![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
Clinical Fabry
|
|
|
|
Synonym
|
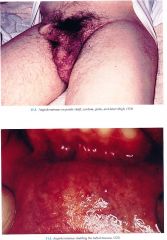
Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum
|
|
|
Inheritance
|
X linked recessive; (x galactosidase A (GLA) gene on Xq2l.33 q22
|
|
|
Prenatal
|
Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)/amniocentesis et galactosidase A enzyme assay DNA analysis
|
|
|
Incidence
Age at Presentation |
Approximately 1:40,000 males; female heterozygotes reported with marked variability in expression
Childhood to adolescence |
|
|
Pathogenesis
|
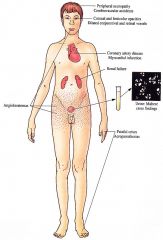
Mutation in GLA leads to defective activity of (x galactosidase A and accumulation of neutral glycosphingolipids with preferential deposition in vascular enclothelium resulting in ischernia and infarction; also deposits within most tissues of the body, including heart and kidney
|
|
|
Clinical
|
Skin
Angiokeratomas dark red to blue black papules with/without overlying hyperker¬atosis concentrated symmetrically between the umbilicus and knees, increase in number and size with age; hypoanhidrosis Mucous Membranes Angiokeratornas oral mucosa, conjunctiva Peripheral Nervous System Painful crises most severe on hands and feet but can spread proximally; exercise, fever, climate/temperature changes, emotional stress may trigger episode Acroparesthesias constant discomfort of hands and feet with burning, tingling paresthesias |
|
|
Clinical
|
Cardiovascular
Angina, myocardial infarction, conduction defects, mitral insufficiency Kidney Progressive renal deterioration with proteinuria, birefringent lipid globules ("maltese crosses") seen with polarizing microscopy, renal failure Central Nervous System Peripheral neuropathy, cerebrovascular accidents Eyes Characteristic corneal opacities with whorl like configuration, lenticular opacities, dilated and tortuous conjunctival and retinal vessels |
|
|
D/Dx
|
Rheumatic fever
Mercury/heavy metal poisoning Erythromelalgia Other angiokeratomas: angiokeratoma of Fordyce, fucosidosis, sialiclosis, P galactosidase deficiency, aspartylglucosaminuria |
|
|
Lab
|
DNA analysis
Enzyme assay deficient (x galactosidase A activity Skin, bone marrow biopsy Urinary sediment examination with polarizing microscopy Slit lamp ophthalmologic examination ECG |
|
|
Management
|
alpha Galactosidase A intravenous replacement therapy Diphenylhydantoin, carbamazepine pain crises Symptomatic care of cardiac, central nervous system (CNS), and ocular manifestations Long term hemodialysis, renal transplantation Advise physical education teachers/occupational advice minimize physical/emo¬tional stresses
|
|
|
Prognosis
|
Premature death during fifth decade secondary to myocardial infarction,
cerebrovascular accidents, and renal failure; enzyme replacement therapy, hemodialysis, renal transplantation may extend life span |

