![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the definition of electrophoresis?
|
The separation of charged molecules by differences in their rate of migration in an electric field. |
|
|
What is separation in electrophoresis based on? |
Mobility of ionised compounds or particles dissolved in a conducting medium under the influence of an electric field |
|
|
What is mobility? |
Mobility, μ, is the average velocity with which ions movie in an applied electric field where the velocity is determined by two opposing forces |
|
|
What are the four different components of an electrophoresis system? |
1. Molecules to be separated 2. Support medium 3. Buffer system 4. DC power source |
|
|
What are two common support media for proteins in electrophoresis? |
1. Native gel (acrylamide or starch) 2. Denaturing (SDS) gel (acrylamide) |
|
|
What are two common support media for nucleic acids in electrophoresis? |
1. Agarose gel 2. Acrylamide gel |
|
|
Name seven factors that influence mobility in electrophoresis |
1. Molecular size (MW) 2. Molecular shape 3. Molecular charge 4. Electric field strength (V/cm) 5. Porosity of support medium (%S) 6. Conductivity of the buffer (k) 7. pH of the buffer |
|
|
What is the significance of buffer pH in electrophoresis? |
Affects charge of molecule |
|
|
What is the effect on mobility as MW decreases? |
Lower MW = higher mobility |
|
|
What is the effect on mobility as field strength increases? |
Increased field strength = higher mobility |
|
|
Name two ways of increasing field strength |
1. Increase voltage 2. Decrease length of gel |
|
|
What is allowable field strength limited by? |
Conductivity of the buffer. High conductivity = high current = heat.) |
|
|
How does conductivity affect mobility? |
High conductivity = higher mobility |
|
|
What is the basis of separation of nucleic acids, and why? |
Based on number of base pairs. Because Charge/BP is constant. Larger molecules move slower due to friction with gel. |
|
|
What is the basis of separation of proteins, and why? |
Charge varies as function of amino acid composition and buffer pH. Separation based on charge/MW. Exact combination of factors varies for each molecule. |
|
|
Outline the conditions for the separation of DNA in agarose gels? |
- 1.5x TAE Agarise gel - TAE = 40mM Tris (pH buffer), 20mM acetic acid (pH regulator), 1mM EDTA (ion chelator) |
|
|
How are nucleic acids stained? |
- Ethidium bromide. DNA intercalator + UV fluorescence. |
|
|
Why are denaturing gels used to separate proteins? |
Too many separation parameters if using agarose gels. |
|
|
Outline the process of separating proteins using denaturing gels |
1. Proteins are heat denatured, this makes them all the same shape (linear). Disulphide bonds reduced using dithiothreitol or β-mercaptoethanol. 2. Proteins are coated with ionic detergent (SDS) which gives all molecules approximately the same overall negative charge. 3. Separation is therefore based on size (MW) alone. |
|
|
What does SDS stand for? |
Sodium dodecyl sulphate |
|
|
Outline the conditions of protein separation |
- Polyacrylamide gel, single percentage or variable gradient. - Variable gradient allows for: separation of large molecules at top due to low percentage, and separation of small molecules at bottom due to high percentage) |
|
|
What is capillary zone electrophoresis? |
Electrophoresis carried out using narrow-bore capillaries (25-125μm internal diameter). It uses a very high electric field. The large SA:volume ratio allows for rapid dissipation of heat. |
|
|
What are two advantages of CZE (capillary zone electrophoresis)? |
1. Very short analysis times 2. High peak efficiency |
|
|
Draw a basic schematic of CZE |
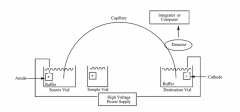
|
|
|
What kind of compounds is CZE ideal for? |
Compounds that present costly and time consuming challenges in chromatography. For example: proteins, peptides, nucleic acids, basic drugs, chiral compounds. |
|
|
Do neutral compounds separate? |
No |
|
|
Do negatively-charged compounds travel towards the negative pole? |
No, they travel towards positive pole. |
|
|
How does electroosmotic flow arise? |
Results from electrical double-layer that exists at the liquid-solid interface between capillary wall and bulk liquid. |
|
|
How is electroosmotic flow different to pressure-driven liquid flow? |
Plug-like, does not have parabolic flow where bulk liquid flows faster than that adjacent to capillary walls. This allows for high efficiency compound separation and high resolution of peaks. |
|
|
How did Sanger sequencing help the human genome project? |
It was the method used to produce the first human genome in 2001 (chromosome 22). |
|
|
When was sanger sequencing most used? |
1980s to the mid-2000s. |
|
|
What was used to visualise the sequence in Sanger sequencing? |
32P-ATP |

