to contribute to significant gains in full neurologic and functional recovery
|
|
|
What is the most accurate parameter during the 2nd trimester to assess Gestational Age? During the 1st trimester?
|
Biparietal diameter
Crown-rump length |
|
|
What is the leading cause of congenital hearing loss?
|
CMV
|
|
|
Define the 2nd stage of labor
|
Period from complete cervical dilation to complete delivery of the baby
|
|
|
Define the 3rd stage of labor
|
delivery of the baby and ends with delivery of the placenta
|
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
When are secondary causes of N/V during pregnancy usually suspected?
|
after 9 WGA
|
|
|
What can be given safely during pregnancy for N/V?
|
Metoclopramide is not associated with an increased risk of adverse effects on the fetus
|
|
|
Herpes gladiatorum caused by herpes simplex
|
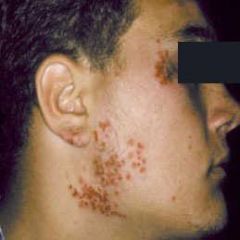
A 12-year old wrestler comes to your office c/o of recurrent painful rash on his arm. There appear to be several dry vesicles. What is the most likely diagnosis?
|
|
|
In a patient with Atrial Fibrillation, what confers the greatest risk of stroke?
|
Previous history of a stroke or TIA
other factors are: CHF, Hypertension, Age greater than 75, DM CHADS is the mnemonic |
|
|
In a patient with HIV infection, the threshold for initiating treatment for TB after PPD screening is an induration greater than or equal to:
|
5 mm
|
|
|
What symptoms are most suggestive of CHF in a 6-mo old white male presenting with tachypnea?
|
Diaphoresis with feeding
|
|
|
What pain reliever should be avoided when managing chronic pain in the elderly? Why?
|
Propoxyphene
Its efficacy is similar to that of aspirin or acetaminophen alone, but drug accumulation, neurotoxicity effects, and ataxia or dizziness may add unnecessary morbidity in older patients. Acetaminophen, hydrocodone, oxycodone, and hydromorphone are options for treating chronic pain in elderly |
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
20 year old female runner has a 1 week history of constant groin pain. There is limited hip motion on flexion and internal rotation of the right hip. Radiographs of the hip and pelvis are normal. What is the most likely diagnosis?
|
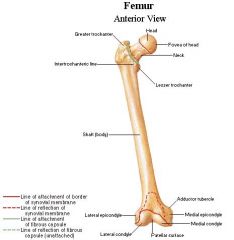
Stress fracture of the right femoral neck
|
|
|
A runner has stinging pain over the lateral femoral epicondyle. What is the most likely diagnosis?
|
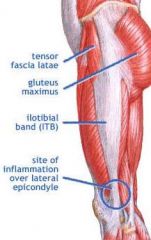
Iliotibial band syndrome
|
|
|
A distance runner presents with pain in the anterior pelvic area and tenderness over the symphisis pubis. Diagnosis?
|
Osteitis pubis
|
|
|
Uterine rupture is a potential complication of attempted VBAC. The most reliable indication that uterine rupture may have occurred is what?
|
Fetal Bradycardia
|
|
|
A 14 year old AA female presents for a routine evaluation. On exam, you note a rubbery, well-defined, nontender breast mass approximately 2 cm in diameter. The patient denies any history of breast tenderness, nipple discharge, or skin changes. Diagnosis?
|
Fibroadenoma
-slow growing, nontender, rubbery, well-defined mass, most commonly in the upper, outer quadrant |
|
|
Breast disease found in older adolescents and is characterized by bilateral nodularity and cyclic tenderness
|
Fibrocystic disease
|
|
|
Spongy, tender breast mass with symptoms exacerbated by menses
|
Benign breast cyst
-frequently multiple and spontaneous regression occurs in 50% of patients |
|
|
Firm, rubbery breast mass that may enlarge rapidly and is associated with skin necrosis.
|
Cystosarcoma phyllodes
|
|
|
A 14 year old AA female presents for a routine evaluation. On exam, you note a rubbery, well-defined, nontender breast mass approximately 2 cm in diameter. The patient denies any history of breast tenderness, nipple discharge, or skin changes. Diagnosis?
|
Fibroadenoma
-slow growing, nontender, rubbery, well-defined mass, most commonly in the upper, outer quadrant |
|
|
Breast disease found in older adolescents and is characterized by bilateral nodularity and cyclic tenderness
|
Fibrocystic disease
|
|
|
Spongy, tender breast mass with symptoms exacerbated by menses
|
Benign breast cyst
-frequently multiple and spontaneous regression occurs in 50% of patients |
|
|
Firm, rubbery breast mass that may enlarge rapidly and is associated with skin necrosis.
|
Cystosarcoma phyllodes
|
|

-
|

-
|
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
When is the probability of pregnancy after unprotected intercourse the highest?
|
1 day before ovulation
|
|

-
|

-
|
|

-
|

-
|
|
|
Patients with Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome who have episodic symptomatic supraventricular tachycardia or Atrial fibrillation benefit most from what treatment?
|
Radiofrequency catheter ablation of bypass tracts
|
|
|
A moderately obese 50 year old AA female presents with colicky right upper quadrant pain that radiates to her right shoulder. What is the most likely diagnosis? What is the best study to confirm the cause?
|
Cholelithiasis
Abdominal sono |
|
|
A 62 yo female with numbness in the LE and macrocytosis has a normal serum folate level and serum B12 level of 200 pg/mL (N 150-800). What lab finding would confirm diagnosis of B12 deficiency?
|
elevated Methylmalonic Acid
|
|
|
What is a reduced haptoglobin level useful to confirm?
|
Hemolytic anemia
|
|
|
What 2 things can lead to an elevated free erythrocyte protoporphyrin level?
|
Lead poisoning and Iron deficiency
|
|
|
In what disease is an elevated ACE found?
|
Sarcoidosis
|
|
|
What 2 drug classes have been found to decrease mortality after MI?
|
Beta-blockers
ACE inhibitors |
|
|
How often should young adults (until age of 40) have a routine physical exam?
|
every 3-5 years
|
|
|
At what age are mammograms recommended?
|
after age 40
|
|

-
|

-
|
|

-
|

-
|
|

-
|

-
|
|
-
|

-
|
|
-
|

-
|
|
-
|

-
|
|
-
|

-
|
|
|
A 23 yo hispanic female at 18 wks gestation presents with a 4 wk hx of a new facial rash. She noticed worsening w/ sun exposure. On exam, you note symmetric, hyperpigmented patches on her cheeks and upper lip. Diagnosis?
|
Melasma (Chloasma)
|
|
|
Herpes gestationis
|
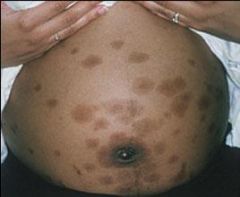
A rare polymorphous skin eruption of unknown origin occurring in late pregnancy that is more common on the extremities than on the trunk. It may recur during each subsequent pregnancy.
|
|
|
Treatment of asymptomatic chlamydial infections in women reduces their risk of developing these 4 things
|
1. PID
2. Tubal infertility 3. Ectopic pregnancy 4. Chronic pelvic pain |
|
|
What is the DOC for chlamydial infections in women?
|
Azithromycin
|
|
|
Sexual contacts of a woman with chlamydial infection during what preceding number of days should be treated empirically or test for infection and treated if positive?
How long should a patient avoid intercourse after initiation of treatment? |
60 days
7 days |
|
|
Cellulitis in patients after breast lumpectomy is thought to be related to lymphedema. What 2 things predispose to these infections?
What is the most common organism associated with this infection? |
Axillary dissection & Radiation
Non-group A hemolytic strep |
|
|
What 3 drugs are used to treat Acute uncomplicated cystitis?
|
Bactrim
Fluoroquinolone Nitrofurantoin |
|
|
Describe the McRoberts maneuver for managing shoulder dystocia
|
Maximal flexion and abduction of the maternal hips
|
|
|
What would be the most appropriate empiric therapy for nursing home-acquired pneumonia in a patient with no other underlying disease?
|
Levaquin
|
|
|
What criteria define Severe Preeclampsia?
|
BP 160/110 on two occasions > 6 hrs apart
Proteinuria > 5 g / 24h Thrombocytopenia with platelet count < 100,000 Liver enzyme abnormalities Epigastric or RUQ pain Alteration of mental status |
|
|
What criteria define MILD Preeclampsia?
|
BP > 140/90 on two occasions > 6 h apart
Proteinuria >300 mg / 24 h |
|
|
What is the best initial screening test for Hereditary Hemochromatosis?
What are the symptoms of this disease? |
Serum Transferrin Saturation
Bronze skin pigmentation, glucose intolerance, hypogonadism, arthropathy of the MCP joints, heart failure, or cirrhosis |
|
|
When is the median age of closure for the anterior fontanelle in newborns?
|
13.8 months of age
|
|
|
Describe the mechanism of Vasovagal syncope
|
Period of high sympathetic tone (often induced by pain or fear), followed by sudden sympathetic withdrawal, which then triggers a paradoxical vasodilation and hypotension
|
|
|
What test is useful in diagnosing Vasovagal Syncope?
|
Tilt testing, which causes pooling in the legs
Demonstrates Hypotension and Bradycardia |
|
|
What is the antibiotic of choice for a dog bite?
|
Amoxicillin/Clavulanate
|
|
|
When evaluating a patient with a solitary thyroid nodule, what are red flags indicating possible thyroid cancer? (8)
|
1. Male gender
2. < 20 years or > 60 years 3. rapid growth of nodule 4. Symptoms of local invasion such as dysphagia, neck pain, & hoarseness 5. Hx of head or neck radiation 6. FH of thyroid CA 7. hard, fixed nodule > 4 cm 8. Cervical lymphadenopathy |
|
|
In a euthyroid patient with a palbable nodule, what is the first test that should be ordered?
|
Fine-needle aspiration
|
|
|
Studies have shown that Epidural analgesia during labor increase the incidence of these things
|
1. increase length of both First and Second stage of labor
2. increase rate of instrument-assisted delivery 3. Fourth degree laceration 4. likelihood of maternal fever |
|
|
A positive flexion abduction external rotation (FABER) test that elicits posterior pain indicates involvement of which joint?
Anterior pain? |
Sacroiliac
Hip involvement |
|
|
What is the most effective long-term management of the majority of patients with Bipolar disorder?
|
Lithium
|
|
|
What is the most appropriate therapy for a patient with DVT? What should the INR be maintained at?
|
Initial SQ LMW-heparin (Enoxaparin) followed by PO Warfarin for 3-6 months
INR: 2-3 |
|
|
What should the INR be maintained at for patients with mechanical heart valves?
|
2.5-3.5
|
|
|
Gamekeeper's thumb is associated with a sprain of what?
How does it occur? |
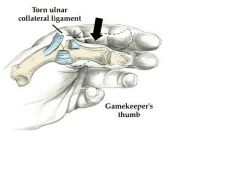
Ulnar Collateral Ligament
Hyperextension and Hyperabduction of the thumb, usually as a result of a fall *also called Skier's thumb |
|
|
Acute Pancreatitis
Grey Turner's sign indicates hemorrhage and a mortality rate approaching 50% |
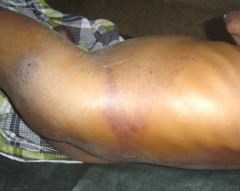
This is seen in a patient with a hx of hypertriglyceridemia and severe abdominal pain with vomiting over the last 6 hours.
-WBC of 20,000 -Glucose 295 -AST 333 -LDH 375 Most likely diagnosis? What is the name of the sign shown in the picture? What does it indicate? |
|
|
What effects does Estrogen have on the laboratory results of HDL and LDL?
|
HDL -> increased
LDL -> decreased |
|
|
Antidote to Atropine poisoning
|
Physostigmine
|
|
|
Antidote for Cyanide poisonig
|
Amyl nitrate
|
|
|
Antidote for Magnesium poisoning
|
Calcium carbonate
|
|
|
Antidote for Ethylene glycol poisoning
|
Ethanol and Pyridoxine
|
|
|
Antidote to Organic phosphates
|
Atropine
|
|
|
What can be taken 45 minutes prior to Niacin administration to decrease flushing?
|
Aspirin
|
|
-
|
-
|
|
|
What joint is usually affected in gout? What is this called?
What are the crystals in Gout? |
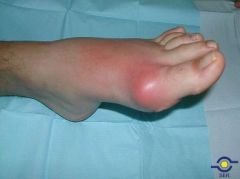
Metatarsophalangeal Joint
Podagra Monosodium urate crystals |
|
|
Dapsone
|
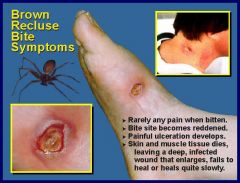
Antibiotic recommended in the treatment of a Brown Recluse spider bite?
|
|
|
What can be done to distinguish Atrial Flutter from Sinus Tachycardia
|
Carotid Massage
Atrial Flutter = regular, rapid cardiac rhythm characterized by an ectopic focus that gives rise to atrial rates from 280-350 per minute. Usually impulses are only transmitted to ventricles every 2nd, 3rd, or 4th impulse |
|
|
DOC for Trigeminal Neuralgia?
|
Carbamazepine (others are Phenytoin and Baclofin)
|
|
|
What ADR's have Methicillin and Nafcillin been associated with?
|
Interstitial Nephritis with Renal Tubular Acidosis
|
|
|
What is the most common inherited bleeding disorder?
How can it be diagnosed? Treatment for bleeding episodes? |
von Willebrand's disease (autosomal dominant)
normal PT, prolonged PTT resulting from Factor 8 deficiency (vWF carries Factor 8); Ristocetin cofactor assay measures ability of vWF to agglutinate platelets in vitro in the presence of ristocetin Cryoprecipitate or Factor 8 concentrate; or DDAVP (vasopressin) causes release of vWF from endothelial cells |
|
|
This murmur is associated with severe chronic aortic regurgitation and may be middiastolic or presystolic. It occurs when there is backflow of blood from the aorta into the LV and flow into the LV from the LA. The regurgitant stream often prevents the full opening of the mitral valve, thus obstructing flow into the ventricle.
|
Austin Flint murmur
|
|
|
This murmur affects children and is described as a humming or musical-sounding systolic murmur that is loudest at the left sternal border. It is a benign murmur. The murmur is usually heard in children 3-7 years of age and disappears before the onset of puberty
|
Still's murmur
|
|
|
What ECG findings may be found in a patient with a Pulmonary Embolism? (3)
|
Right Axis Deviation
S1-Q3-T3 pattern Right Bundle Branch Block |
|
|
When are children allowed to go back to school or daycare after having Strep Throat?
|
After having taken the antibiotic for 24 hours and temperature has returned to normal
|
|
|
A 17 year old girl presents to your office. She had a URI 1 wk before the visit. She now complains of severe vertigo. Diagnosis?
|
Vestibular Neuronitis = Acute Labrinthitis
|
|
|
Where is the most common location for the development of Morton's Neuroma?
|
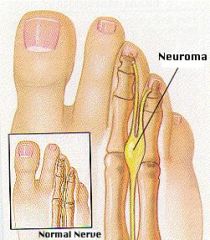
interdigital nerves b/w the 3rd and 4th metatarsal heads
|
|
|
What characterizes PVC's (premature ventricular contractions)? What can make them disappear?
|
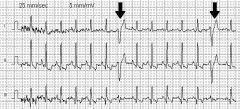
wide QRS complexes without a preceding P wave
Exercise |
|
|
Severe complication of Warfarin that is unrelated to bleeding?
|
Skin necrosis
|
|
|
Alternate name for Shin Splints?
|
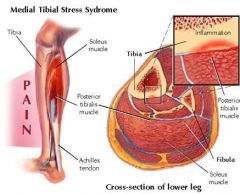
Medial Tibial Stress Syndrome
Physical examination reveals tenderness along several centimeters at the posteromedial border of the tibia, whereas a more focal anterior tibial tenderness suggests a stress fracture |
|
|
Steroid therapy
Pyoderma gangrenosum also may develop in surgical scars, fistulas, and ostomy sites. However, pyoderma gangrenosum is an immune-mediated, inflammatory condition commonly associated with inflammatory bowel disease and immunodeficient states. These ulcers are painful with well-demarcated, undermined edges. They have a purulent, dusky purple base, surrounding erythema, and satellite pustules |
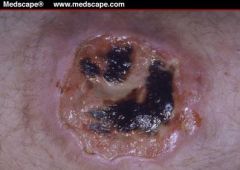
Treatment of choice for Pyoderma Gangrenosum?
|
|
|
Best treatment for chronic allergic rhinitis?
|
Intranasal steroids
|
|
|
A 72 y/o smoker with a positive hx of severe DJD, diabetes, and CVD presents c/o bilateral leg pain that occurs after walking 200 yards. He reports that rest improves his Sx's. Diagnosis and testing
|
Claudication + Ankle/Brachial indices
|
|
|
36 y/o runner presents with pain associated with the anterior heel. The pt reports his Sx's are worse on awakening and improve as the day progresses. Diagnosis?
|
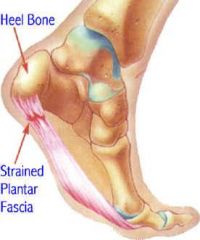
Plantar Fascitis
|
|
|
52 y/o man is seen for fevers & wt loss. CXR shows mediastinal lymphadenopathy. Labs show hypercalcemia, elevated Alk Phos, and elevated ACE. Diagnosis?
|
Sarcoidosis
|
|
|
What EKG finding is associated with Hypothermia?
|
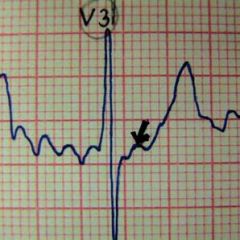
J (Osborne) wave = positive deflection after the QRS complex
|
|
|
A BUN:Cr ratio greater than 20 indicates?
|
Prerenal causes
-hypovolemia -cardiogenic shock -sepsis -anaphylaxis -drugs -renal artery stenosis FeNa < 1% because kidneys are trying to conserve Na |
|
|
What test is used in the initial evaluation of persistent hemoptysis
|
CXR then if mass is noted then do flexible bronchoscopy
Hemoptysis = bright red blood and alkaline from the lungs |
|
|
Progressive motor neuron disease that affects the corticospinal tracts &/or anterior horn cells &/or bulbar motor nuclei = ?
|
ALS
|
|
|
32-year-old man presents with recurrent oral and genital ulcers. He also has had arthalgias. Recently he was administered a tetanus vaccination and developed a sterile abscess at the site of the injection. Most likely diagnosis?
|
Behcet's Syndrome
Behçet's disease is a multisystem inflammatory condition, probably of autoimmune origin, that is triggered by infectious antigens or other antigens in genetically predisposed persons. Recurrent, painful ulcerations of the oral and genital mucosa are the most common symptoms. Therapeutic agents, such as topical or intralesional corticosteroids, generally are used only for palliative therapy. Sucralfate, which is commonly used in the treatment of peptic ulcers, can also heal ulcers of the gastrointestinal tract. However, its effectiveness in healing oral and genital ulcerations is unknown. Behçet disease (BD), also known as Behçet syndrome, is a chronic form of vasculitis (inflammation of the blood vessels) involving four primary symptoms: oral and genital ulcers, ocular inflammation, and arthritis. |
|
|
Osteochondritis dissecans
In osteochondritis dissecans, a loose piece of bone and cartilage separates from the end of the bone because of a loss of blood supply. The loose piece may stay in place or fall into the joint space, making the joint unstable. This causes pain and feelings that the joint is "catching" or "giving way." These loose pieces are sometimes called "joint mice." Osteochondritis dissecans usually affects the knees and elbows. |
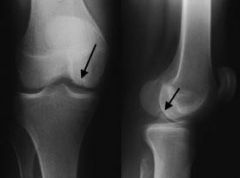
A boy who plays Little League baseball presents with swelling over the lateral elbow and pain with valgus and varus stress while flexing and extending the elbow. The patient reports locking of the elbow. Radiographs show the presence of loose bodies. Diagnosis?
|
|
|
Describe Ludwig's Angina
What is a serious complication? |
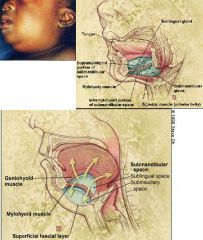
Infection invloving the sublingual and submaxillary space usually due to poor dental hygiene, tooth extraction, or trauma
Tongue displacement upwards compromising the airway |
|
|
Pneumocystis
IV Bactrim |
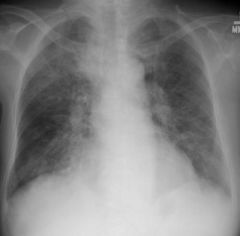
A 28 year old homosexual man presents to your office c/o of nonproductive cough, SOB, fever, chills. CXR shows bilateral interstitial infiltrates. Diagnosis? Treatment?
|
|
|
What is the treatment for a patient suspected of Wernicke-Korsakoff Syndrome?
|
Thiamine followed by IV Dextrose
|
|
|
What is the name of the test that confirms Benign Positional Vertigo?
|
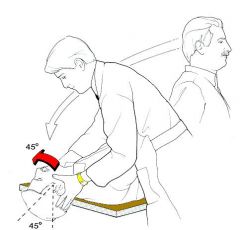
Dix-Hallpike maneuver = turn patient's head to the side while having them go from a sitting to lying position with head positioned below the level of the bed
BPV = severe episodes of vertigo that usually last less than 1 minute and are precipitated by certain head movements. Nystagmus is usually associated. Pathophysiology - caused by free-floating particulate matter in the semi-circular canals, usually the posterior canal (the most dependent structure of the labyrinth). - movement of this debris causes endolymph movement/pressure and cupular deflection - this causes an imbalance in the signals from the labyrinths resulting in vertigo - the particles are calcium carbonate crystals and are referred to as “otoliths” |
|
|
If an elderly man is diagnosed with Myasthenia Gravis what else should you suspect?
|
Thymoma
|
|
|
A 60-year-old woman presents with complaints of diffuse proximal muscle pain, low-grade fevers, and generalized fatigue. Labs show elevated ESR and mild anemia. Diagnosis? Rx?
|
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
-inflammatory disease with pain and stiffness associated with proximal muscles -more common in women -symmetrical pain and morning stiffness in neck, shoulders, and hips -fever, generalized fatigue, anorexia, & wt. loss -elevated ESR and anemia of chronic disease Rx = oral corticosteroids (prednisone) |
|
|
A 16 yo girl presents c/o throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and trismus (spasm of jaw muscles). PE shows redness and enlargement of the left tonsillar pillar. The patient holds her head to the left side and has muffled speech. Diagnosis?
|
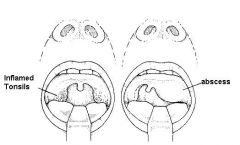
Peritonsillar abscess
|
|
|
A 65 year old man c/o gynecomastia and galactorrhe with erectile dysfunction. Most likely diagnosis? Rx?
|
Prolactinoma
Dopamine agonist -Cabergoline, Bromocriptine, Pergolide |
|
|
MCC of chronic cough?
|
Postnasal drip
|
|
|
A 62 yo woman presents c/o joint pain, polyuria, polydipsia, and generalized fatigue. The woman reports a history of recurrent kidney stones and depression. Radiographs show osteopenia and subperiosteal resorption on the phalanges. What blood test may help determine the cause of her symptoms?
|
Parathyroid hormone level for Primary Hyperparathyroidism
|
|
|
What is the treatment for someone under the age of 35 who has a + PPD test but no evidence of disease (including a - CXR)?
|
INH for 6 months
|
|
|
What is the name of a test that can be performed to diagnose Raynaud's phenomenon?
|
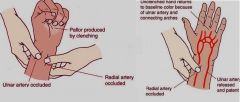
Allen's Test = occlude the radial and ulnar arteries while the patient makes a fist, the hand is the opened and one side of the wrist is released. Blood flow to the hand should be detected by color, which is restored to the hand. If the hand remains pale and cyanotic with either of the 2 sides, Raynaud's phenomenon should be suspected
|
|
|
Recurrent vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss are all hallmark findings of what? What is the treatment?
|
Meniere's Disease = endolymphatic hydrops (increased fluid pressure within the inner ear)
Salt restriction + HCTZ |
|
|
DOC for Cryptococcal meningeal infection?
|
Amphotericin B & Flucytosine
|
|
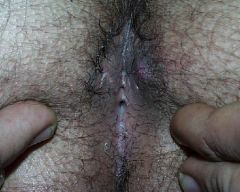
A 28 year old man presents to your office c/o pain in the perirectal area for the last week. Exam shows an area of tenderness, redness, and induration (hardened) lateral to the anus. The area is warm and fluctuant. Most likely diagnosis? Treatment?
|
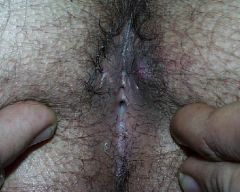
Pilonidal cyst
Surgical incision and drainage |
|
|
A 78 year old retired carpenter presents c/o gradually increasing right-sided shoulder pain. Pt is unable to sleep on his right side and has difficulty raising right arm. PE shows ROM is significantly restricted. X-rays show osteopenia of humeral head. Most likely diagnosis?
|
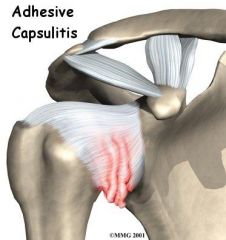
Adhesive capsulitis
|
|
|
What supplement has been associated with an increased risk of lung cancer in smokers?
|
Beta-carotene
|
|
|
What 3 groups of people should be treated for Asymptomatic Bacteriuria?
|
1. pregnant women
2. pts with renal transplants 3. pts who are about to undergo GU tract procedures |
|
|
A 2 cm nodule is found on the left lobe of the thyroid in a healthy 40 year old woman. What is the most appropriate management at this time?
|
Fine-needle aspiration
|
|
|
A 38 year old describes severe rectal pain associated with pallor, diaphoresis, and tachycardia that lasts for only a few minutes. The pain occurs mostly at night and are described as spasms. Diagnosis?
|
Proctalgia fugax is a unique anal pain. Patients with proctalgia fugax experience severe episodes of spasm-like pain that often occur at night. Proctalgia fugax may only occur once a year or may be experienced in waves of three or four times per week. Each episode lasts only minutes, but the pain is excruciating and may be accompanied by sweating, pallor and tachycardia. Patients experience urgency to defecate, yet pass no stool. No specific etiology has been found, but proctalgia fugax may be associated with spastic contractions of the rectum or the muscular pelvic floor in irritable bowel syndrome. Other unproven associations are food allergies, especially to artificial sweeteners or caffeine. Reassurance that the condition is benign may be helpful, but little can be done to treat proctalgia fugax. Medications are not helpful since the episode is likely to be over before the drugs become active. Sitting in a tub of hot water or, alternatively, applying ice may provide symptomatic relief. A low dose of diazepam (Valium) at bedtime may be beneficial in cases of frequent and disabling proctalgia fugax
|
|
|
A 21 yo returns from a camping trip early c/o dull numbness affecting his upper left extremity He recalls a sharp pinprick sensation before the development of symptoms. The pt now describes a cramping pain & muscle rigidity of the back and chest area. A red, indurated area is found on the distal left arm. The pt has profuse sweating, nausea, vomiting, and SOB. Diagnosis?
|
Black Widow spider envenomation
|
|
|
A 75 year old man presents to your office c/o flashes of light and blurred vision. He reports no pain. In-office exam reveals no findings other than decreased visual acuity. Most likely diagnosis?
|
Retinal detachment
-painless -dark floaters -flashes of light -blurred vision REFER TO OPHTHALMOLOGIST |
|
|
A 75 year old man presents to your office c/o flashes of light and blurred vision. He reports no pain. In-office exam reveals no findings other than decreased visual acuity. Most likely diagnosis?
|
Retinal detachment
-painless -dark floaters -flashes of light -blurred vision REFER TO OPHTHALMOLOGIST |
|
|
Subnormal visual acuity in one or both eyes despite correction of refractive error = ?
|
Amblyopia
-lazy eye -results when a child suppresses the vision in one eye to avoid diplopia -most common cause is strabismus (misalignment of the eyes) |
|
|
12 year old boy presents c/o gradual, increasing hip pain that radiates to the thigh and knee. PE shows an obese boy with pain associated with hip abduction and adduction. Radiographs show evidence of acetabular dysplasia. Diagnosis?
|
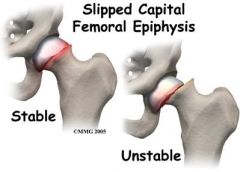
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphyses
-femoral head slips posteriorly and inferiorly exposing the anterior and superior aspects of the metaphysis of the femoral neck |
|
|
Idiopathic aseptic necrosis of the femoral head is also known as?
|
Legg-Calve-Perthes disease
|
|
|
The most common cause of a limp in a 5 year old boy is?
|
Transient Synovitis of the hip
Transient synovitis is the most common cause of hip pain in children. Many children will have a history of recent minor trauma, although this is obviously nonspecific in this age group. Transient synovitis typically affects young children who present with a limp of acute onset. On examination, the child will often refuse to use the affected leg and will have pain with any motion. Most children rapidly improve over two to three days, and more serious conditions such as a septic arthritis or juvenile rheumatoid arthritis should be considered if this rapid improvement is not seen. |
|
|
What is the most common bacterial pathogen associated with lung infections in adolescents? Rx?
|
Mycoplasma pneumonia -> malaise, sore throat, coryza, myalgias, and increasing productive cough of mucopurulent or blood-streaked sputum
Erythromycin |
|
|
What 3 criteria can define boys as having "delayed sexual maturation"?
|
1. no testicular development by age 13.5 years
2. no pubic hair by age 15 years 3. more than 5 years between initial and completed growth of the genitalia |
|
|
Describe Posterior Urethral Valves
|
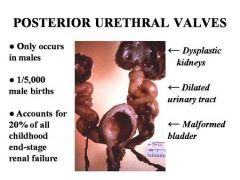
Valves are secondary to abnormal folds in the prostatic urethra that enlarge with voiding and cause obstruction of the urethral lumen
Symptoms include decreased urinary stream, overflow incontinence, and UTI's with dysuria. |
|
|
What is the most common curvature in scoliosis?
|
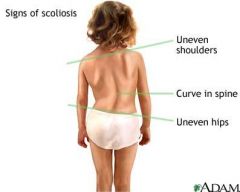
to the right in the thoracic spine, causing the right shoulder to be higher than the left
|
|
|
List the features of Kawasaki Disease
|
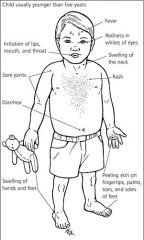
-
|
|
|
The most common cause of septic joint in an immigrant 3-year-old boy with no prior immunizations would be?
|
H. influenza
|
|
|
Tranposition of Great Vessels
|
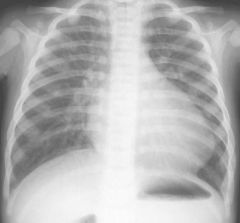
A newborn is cyanotic shortly after birth and CXR shows the characteristic "egg on a string". Diagnosis?
|
|
|
A 3-month-old girl is brought in b/c she has been having excessive non-purulent tearing from the left eye for the past 4 weeks. Diagnois and treatment?
|
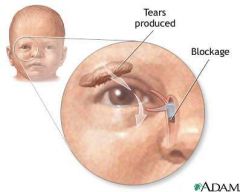
Dacryostenosis
Massage the duct twice daily as it usually resolves by 6 months of age |
|
|
Transient Cortical Blindness:
-Cause? -How long before resolves? -CT and EEG findings? |
Cause: mild head trauma
Resolves within 24 hours CT: unremarkable EEG: initially shows slowing but resolves as blindness dissipates |
|
|
A painless, cystic structure in the scrotum that transilluminates but is not associated with the presence of sperm is most likely?
|
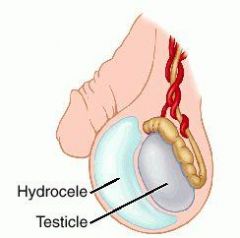
Hydrocele
(vs. a Varicocele, which is an enlargement of the pampiniform plexus due to incompetent valves of the veins) |
|
|
Explain Tick Paralysis
|
Dermacentor and Amblyomma have been linked to tick paralysis that causes muscle weakness, anorexia, lack of coordination, lethargy, nystagmus, and an ascending flaccid paralysis
Caused by inoculation of a neurotoxin found in the tick's salivary gland Antibiotics are not indicated, but symptomatic treatment is |
|
|
Syringomyelia may expand during adolescent years. Typically, what is the first neurologic deficit seen?
|

Pain and temperature sensation
|
|
|
Describe Infant Colic
|

-
|
|
|
Are high or low frequency sounds affected first in Presbycusis?
|
High frequency sounds
Pt. usually c/o trouble hearing normal conversations in crowds |
|
|
Describe each of the 4 stages of pressure ulcers
|
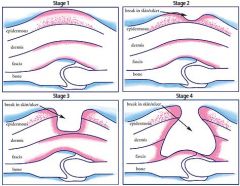
1. localized area of nonblanchable, red skin
2. break in the skin with surrounding redness and induration 3. full-thickness ulcer that extends to the subcutaneous layer but not thru the underlying fascia 4. ulcer penetrates the deep fascia exposing bone or underlying muscle |
|
|
A 79 year-old woman with a hx of atherosclerosis and HTN is seen in the ER. The pt reports she suddenly lost her vision in her left eye on awakening this morning. She reports no pain associated with the eye and has no other symptoms. Funcuscopic examination shows disk swelling, extensive retinal hemorrhages, and cotton-wool spots. The most likely diagnosis is?
|
Central Retinal Vein Occlusion
|
|
|
What is the triad characteristic of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus?
|
1. Dementia
2. Gait ataxia = stuttering gait in which the initiation of gait is hesitant but gives way to walking 3. Urinary incontinence Due to inadequate absorption of CSF |

