![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a parasympathetic pathway? |
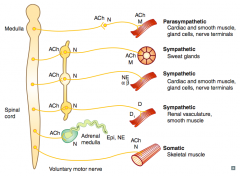
- Preganglionic (long) releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor
- Postganglionic (short) releases ACh on Muscarinic receptor (eg, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, gland cells, nerve terminals) |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a sympathetic pathway to sweat glands?
|
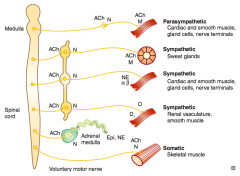
- Preganglionic (short) releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor (sympathetic chain)
- Postganglionic (long) releases ACh on Muscarinic receptor (same NTs and receptors as parasympathetic) |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a sympathetic pathway to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, gland cells, and nerve terminals?
|
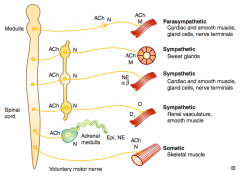
- Preganglionic (short) releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor (sympathetic chain)
- Postganglionic (long) releases NE on α and β receptors |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a sympathetic pathway to renal vasculature and smooth muscle?
|
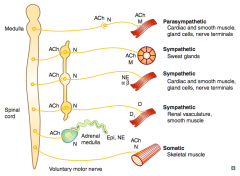
- Preganglionic (short) releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor (sympathetic chain)
- Postganglionic (long) releases Dopamine on D1 receptors |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a pathway to the adrenal medulla?
|
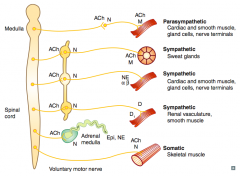
- Preganglionic releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor on adrenal medulla
- Adrenal medulla releases Epi and NE |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a somatic pathway to the skeletal muscle?
|
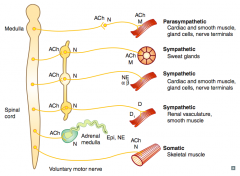
Voluntary motor nerve releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor on skeletal muscle
|
|
|
What nerve terminals does botulinum toxin affect?
|
Botulinum toxin prevents release of Ach at all cholinergic terminals |
|
|
What are the types of ACh receptors?
|
- Nicotinic ACh receptors
- Muscarinic ACh receptors |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a nicotinic ACh receptors?
|
Ligand-gated Na+/K+ channels |
|
|
Which type of receptor is found in autonomic ganglia?
|
Nn - Nicotinic ACh receptors, ligand-gated Na+/K+
|
|
|
Which type of receptor is found in neuromuscular junctions?
|
Nm - Nicotinic ACh receptors, ligand-gated Na+/K+
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of muscarinic ACh receptors?
|
G-protein coupled receptors that usually act through 2nd messengers
|
|
|
What are the types of Muscarinic ACh receptors?
|
- M1
- M2 - M3 - M4 - M5 |
|
|
What are the types of G-protein receptors?
|
- Sympathetic: α1, α2, β1, β2
- Parasympathetic: M1, M2, M3 - Dopamine: D1, D2 - Histamine: H1, H2 - Vasopressin: V1, V2 |
|
|
What are the sympathetic G-protein receptors? Class?
|
QISS and QIQ till you're SIQ of SQS (super qinky sex): |
|
|
What are the parasympathetic G-protein receptors? Class?
|
QISS and QIQ till you're SIQ of SQS (super qinky sex):
"qiq" - "kickin' it" - chillin (PANS)
A - B - M - D - H - V |
|
|
What are the dopamine G-protein receptors? Class?
|
QISS and QIQ till you're SIQ of SQS (super qinky sex):
A - B - M - D - H - V |
|
|
What are the histamine G-protein receptors? Class?
|
QISS and QIQ till you're SIQ of SQS (super qinky sex):
A - B - M - D - H - V |
|
|
What are the vasopressin G-protein receptors? Class?
|
QISS and QIQ till you're SIQ of SQS (super qinky sex):
A - B - M - D - H - V |
|
|
What G-protein class are α1 receptors? Major functions? |
"q" |
|
|
What G-protein class are α2 receptors? Major functions? |
"i" - ↓ aqueous humor production |
|
|
What G-protein class are β1 receptors? Major functions?
|
"s" |
|
|
What G-protein class are β2 receptors? Major functions? |
"s" |
|
|
What G-protein class are M1 receptors? Location? |
"q" |
|
|
What G-protein class are M2 receptors? Major functions? |
"i" |
|
|
What G-protein class are M3 receptors? Major functions? |
"q" |
|
|
What G-protein class are D1 receptors? Major functions?
|
"s" |
|
|
What G-protein class are D2 receptors? Major functions?
|
"i" |
|
|
What G-protein class are H1 receptors? Major functions?
|
"q" |
|
|
What G-protein class are H2 receptors? Major functions?
|
"s" |
|
|
What G-protein class are V1 receptors? Major functions?
|
"q" |
|
|
What G-protein class are V2 receptors? Major functions?
|
"s" |
|
|
Which receptors use the Gq receptor?
|
H1, α1, V1, M1, M3
(HAVe 1 M&M) |
|
|
Which is the mechanism of activation of the Gq receptor?
|
- Gq activation → Phospholipase C → PIP2 cleaved to DAG and IP3 |
|
|
Which receptors use the Gs receptor?
|
β1, β2, D1, H2, V2
|
|
|
Which is the mechanism of activation of the Gs receptor?
|
Activate Gs → ↑ Adenylyl Cyclase → ↑ cAMP → PKA
- ↑ [Ca2+]in (heart) - Myosin light chain kinase (smooth muscle) |
|
|
Which receptors use the Gi receptor? |
M2, α2, D2
MAD 2's |
|
|
Which is the mechanism of activation of the Gi receptor?
|
Activated Gi → inhibits Adenylyl Cyclase → ↓ cAMP |
|
|
What modulates NE release from a sympathetic nerve ending?
|
Modulated by NE itself, acting on pre-synaptic α2-autoreceptors, Ang II, and other substances
|
|
|
What are the direct cholinomimetic agonists?
|
- Bethanechol |
|
|
What are the indirect cholinomimetic agonists (anticholinesterases)?
|
- Neostigmine |
|
|
What drug is used to treat post-operative ileus, neurogenic ileus, and urinary retention? Action?
|
Bethanechol |
|
|
What drug is used to constricts pupils and relieve intraocular pressure in glaucoma? |
Carbachol |
|
|
What drug is a potent stimulator of sweat, tears, and saliva and is used to treat open-angle and closed-angle glaucoma? Action? |
Pilocarpine |
|
|
What drug is used to test for a diagnosis of asthma? Action?
|
Methacholine |
|
|
What drug is used to treat post-operative and neurogenic ileus and urinary retention, in addition to myasthenia gravis and reversal of NMJ blockade (post-op)? Action? |
Neostigmine |
|
|
What drug is used to treat myasthenia gravis (long acting)? Action?
|
Pyridostigmine |
|
|
What drug is used to treat anti-cholinergic toxicity? Action? |
Physostigmine |
|
|
What drugs are used to treat Alzheimer Disease? Action? |
Donepezil, Rivastigmine, and Galantamine |
|
|
What drug was historically used to diagnose myasthenia gravis? Mechanism? |
Edrophonium |
|
|
What is used to diagnose Myasthenia Gravis now?
|
Anti-AChR Ab (anti-ACh receptor antibody) test
|
|
|
What do you need to watch for when giving cholinomimetic agents to patients?
|
Watch for exacerbation of COPD, asthma, and peptic ulcers when giving to susceptible patients
|
|
|
What can cause cholinesterase inhibitor poisoning? Action?
|
Often due to organophosphates, such as parathion - irreversibly inhibits AChE |
|
|
What does cholinesterase inhibitor poisoning cause? |
DUMBBELSS: |
|
|
Who is likely to get cholinesterase inhibitor poisoning?
|
Farmers because organophosphates are components of insecticides (these irreversibly inhibit AChE)
|
|
|
How do you treat an irreversible inhibitor of AChE?
|
- Atropine (competitive inhibitor) +
- Pralidoxime (regenerates AChE if given early) |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Bethanechol?
|
Direct Cholinomimetic agent:
- Post-operative ileus, neurogenic ileus, and urinary retention - Activates bowels and bladder smooth muscle - Resistant to AChE |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Carbachol?
|
Direct Cholinomimetic agent:
- Treats glaucoma, pupillary constriction, and relief of intra-ocular pressure - Carbon copy of ACh |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Pilocarpine?
|
Direct Cholinomimetic agent:
- Potent stimulator of sweat, tears, and saliva - Treats open angle glaucoma (contracts ciliary muscle of eye) - Treats closed angle glaucoma (contracts pupillary sphincter) - Resistant to AChE "You cry, drool, and sweat on your PILOw" |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Methacholine?
|
Direct Cholinomimetic agent:
- Challenge test for diagnosis of asthma - Stimulates muscarinic receptors in airway when inhaled |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Neostigmine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats post-operative and neurogenic ileus and urinary retention, myasthenia gravis, and reverses NMJ blockade (post-op) |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Pyridostigmine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats myasthenia gravis (long acting), ↑ strength - Does not penetrate CNS "pyRIDostiGMine gets RID of Myasthenia Gravis" |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Physostigmine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats anti-cholinergic toxicity (crosses BBB → CNS) "PHYsostigmine "phyxes" atropine overdose" |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Donepezil?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats Alzheimer Disease |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Rivastigmine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats Alzheimer Disease |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Galantamine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats Alzheimer Disease |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Edrophonium?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Historically used to diagnose Myasthenia Gravis (extremely short acting) |
|
|
What are the muscarinic antagonists?
|
- Atropine, Homatropine, Tropicamide |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the eye? Applications?
|
Atropine, Homatropine, Tropicamide |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the CNS? Applications?
|
- Benztropine → Parkinson Disease ("Park my Benz"); acute dystonia |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the Respiratory Tract? Applications? |
Ipratropium and Tiotropium |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the Genitourinary Tract? Applications? |
Oxybutinin, Darifenacin, and Solifenacin - Reduce bladder spasms and treat urge urinary incontinence (overactive bladder)
(they inhibit M3, which is responsible for bladder muscle contraction) |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the Gastrointestinal Tract? Applications? |
Glycopyrrolate: |

