![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Patellar (knee-jerk) reflex
|
hit below the patella
|
|
|
Calcaneal (ankle-jerk) reflex
|
just above its insert on the calcaneus
|
|
|
Biceps (biceps-jerk) reflex
|
anticubital region
|
|
|
Triceps (triceps-jerk) reflex
|
strike the tendon of the triceps, just proximal to the olecranon
|
|
|
Plantar reflex
|
draw the metal tip of the firm pressure over the sole
|
|
|
Beta
|
12-30 Hz
Bigger waves for astrongly awake mind, Berry Awake |
|
|
Alpha
|
8-13 Hz
chill waves, relaxed brain waves, dominant during tv watching |
|
|
Theta
|
4-7 Hz
Spacey, day dreamers, sorority girls, brushing your teeth, long drive |
|
|
Delta
|
.1-4 Hz
Deep Sleep |
|
|
Parasympathetic
|
Maintaining homeostasis, resting
|
|
|
Sympathetic
|
fight or flight
short term conservation of energy |
|
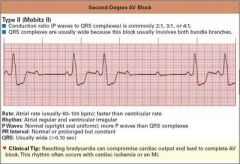
|
Heat Block
P waves are all over the place (1st, 2nd and 3rd degrees) |
|
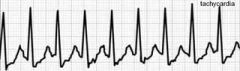
|
Tachycardia
Super Fast!! Normal heart rhythm |
|
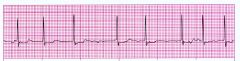
|
Atrial Fibrillation
No P waves and Rapid QRS (looks like upside down QRS) |
|
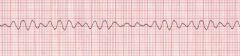
|
Ventricular Fibrillation
Looks like a snake |
|
|
Olfactory Nerve (I)
|
Smell
Sniff aromatic oil, spice, or coffee grounds |
|
|
Optic Nerve (II)
|
Vision
Read a Snellen eye chart at 20 ft. |
|
|
Oculomotor Nerve (III)
|
Pupil constriction, eye movements, and opens eyelid
Observe eyelids |
|
|
Trochlear Nerves (IV)
|
Stimulate superior oblique muscle
Look up, down, medially, laterally, upper lateral, lower lateral |
|
|
Trigeminal Nerves (V)
|
Sensory from face and teeth and mastication movements
Shine penlight on pupils |
|
|
Abducens Nerves (VI)
|
lateral eye movements
Lightly touch the cornea of the subject with a wisp of cotton Subject bites down on tongue depressor, try to pull it out |
|
|
Facial Nerves (VII)
|
Control facial expression muscles and salivation, tear secretions, and taste
Have subject smile, raise eyebrows, whistle, and close the eyes Check tip of tongue for taste with sugar |
|
|
Vestibulocochlear Nerves (VIII)
|
hearing and balance
use a tuning for, to check hearing in each ear Have the subject stand straight with eyes closed |
|
|
Glossopharyngeal Nerves (IX)
|
monitor blood pressure from baroreceptors, salivation, and swallowing
Have subject say "Ah"; check uvula position with mouth open |
|
|
Vagus Nerves (X)
|
regulation of many visceral organs, including the heart rate
Using a cotton-tipped applicator, gently touch the subject's uvula to elicit a gag reflex The posterior 1/3 of tongue can be tested with cotton applicator dipped in quinine |
|
|
Accessory Nerves (XI)
|
control neck, larynx, and shoulder muscles
Have subject shrug shoulders against resistance as you are holding them down |
|
|
Hypoglossal Nerves (XII)
|
control tongue movements
Ask your lab partner to stick out and retract his/her tongue |
|
|
Snellen Eye chart
|
Measures Visual Acuity
|
|
|
Astigmatism Test
|
Irregularities in the cornea, shaped like a football instead of what is supposed to
|
|
|
Accomodation Test
|
changing of the shape of the lens, has to do with the ciliary bodies, decreases with age
|
|
|
Color Vision Test
|
Most common is the red/green, but all color blindness is more common in males versus females because it is inherited on the X chromosome and females have two copies
|
|
|
Blind-Spot demonstration
|
there are no photoreceptors in the optic disc, located where the nerve fibers of the retina leave the eye and enter the optic nerve
|
|
|
Photopupillary reflex
|
smooth muscles of the iris control the size of the pupil. For example, when the intensity of light entering the eye increases, a phopupillary reflex is triggered, and the circular muscles of the iris are stimulated to contract. As a result, the size of the pupil decreases, and less light enters the eye
|
|
|
Convergence Reflex
|
the eyes converge as a normal convergence response to focusing on close objects
|
|
|
Rinne Test
|
It compares perception of sounds transmitted by air conduction to those transmitted by bone conduction through the mastoid. Thus, one can quickly screen for the presence of conduction hearing loss. involves outer or middle ear problems.
|
|
|
Weber Test
|
It can detect unilateral (one-sided) conductive hearing loss and unilateral sensorineural hearing loss (dysfunction of the cochlea) Conduction deafness.
|
|
|
Auditory Acuity Test
|
Using a meter stick to determine how far away a ticking sound can be heard. One ear at a time, the other is stuffed with cotton.
|
|
|
Sound Localization Test
|
Use a ticking watch and move it around person to see if they can pinpoint which direction the sound is coming from
|
|
|
Vision and Equilibrium
|
demonstrates the importance of vision in the maintenance of equilibrium (standing and closed eyes swaying test)
|
|
|
Romberg Test
|
used to evaluate a person's ability to integrate sensory information from proprioceptors and receptors within the organs of static equilibrium and to relay appropriate motor impulses to postural muscles. A person who shows little unsteadiness when standing with feet together and eyes open, but who becomes unsteady when the eyes are closed, as a positive Romberg test.
|
|
|
Barany Test
|
(Chair Spinning Test) - when the head is tilted about 30 degrees the lateral semicircular canals receive maximal stimulation, and the nystagmus is up and down. When the head is bent forward with the chin on the chest, the posterior canals are stimulated and the nystagmus is rotary
|
|
|
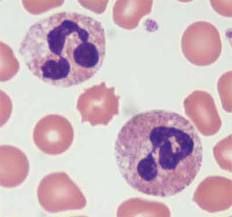
Neutrophil
60% - elevated levels may indicate bacterial infections or stress |
|
|
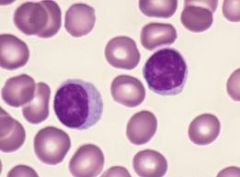
Lymphocytes
35% - Elevated levels may indicate mononucleosis, whooping cough, viral infections |
|
|
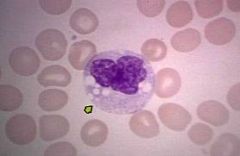
Monocytes
5% - LARGEST WBC Elevated levels may indicate malaria, tuberculosis, fungal infections |
|
|
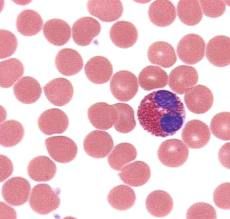
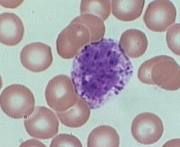
Eosinophils
1-2% - REDDISH Elevated levels may indicate allergic reactions, autoimmune diseases, parasitic worms |
|
|
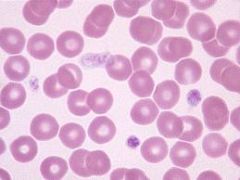
Basophil
.5% - Deep blue Elevated levels may indicate cancers, chicken pox, hypothyroidism |
|
|
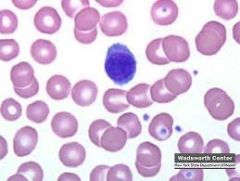
Platelets
|
|
|
Erythrocytes
|
|
|
A blood type
|
Can receive A, O
|
|
|
B blood type
|
Can receive B, O
|
|
|
AB blood type
|
Can receive AB, A, B, O
|
|
|
O blood type
|
Can receive O
|
|
|
P wave
|
.06-.11
Depolarization of atrial fibers |
|
|
P-Q (P-R) interval
|
.12-.2
Time for cardiac impulse from SA node through AV node |
|
|
QRS Complex
|
<.12
Depolarization of ventricular fibers |
|
|
S-T segment
|
.12
Time for ventricles to contract |
|
|
Q-T interval
|
.32-.42
Time from ventricular depolarization to end of ventricular repolarization |
|
|
T wave
|
.16
Repolarization of ventricular fibers (ends pattern) |
|
|
Artery/Veins layers
|
Tunica externa
Tunica Media Tunica Interna Lumen |
|
|
Oral cavity - Salivary glands
|
salivary amylase
Polysaccharides (starch) → Disaccharides (maltose) |
|
|
Esophagus and then to
Stomach |
Hydrochloric acid deactivates salivary amylase and its action
|
|
|
Small intestine -- Pancreas
|
Pancreatic amylase
Disaccarides/Polysaccharides → Disaccharides |
|
|
Small intestine - Intestinal mucosa
|
Maltase
→Monosaccharides (glucose) |
|
|
Urinalysis - Color
|
Color – normal urine varies from light yellow to amber, depending on the presence of urochromes, end-product pigments produced during the decomposition of hemoglobin. Dark urine indicates a high concentration of pigments.
Abnormal urine colors include yellow-brown or green, due to elevated concentrations of bile pigments, and red to dark brown, due to the presence of blood. |
|
|
Urinalysis - Transparency
|
Transparency – Normal urine is clear enough to see through. You can read newsprint through slightly cloudy urine; you can no longer read newsprint through cloudy urine. Cloudy urine indicates the presence of various substances that may include mucus, bacteria, epithelial cells, fat droplets, or inorganic salts.
|
|
|
Urinalysis - Specific gravity
|
Specific gravity – is the ratio of the weight of something to the weight of an equal volume of pure water. Actually, the specific gravity of normal urine varies from 1.003 to 1.035.
|
|
|
Urinalysis - pH test
|
pH test – The pH of normal urine varies from 4.6 to 8.0, but most commonly, it is near 6.0. The pH of urine may decrease as a result of a diet high in protein, or it may increase with a vegetarian diet. Significant daily variations within the broad normal range are results of concentrations of excesses from variable diets.
Alkaline = vegetables Acid = meat |
|
|
Urinalysis - glucose test
|
Glucose test – Normally, there is no glucose in urine, However, glucose may appear in the urine temporarily following a meal high in carbohydrates. Glucose also may appear in the urine as a result of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
|
|
|
Urinalysis - Protein test
|
Protein test – Normally, proteins of large molecular size are not present in urine. However, those of small molecular sizes, such as albumins, may appear in trace amounts, particularly following stenuous exercise. Increased amounts of proteins also may appear as a result of kidney diseases in which the glomeruli are damaged or as a result of high blood pressure.
|
|
|
Urinalysis - Ketone test
|
Ketone test – Ketones are products of fat metabolism. Usually they are not present in urine. However, they may appear in the urine if the diet fails to provide adequate carbohydrate, as in the case of prolonged fasting of starvation or starvation or as a result of insulin deficiency. (Breakdown of Fats).
|
|
|
Urinalysis - billirubin test
|
Bilirubin test – Bilirubin, which results from hemoglobin decomposition in the liver, normally is absent in urine. It may appear, however, as a result of liver disorders that cause obstructions of the biliary tract. Urochrome, a normal yellow component of urine, is a result of additional breakdown of bilirubin.
|
|
|
urinalysis - Hemoglobin/Occult blood test
|
Hemoglobin/Occult blood test – Hemoglobin occurs in the red blood cells, and because such cells normally do not pass into the renal tubules, hemoglobin is not found in normal urine. Its presence in urine usually indicates a disease process, a transfusion reaction, an injury to the urinary organs, or menstrual blood.
|
|
|
Name of the instrument that studies sight
|
opthalmoscope
|
|
|
Name of the instrument that studies ears
|
otoscope
|

