![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
102 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomy
|
the structure of the body
|
|
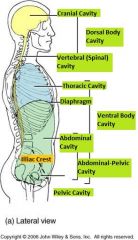
Body Cavities - Name
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
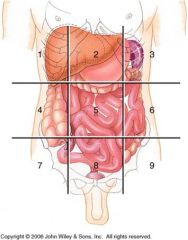
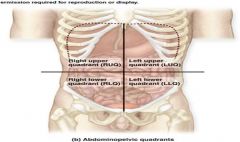
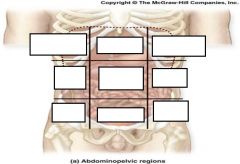
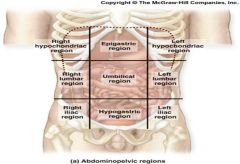
What are the Major Organs inside each Region
|
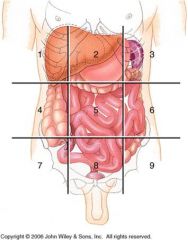
Right Hypochondriac Region= Epigastric= Left Hypochondriac Region=
Liver Esophagus Stomach Gall Bladder Stomach Small Intestines Small Intestine Liver D & Transverse Colon A & Transverse Colon Pancreas L Kidney R Kidney Small Intestine Spleen Transverse Colon R&L Adrenal Glands R&L Kidneys R&L Ureters Spleen Right Lumbar Region= Umbilical Region= Left Lumbar Region= Gall Bladder Stomach Small Intestine Small Intestine Pancreas D Colon A Colon Small Intestine L Kidney R Kidney Transverse Colon R&L Kidneys R&L Ureters Cisterna chyli Right Illiac Region= Hypogastric Region= Left Illiac Region= Small Intestine Small Intestine Small Intestine Appendix Segmoid Colon D Colon Cecum & Ascending Colon Rectum Sigmoid Colon (F) R Ovary R&L Ureters (F) L Ovary (F) R Fallopian Tube Urinary Bladder (F) L Fallopian Tube (F) Uterus (F) Right & Left Ovaries (F) Right & Left Fallopian Tubes (M) Vas Deferens (M) Seminal Vessicle (M) Prostate |
|
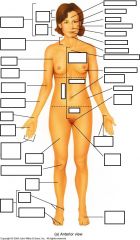
Anatomical Terms Anterior View
|
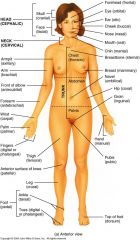
|
|
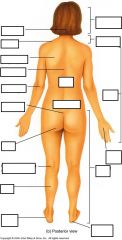
Anatomical Terms Posterior View
|
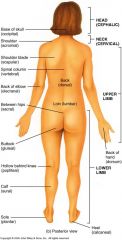
|
|
|
Nasal
|
nose
|
|
|
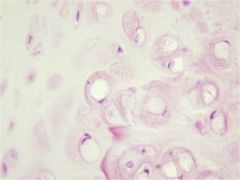
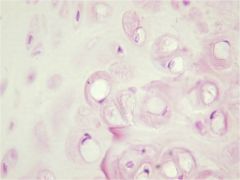
Hyaline Cartilage
|
|
|
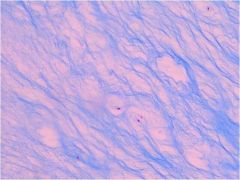
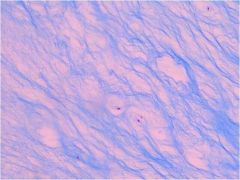
Fibrocartilage
|
|
|
Elastic Cartilage
|
|
|
Compact Bone
|
|
|
Spongy (Cancellous) Bone
|
|
|
Blood (Liquid) Connective
|
|
|
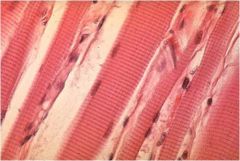
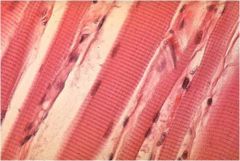
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
|
|
|
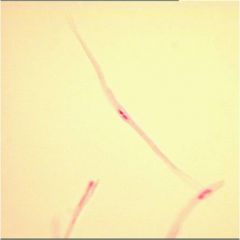
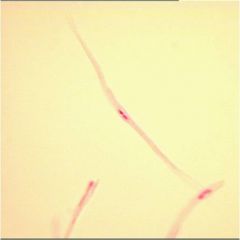
Smooth Muscle Tissue
|
|

|

Cardiac Muscle Tissue
|
|
|
Neurons - nerve cells
|
|
|
Neuroglia - Glial Cells
|
|
|
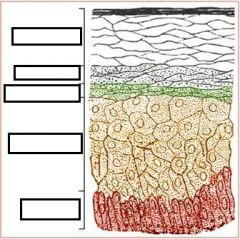
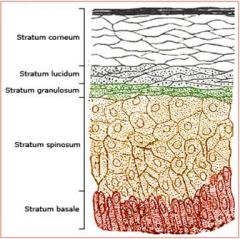
Stratum Lucidum
|
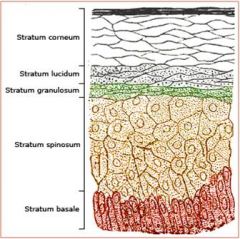
keratinocytes
Thick Skin Only |
|
|
Stratum Granulosum
|
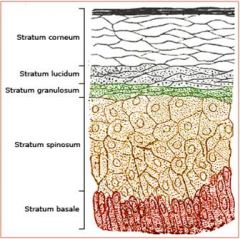
keratinocytes
Filled with Granules |
|
|
Statum Spinosum
|
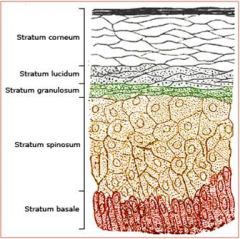
keratinocytes
Spiny |
|
|
Papillary region of Dermis
|
Areolar Connective
|
|
|
Reticular Region of Dermis
|
Dense Irregular Fibrous
|
|
|
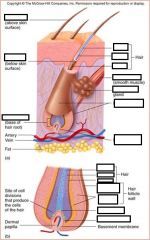
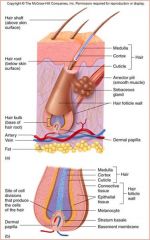
Arrector Pili Muscle
|
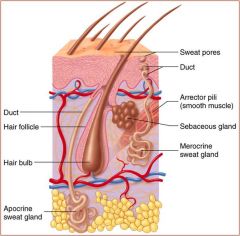
Controls goosebumps
Smooth Muscle |
|
|
Papilla
|
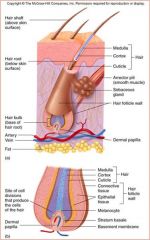
Stratum Basale
Produces the hair |
|
|
hair Follicle
|
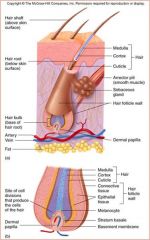
Epidermal Sheath
|
|
|
Hair Root
|
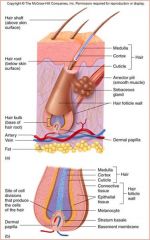
Hair within follicle
|
|
|
Hair Shaft
|
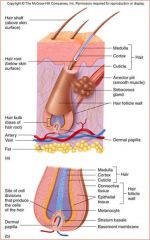
Hair without follicle
|
|
|
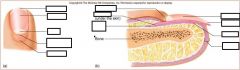
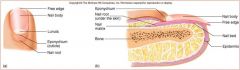
Nail body
|
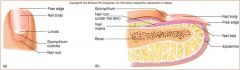
visible
|
|
|
nail root
|
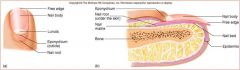
nail under epidermal fold
|
|
|
nail lunula
|
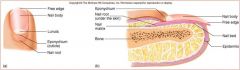
part of matrix visible
|
|
|
nail eponychium
|
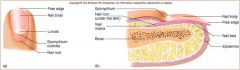
cuticle
|
|
|
nail bed
|
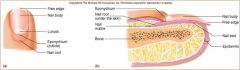
skin under nail
|
|
|
nail matrix
|
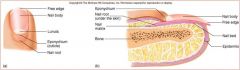
stratum basale/ germinativum
|
|
|
Which is the most present type of fingerprint?
|
Loops are the most often seen 68.9%
Whorl 26.1% Arch 5% |
|
|
Stratum
Call Little Green Spiders Back |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Type?
Tri-Radii? |

Arch
None |
|

Type?
Tri-Radii? |

Double Loop
Two Tri-Radii |
|

Type?
Tri-Radii? |

Left Loop
One Tri-Radii |
|

Type?
Tri-Radii? |

Right Loop
One Tri-Radii |
|

Type?
Tri-Radii? |

Tented Arch
None |
|

Type?
Tri-Radii? |

Whorl
None |
|
|
Articulation
|
Where two bones join
|
|
|
Fibrous Articulation
|
little or no movement; fetal skull
|
|
|
Synovial Articulation
|
free movement; joints of appendicular skeleton; filled with synovial fluid
|
|
|
Cartilaginous Articulation
|
united by cartilage; epiphyseal plates, costal cartilage and intervertebral discs
|
|
|
On Average How many bones are in the skeleton?
|
206
Some people may have extra bones known as sutural bones (skull) or sesmoid bones (found by tendons) |
|
|
Axial Skeleton?
|
80 bones total
contains: Skull and associated bones (29) Thoracic Cage (25 and Vertebral Column (26) |
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton?
|
126 bones total
contains: Pectoral girdles (4) Upper limbs (60) Pelvic Girdle (2) Lower Limbs (60) |
|
|
Fossa
|
shallow basin
Ex: humerus |
|
|
Fovea
|
tiny pit
Ex: femur |
|
|
Canal
|
tubular passage
Ex: skull |
|
|
Fissure
|
Slit
Ex: skull |
|
|
Meatus
|
tubelike
Ex: skull |
|
|
Fovea
|
tiny pit
Ex: femur |
|
|
Canal
|
tubular passage
Ex: Skull |
|
|
fissure
|
slit
Ex: skull |
|
|
Foramen
|
hole
Ex: vertebra |
|
|
Sinus
|
cavity
Ex: skull |
|
|
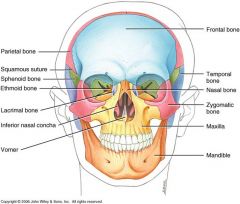
Skull
|
22 bones
8 from cranium 14 from facial |
|
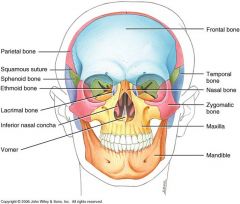
Frontal Bone
|
1 bone
Supraorbital ridge (ridge of eyebrows) Supraorbital Foramen (holes or slits above/beside eye) Glabella (between the eminences above nose) Eminences (rounded areas) |
|
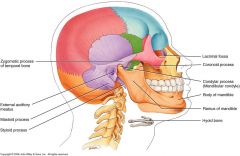
Parietal
|
2 bones
|
|
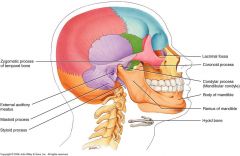
Temporal
|
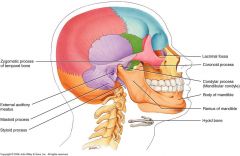
2 bones
*purple* External Auditory meatus (hole for ear) Mastoid process (looks like breast, behind ear) Zygomatic process (posterior cheek bone or back half) Styloid process (below jaw and looks like the end of a pen) |
|
|
Occipital
|
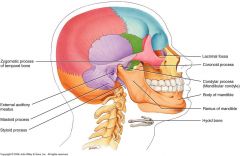
1 bone
External occipital protruberance Superior and Inferior Nuchal Lines Occipital Condyles Foramen Magnum |
|
|
Ethmoid
|
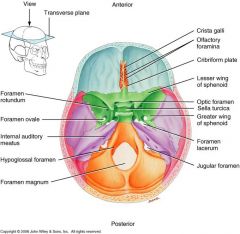
1 bone
Crista galli Mid and Superior nasal conchae (resembles a conch shell) Cribiform plate (This is where Egyptians pulled brains, cuz its easy to invade) Perpendicular plate (upper wall of the septum) |
|
|
Epithelium
|
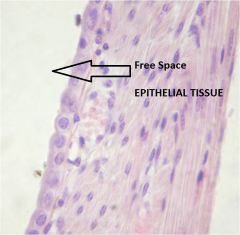
covers internal and external surfaces throughout the body. it also forms most glands.
No blood vessels in the epithelial tissue. Gets blood from the basement membrane. Purpose: protection, selective barrier, secretion, absorption, propulsion Identification: Open space |
|
|
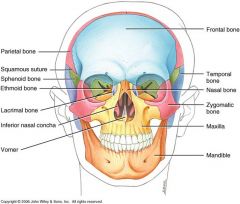
Facial Bones
|
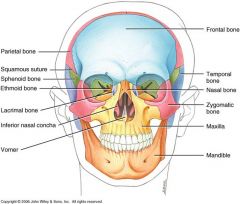
14 total
Mandible Nasal Lacrimal Vomer Zygomatic Palatine Maxilla Inferior Nasal Concha |
|
|
Basement Membrane
|
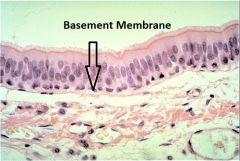
Secreted partly by epithelial cells and partly by the cells of the underlying tissues. It consists of a meshwork of protein molecules with other molecules bound to them.
Has blood vessels Purpose: filter and barrier ex: prevent metastasis (moving of disease) Made of collagen and adhesives; acellular |
|
|
Mandible
|
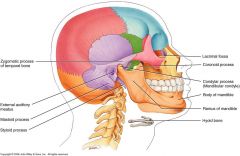
1 bone
Mental foramen body symphasis angle ramus alveoli condylar process coronoid process |
|
|
Cilia
|
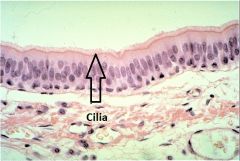
propel materials along the free surface of cells. The nasal cavity and trachea are lined with pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium.
Require energy cuz they are constantly beating |
|
|
Nasal
|
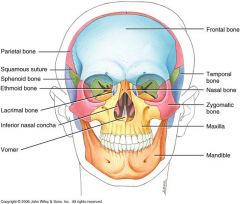
2 bones
bridge odf your nose |
|
|
Microvilli
|
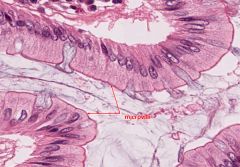
cylindrical extensions of the cell membrane that increase the free surface area. Normally many microvilli cover the free surface of each cell involved in absorption or secretion, such as the cells lining the small intestine or kidneys.
|
|
|
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
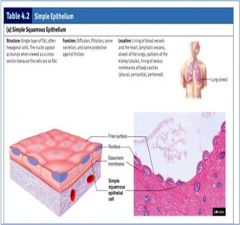
Location: air sacs (alveoli) of lungs and inner linings of the heart and blood vessels
Purpose: Diffusion and Filtration - It is found lining surfaces of passive transport or gasses. |
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
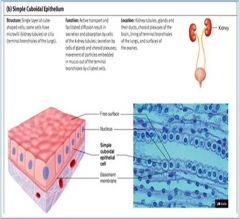
Location: Kidney tubules, thyroid gland, liver, and ducts of salivary glands
Function: Secretion, excretion, absorption |
|
|
Simple Columnar Epithelium
|
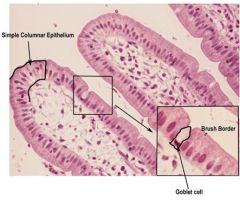
Location: Anywhere that requires absorption.
Nonciliated: uterus, stomach, and intestines. Ciliated: Uterine tubes Function: Protection, Secretion, and Absoption |
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
|
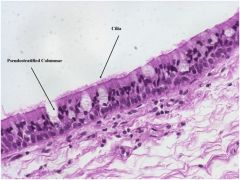
Location: Linings of the Upper respiratory tubes
Function: trap and move pollutants to the mouth where they are swallowed |
|
|
Stratified Squamous Epithelium
|
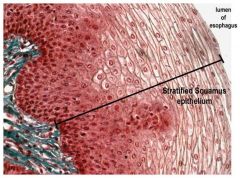
Location: Keratinized - Epidermis of the skin
Nonkeratinized - linings of the oral cavity, esophagus, vagina, and anal canal |
|
|
Transitional Epithelium
|
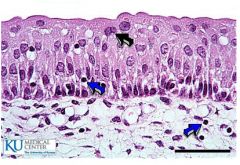
Location: Line the urinary bladder, ureters, and part of the urethra
Function: distention or fluctuation |
|
|
Goblet Cells
|
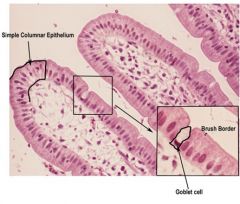
modified columnar epithelial cells that synthesize and secrete mucous
|
|
|
Endocrine Glands
|
No ducts
Empty secretions into the blood (Hormones) Includes: Thyroid gland and insulin-secreting portions of the pancreas |
|
|
Connective Tissue
|
found throughout body.
It is usually characterized by large amounts of extracellular material that separates cells from one another (Extracellular Matrix) Functions: Enclosing tissues, Support and movement, Energy storage, Cushioning and insulation, Protection |
|
|
Extracellular Matrix
|
Extracellular material that separates cells (connective Tissue).
Major Components: protein fibers, ground substance consisting of nonfibrous protein and other molecules and fluid |
|
|
Exocrine Glands
|
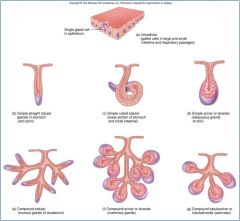
Have Ducts
simple or compound or tubular Includes: sweat glands and sebaceous glands |
|
|
Areolar Connective
|
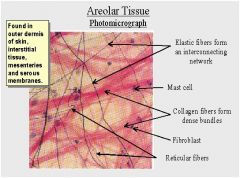
Location: around body organs
Function: binds skin to deeper organs Makes up membranes Loose packing support, and nourishment for the structures with which it is associates |
|
|
Adipose Connective
|
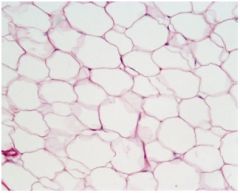
Locations: subcutaneous layer; around kidneys and heart; yellow bone marrow; breasts
Function: Packing material, thermal insulator, energy storage, and protection of organs against injury from being bumped or jarred |
|
|
Reticular Connective
|
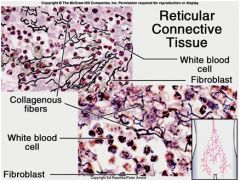
Location: spleen; thymus; lymph nodes; red bone marrow
Function: forms a soft skeleton to support lymphatic organs, also holds adipose tissue together |
|
|
Dense Regular Connective
|
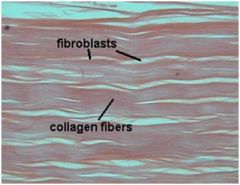
Location: Ligaments and Tendons
Functions: Withstanding great pulling forces exerted in the direction of fiber orientation due to great tensile strength and stretch resistance |
|
|
Elastic Connective
|
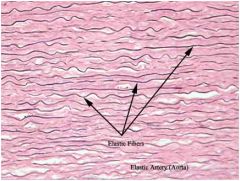
Locations: larger artery walls; vocal cords; ligaments between vertebrae
Function: Capable of Stretching and recoiling like a rubber band with strength in the direction of fiber orientation |
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage
|
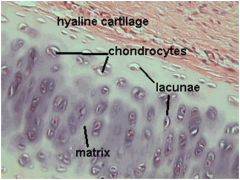
Locations: Nasal Septum, larynx, costal cartilage, ends of long bones, fetal skeleton
Functions: Allows growth of long bones; provides rigidity with some flexibility in the trachea, bronchi, ribs and nose; forms rugged, smooth yet somewhat articulated surfaces; forms the embryonic skeleton |
|
|
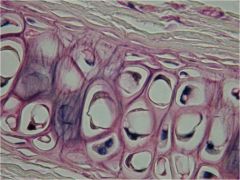
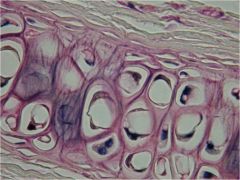
Fibrocartilage
|
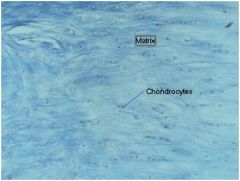
Locations: between vertebrae; between pubic bones; pads (meniscus) in knee
Functions: More collagen than hyaline; somewhat flexible and capable of withstanding considerable pressure, connects structures subjected to great pressure |
|
|
Elastic Cartilage
|
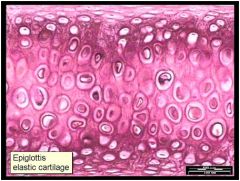
Locations: outer ear; epiglottis
functions: contains elastin and collagen and proteoglycans; provides rigidity with even more flexibility than hyaline cartilage because elastic fibers return to their original shape after being stretched |
|
|
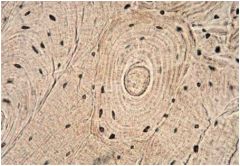
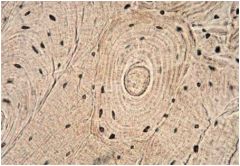
Compact Bone
|
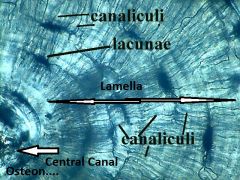
Locations: Bone Shafts (Sides of Bones), beneath periosteum
Functions: provides great strength and support and protects internal organs such as the brain, bone also provides attachment sites for muscles and ligaments |
|
|
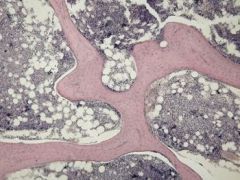
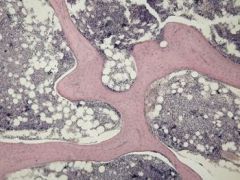
Spongy (Cancellous) Bone
|
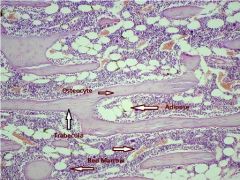
locations: ends of long bones; inside flat and irregular bones
Functions; holds marrow, provides strength and support |
|
|
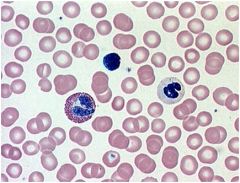
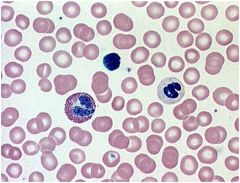
Blood (Liquid) Connective
|
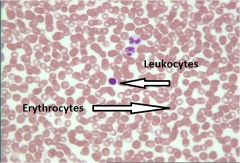
Locations: Lumens of blood vessels; heart chambers
Functions: Transports oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, nutrients, waste products, and other substances protects the body from infection and is involved in temperature regulation. |
|
|
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
|
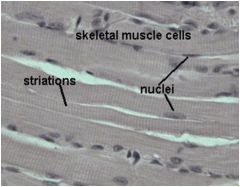
Voluntary Control, Striated
Locations: Attached to bones via tendons, tongue, facial muscles, and voluntary sphincters Functions: body movement, maintaining posture, breathing, speaking, controlling waste eliminations, and protection |
|
|
Smooth Muscle Tissue
|
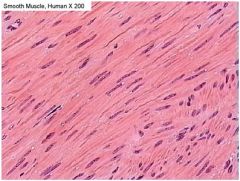
Involuntary, non-striated
Locations: visceral organs, the iris, blood vessels, respiratory tubes, attached to hair follicles Functions: visceral organs, controlling pupil size, blood flow, and airflow, and creating "goose bumps" if we are too cold or frieghtened |
|
|
Cardiac Muscle Tissue
|
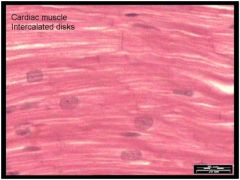
Involuntary, Striated
Locations: Only in heart wall Functions: Pumping Blood |
|
|
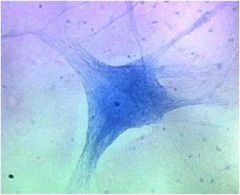
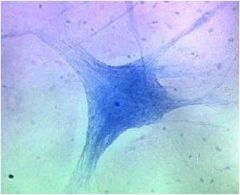
Neurons
|
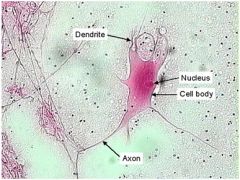
Contain a cell body with the nucleus and most of the cytoplasm, and cellular processes that extend from the cell body
Cellular processes include one to many dendrites and a single axon (nerve fiber) Functions: Considered excitable cells because they can exhibit signals called action potentials (nerve impulses) along the neuron to another neuron or a muscle or gland |
|
|
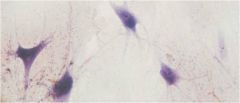
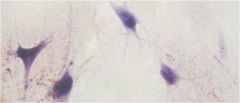
Neuroglia
|
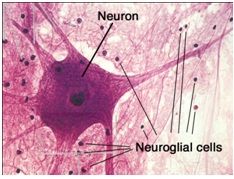
Glial Cells
More abundant than neurons Cannot conduct nerve impulses Functions: they have important supportive and protective functions for neurons |

