![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomic pathology vs. Clinical Pathology
|
Anatomic Pathology
- gold standard - necropsy - autopsy - biopsy - antemortem - postmortem - gross pathology - histopathology - ultrastructure (EM) Clinical Pathology - silver standard - hematology - clinical chemistry - cytology |
|
|
anything wrong, structural or fxnal is termed _____
|
lesion
|
|
|
_____ is a lesion so characteristic that you can make dx just from the lesion
|
pathognomonic lesion
|
|
|
Description should include
|
size (metric)
color consistency shape surface margins distribution location |
|
|
morphologic diagnosis should include
|
severity
- mild - moderate - severe duration - acute - subacute - chronic distribution - focal - multifocal - diffuse anatomic site - nephro - hepato - dermato modifier - suppurative - necrotizing lesion - necrosis - hemorrhage - inflammation |
|
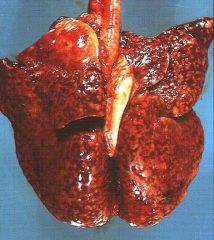
|
severe
chronic multifocal to coalescing granulomatous pneumonia |
|
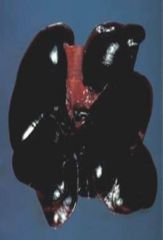
|
severe
acute diffuse pulmonary congestion |
|
|
Typhlitis is inflammation of
a. middle ear b. tongue c. cecum d. cloaca e. crop |
c. cecum
|
|
|
etiology
|
MINI VAN DITTI
(or it's D MINI TITI VAN) Degenerative Metabolic Inflammatory Neoplastic Infectious Traumatic Idiopathic Toxic Iatrogenic Vascular Anomalies Nutritional |
|
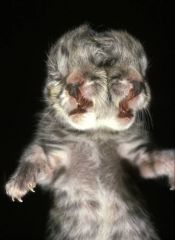
|
Etiology = Anomaly
|
|
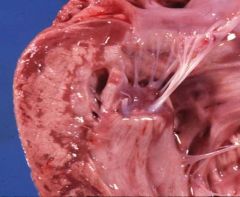
|
White Muscle Dz
Etiology = Nutritional |
|
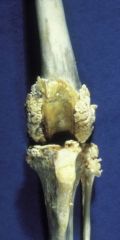
|
degenerative joint dz
Etiology = Degenerative |
|
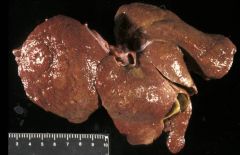
|
chronic-active hepatitis
Etiology = Idiopathic |
|
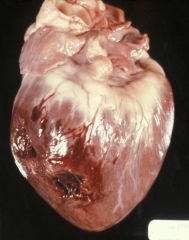
|
Etiology = traumatic
|
|
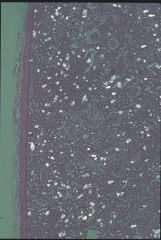
|
ethylene glycol toxicity
Etiology = Toxic |
|
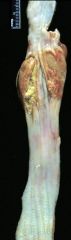
|
pill esophagitis
Etiology = Iatrogenic |
|
|
___ is the mechanism involved in the development of a dz
|
pathogenesis
|
|
|
define pathogenesis
|
the mechanism involved in the development of a dz
often a sequence of events initiated by the cause (etiology) the path b/w etiology and outcome |
|
|
_____ is a sequence of events initiated by the cause (etiology) of a dz
|
pathogenesis
|
|
|
____ is what comes b/w etiology and outcome
|
pathogenesis
|
|
|
how do you describe distribution (terminology used)
|
Focal
Multi-focal Coalescing Diffuse: homogenous everywhere Regionally extensive: like a really big focal one |
|
|
how do you describe margins (terminology used)
|
distinct/ discrete
diffuse |
|
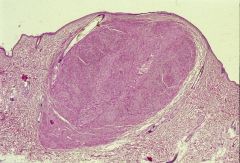
|
dome shaped
|
|
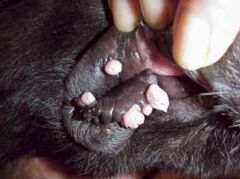
|
exophytic
aka pokey-outey |
|
|
____ is the term for a lesion that is pokey-outy (couldn't easily shave over it)
|
exophytic
|
|
|
exophytic
|
pokey outey
|
|

|
pedunculated (has a stalk)
|
|
|
_____ is the term for a lesion with a stalk
|
pedunculated
|
|
|
What terms are used to describe shape of lesions
|
diamond- shaped, square, rectangular
multinodular irregular pedunculated - has a stalk exophytic - pokey outey dome shaped - raised w/ a gradual lump |
|
|
which of the following is a good description
a. dark regionally extensive b. brownish diffuse c. red-brown multifocal firmish |
none of them
|
|
|
define each of the following
1. general pathology 2. Systemic pathology 3. Clinical pathology 4. pathology |
general pathology
- study of the underlying mechanisms common to all diseases Systemic Pathology - study of the pathology of each organ system clinical pathology - use of laboratory tests to study dz in living patient pathology - study of the structural and funcitonal manifestations of dz |
|
|
define
hematology clinical chemistry cytology they are all a part of what branch of pathology |
hematology
- study of blood and blood forming tissues clinical chemistry - interpretation of lab tests of serum or plasma cytology - examination of fluids and cells removed from a living animal they are all part of clinical pathology |
|
|
1. ______ means before death
2. ______ means after death |
1. antemortem
2. postmortem |
|
|
_____ is the study of the structural and fxnal manifestations of dz
|
pathology
|
|
|
morphologic diagnosis should include what 6 things
|
1. severity (mild/mod/sev)
2. duration (acute/subacute/chronic) 3. distribution (focal/multifocal/diffuse) 4. modifier (suppurative/granulomatous/necrotizing) 5. anatomic site (nephro/hepato/dermato) 6. lesion (necrosis/hemorrhage/inflamation/neoplasia) |
|
|
define lesion
|
structural or functional alteration in cells or organs of the body
|
|
|
metabolic (as etiologic category) includes
|
deficiency of enzyme or hormone
|
|
|
toxic (as etiologic category) includes
|
chemicals
toxic plants radiation injury |
|
|
what is the pathogenesis of canine parvovirus
|
virus infects rapidly dividing cells
necrosis of intestinal mucosa diarrhea and entrance of gram neg bacteria into bloodstream endotoxic shock and dehydration death |
|
|
what is the pathogenesis of a fat yellow cat
|
fat cat stops eating
excessive body fat mobilized to liver hepatic fatty change liver dysfunction icterus |

