![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
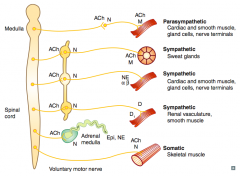
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a parasympathetic pathway?
|
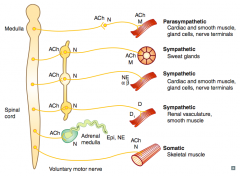
- Preganglionic (long) releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor
- Postganglionic (short) releases ACh on Muscarinic receptor (eg, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, gland cells, nerve terminals) |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a sympathetic pathway to sweat glands?
|
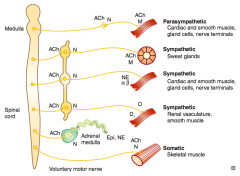
- Preganglionic (short) releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor (sympathetic chain)
- Postganglionic (long) releases ACh on Muscarinic receptor (same NTs and receptors as parasympathetic) |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a sympathetic pathway to cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, gland cells, and nerve terminals?
|
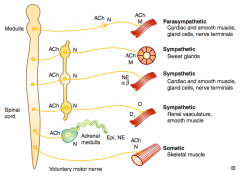
- Preganglionic (short) releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor (sympathetic chain)
- Postganglionic (long) releases NE on α and β receptors |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a sympathetic pathway to renal vasculature and smooth muscle?
|
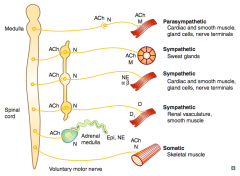
- Preganglionic (short) releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor (sympathetic chain)
- Postganglionic (long) releases Dopamine on D1 receptors |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a pathway to the adrenal medulla?
|
- Preganglionic releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor on adrenal medulla
- Adrenal medulla releases Epi and NE |
|
|
What types of NTs / receptors are involved in a somatic pathway to the skeletal muscle?
|
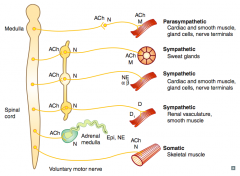
Voluntary motor nerve releases ACh on Nicotinic receptor on skeletal muscle
|
|
|
What nerve terminals does botulinum toxin affect?
|
Botulinum toxin prevents release of NT at all cholinergic terminals
|
|
|
What are the types of ACh receptors?
|
- Nicotinic ACh receptors
- Muscarinic ACh receptors |
|
|
What are the characteristics of a nicotinic ACh receptors?
|
Ligand-gated Na+/K+ channels
- Nn - found in autonomic ganglia - Nm - found in neuromuscular junction subtypes |
|
|
Which type of receptor is found in autonomic ganglia?
|
Nn - Nicotinic ACh receptors, ligand-gated Na+/K+
|
|
|
Which type of receptor is found in neuromuscular junctions?
|
Nm - Nicotinic ACh receptors, ligand-gated Na+/K+
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of muscarinic ACh receptors?
|
G-protein coupled receptors that usually act through 2nd messengers
|
|
|
What are the types of Muscarinic ACh receptors?
|
- M1
- M2 - M3 - M4 - M5 |
|
|
What are the types of G-protein receptors?
|
- Sympathetic: α1, α2, β1, β2
- Parasympathetic: M1, M2, M3 - Dopamine: D1, D2 - Histamine: H1, H2 - Vasopressin: V1, V2 |
|
|
What are the sympathetic G-protein receptors? Class?
|
QISS and kick till you're sick of sqs (super qinky sex):
- α1: q - α2: i - β1: s - β2: s |
|
|
What are the parasympathetic G-protein receptors? Class?
|
kiss and QIQ till you're sick of sqs (super qinky sex)
- M1: q - M2: i - M3: q |
|
|
What are the dopamine G-protein receptors? Class?
|
kiss and kick till you're SIq of sqs (super qinky sex)
- D1: s - D2: i |
|
|
What are the histamine G-protein receptors? Class?
|
kiss and kick till you're siQ of Sqs (super qinky sex)
- H1: q - H2: s |
|
|
What are the vasopressin G-protein receptors? Class?
|
kiss and kick till you're sick of sQS (super qinky sex)
- V1: q - V2: s |
|
|
What G-protein class are α1 receptors? Major functions?
|
"q"
- ↑ Vascular smooth muscle contraction - ↑ Pupillary dilator muscle contraction (mydriasis) - ↑ Intestinal and bladder sphincter muscle contraction |
|
|
What G-protein class are α2 receptors? Major functions?
|
"i"
- ↓ Sympathetic outflow - ↓ Insulin release - ↓ Lipolysis - ↑ Platelet aggregation |
|
|
What G-protein class are β1 receptors? Major functions?
|
"s"
- ↑ Heart rate - ↑ Contractility - ↑ Renin release - ↑ Lipolysis |
|
|
What G-protein class are β2 receptors? Major functions?
|
"s"
- Vasodilation and bronchodilation - ↑ HR - ↑ Contractility - ↑ Lipolysis - ↑ Insulin release - ↓ Uterine tone (tocolysis) - Ciliary muscle relaxation - ↑ Aqueous humor production |
|
|
What G-protein class are M1 receptors? Location?
|
"q"
- CNS and enteric nervous system |
|
|
What G-protein class are M2 receptors? Major functions?
|
"i"
- ↓ HR - ↓ Contractility of atria |
|
|
What G-protein class are M3 receptors? Major functions?
|
"q"
- ↑ Exocrine gland secretions (eg, lacrimal, salivary, gastric acid) - ↑ Gut peristalsis - ↑ Bladder contraction - Bronchoconstriction - ↑ Pupillary sphincter muscle contraction (miosis) - Ciliary muscle contraction (accommodation) |
|
|
What G-protein class are D1 receptors? Major functions?
|
"s"
- Relaxes renal vascular smooth muscle |
|
|
What G-protein class are D2 receptors? Major functions?
|
"i"
- Modulates transmitter release - Especially in brain |
|
|
What G-protein class are H1 receptors? Major functions?
|
"q"
- ↑ Nasal and bronchial mucus production - ↑ Vascular permeability - Contraction of bronchioles - Pruritus - Pain |
|
|
What G-protein class are H2 receptors? Major functions?
|
"s"
- ↑ Gastric acid secretion |
|
|
What G-protein class are V1 receptors? Major functions?
|
"q"
- ↑ Vascular smooth muscle contraction |
|
|
What G-protein class are V2 receptors? Major functions?
|
"s"
- ↑ H2O permeability and reabsorption in the collecting tubules of the kidney (V2 is found in the 2 kidneys) |
|
|
Which receptors use the Gq receptor?
|
H1, α1, V1, M1, M3
(HAVe 1 M&M) |
|
|
Which is the mechanism of activation of the Gq receptor?
|
- Gq activation → Phospholipase C → PIP2 cleaved to DAG and IP3
- DAG → activates Protein Kinase C - IP3 → ↑ [Ca2+]in → smooth muscle contraction |
|
|
Which receptors use the Gs receptor?
|
β1, β2, D1, H2, V2
|
|
|
Which is the mechanism of activation of the Gs receptor?
|
Activate Gs → ↑ Adenylyl Cyclase → ↑ cAMP → PKA
- ↑ [Ca2+]in (heart) - Myosin light chain kinase (smooth muscle) |
|
|
Which receptors use the Gi receptor?
|
M2, α2, D2
MAD 2's |
|
|
Which is the mechanism of activation of the Gi receptor?
|
Activated Gi → inhibits Adenylyl Cyclase → ↓ cAMP
|
|
|
What modulates NE release from a sympathetic nerve ending?
|
Modulated by NE itself, acting on pre-synaptic α2-autoreceptors, Ang II, and other substances
|
|
|
What are the direct cholinomimetic agonists?
|
- Bethanechol
- Carbachol - Pilocarpine - Methacholine |
|
|
What are the indirect cholinomimetic agonists (anticholinesterases)?
|
- Neostigmine
- Pyridostigmine - Physostigmine - Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine - Edrophonium |
|
|
What drug is used to treat post-operative ileus, neurogenic ileus, and urinary retention? Action?
|
Bethanechol
- Direct cholinomimetic agent - Activates Bowel and Bladder smooth muscle - Resistant to AChE "Bethany, call me, maybe, if you want to activate your Bowels and Bladder" |
|
|
What drug is used to glaucoma, pupillary constriction, and relief of intraocular pressure? Action?
|
Carbachol
- Direct cholinomimetic agent "CARBon copy of AcetylCHOLine" |
|
|
What drug is a potent stimulator of sweat, tears, and saliva and is used to treat open-angle and closed-angle glaucoma? Action?
|
Pilocarpine
- Direct cholinomimetic agent - Contracts ciliary muscle of eye (open-angle glaucoma), pupillary sphincter (closed-angle glaucoma) - Resistant to AChE "You cry, drool, and sweat on your PILOw" |
|
|
What drug is used to test for a diagnosis of asthma? Action?
|
Methacholine
- Direct cholinomimetic agent - Stimulats Muscarinic receptors in airway when inhaled |
|
|
What drug is used to treat post-operative and neurogenic ileus and urinary retention, in addition to myasthenia gravis and reversal of NMJ blockade (post-op)? Action?
|
Neostigmine
- Indirect cholinomimetic (anticholinesterase) - ↑ Endogenous ACh Neo CNS = No CNS penetration |
|
|
What drug is used to treat myasthenia gravis (long acting)? Action?
|
Pyridostigmine
- Indirect cholinomimetic agent (anticholinesterase) - Does not penetrate CNS - ↑ Strength "pyRIDostiGMine = get RID of Myasthenia Gravis" |
|
|
What drug is used to treat anti-cholinergic toxicity? Action?
|
Physostigmine
- Indirect cholinomimetic agent (anticholinesterase) - Crosses blood-brain barrier → CNS - ↑ Endogenous ACh "PHYsostigmine "PHYxes" atropine overdose" |
|
|
What drugs are used to treat Alzheimer Disease? Action?
|
Donepezil, Rivastigmine, and Galantamine
- Indirect cholinomimetic agent (anticholinesterase) - ↑ Endogenous ACh |
|
|
What drug was historically used to diagnose myasthenia gravis? Mechanism?
|
Edrophonium
- Indirect cholinomimetic agent (anticholinesterase) - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Extremely short acting |
|
|
What is used to diagnose Myasthenia Gravis now?
|
Anti-AChR Ab (anti-ACh receptor antibody) test
|
|
|
What do you need to watch for when giving cholinomimetic agents to patients?
|
Watch for exacerbation of COPD, asthma, and peptic ulcers when giving to susceptible patients
|
|
|
What can cause cholinesterase inhibitor poisoning? Action?
|
Often due to organophosphates, such as parathion - irreversibly inhibits AChE
|
|
|
What does cholinesterase inhibitor poisoning cause?
|
DUMBBELSS:
- Diarrhea - Urination - Miosis - Bronchospasm - Bradycardia - Excitation of skeletal muscle and CNS - Lacrimation - Sweating - Salivation |
|
|
Who is likely to get cholinesterase inhibitor poisoning?
|
Farmers because organophosphates are components of insecticides (these irreversibly inhibit AChE)
|
|
|
How do you treat an irreversible inhibitor of AChE?
|
- Atropine (competitive inhibitor) +
- Pralidoxime (regenerates AChE if given early) |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Bethanechol?
|
Direct Cholinomimetic agent:
- Post-operative ileus, neurogenic ileus, and urinary retention - Activates bowels and bladder smooth muscle - Resistant to AChE |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Carbachol?
|
Direct Cholinomimetic agent:
- Treats glaucoma, pupillary constriction, and relief of intra-ocular pressure - Carbon copy of ACh |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Pilocarpine?
|
Direct Cholinomimetic agent:
- Potent stimulator of sweat, tears, and saliva - Treats open angle glaucoma (contracts ciliary muscle of eye) - Treats closed angle glaucoma (contracts pupillary sphincter) - Resistant to AChE "You cry, drool, and sweat on your PILOw" |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Methacholine?
|
Direct Cholinomimetic agent:
- Challenge test for diagnosis of asthma - Stimulates muscarinic receptors in airway when inhaled |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Neostigmine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats post-operative and neurogenic ileus and urinary retention, myasthenia gravis, and reverses NMJ blockade (post-op) |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Pyridostigmine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats myasthenia gravis (long acting), ↑ strength - Does not penetrate CNS "pyRIDostiGMine gets RID of Myasthenia Gravis" |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Physostigmine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats anti-cholinergic toxicity (crosses BBB → CNS) "PHYsostigmine "phyxes" atropine overdose" |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Donepezil?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats Alzheimer Disease |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Rivastigmine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats Alzheimer Disease |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Galantamine?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Treats Alzheimer Disease |
|
|
What are the clinical applications and actions of Edrophonium?
|
Indirect Cholinomimetic agent:
- Anticholinesterase - ↑ Endogenous ACh - Historically used to diagnose Myasthenia Gravis (extremely short acting) |
|
|
What are the muscarinic antagonists?
|
- Atropine, Homatropine, Tropicamide
- Benztropine - Scopolamine - Ipratropium and Tiotropium - Oxybutynin, Darifenacin, and Solifenacin - Glycopyrrolate |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the eye? Applications?
|
Atropine, Homatropine, Tropicamide
- Produces mydriasis (dilation) and cycloplegia (paralysis of ciliary muscle) |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the CNS? Applications?
|
- Benztropine → Parkinson Disease ("Park my Benz")
- Scopolamine → Motion sickness |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the Respiratory Tract? Applications?Which muscarinic antagonists act on the CNS? Applications?
|
Ipratropium and Tiotropium
- COPD, asthma (I pray I can breath soon) Glycopyrrolate: - Parenteral administration: pre-operative use to reduce airway secretions |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the Genitourinary Tract? Applications?
|
Oxybutinin, Darifenacin, and Solifenacin
- Reduces urgency in mild cystitis - Reduces bladder spasms - Other agents: tolterodine, fesoterodine, trospium |
|
|
Which muscarinic antagonists act on the Gastrointestinal Tract? Applications?
|
Glycopyrrolate:
- Oral administration: drooling, peptic ulcer |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Atropine? Uses?
|
- Muscarinic antagonist
- Used to treat bradycardia and for ophthalmic applications |
|
|
What are the actions of Atropine on the eye?
|
↑ Pupil dilation and Cycloplegia (paralyzes ciliary muscle)
|
|
|
What are the actions of Atropine on the airway?
|
↓ Secretions
|
|
|
What are the actions of Atropine on the stomach?
|
↓ Acid secretion
|
|
|
What are the actions of Atropine on the gut?
|
↓ Motility
|
|
|
What are the actions of Atropine on the bladder?
|
↓ Urgency in cystitis
|
|
|
What are the side effects of Atropine?
|
- HOT as a hare: ↑ body temperature (↓ sweating)
- DRY as a bone: dry mouth, dry skin - RED as a beet: flushed skin - BLIND as a bat: cycloplegia - MAD as a hatter: disorientation - Constipation - Rapid pulse |
|
|
What undesirable conditions can Atropine cause?
|
- Can cause acute angle-closure glaucoma in elderly (d/t mydriasis)
- Urinary retention in men with prostatic hyperplasia - Hyperthermia in infants |
|
|
What is the cause of mydriasis in gardners?
|
Jimson Weed → gardners pupil
Mydriasis due to plant alkaloids |
|
|
What are the direct sympathomimetics?
|
- Epinephrine
- Norepinephrine - Isoproterenol - Dopamine - Dobutamine - Phenylephrine - Albuterol, Salmeterol, and Terbutaline |
|
|
What are the relative effects of Epinephrine on the adrenergic receptors? Applications of use?
|
β > α
- Anaphylaxis - Open angle glaucoma - Asthma - Hypotension - α effects predominate at high doses |
|
|
What are the relative effects of Norepinephrine on the adrenergic receptors? Applications of use?
|
α1 > α2 > β1
- Hypotension (but ↓ renal perfusion) |
|
|
What are the relative effects of Isoproterenol on the adrenergic receptors? Applications of use?
|
β1 = β2
- Electrophysiologic evaluation of tachyarrhythmias - Can worsen ischemia |
|
|
What are the relative effects of Dopamine on the different receptors? Applications of use?
|
D1 = D2 > β > α
- Unstable bradycardia - Heart failure - Shock - Inotropic and chronotropic α effects predominate at high doses |
|
|
What are the relative effects of Dobutamine on the adrenergic receptors? Applications of use?
|
β1 > β2, α
- Heart failure (inotropic > chronotropic) - Cardiac stress testing |
|
|
What are the relative effects of Phenylephrine on the adrenergic receptors? Applications of use?
|
α1 > α2
- Hypotension (vasoconstrictor) - Ocular procedures (mydriatic) - Rhinitis (decongestant) |
|
|
What are the relative effects of Albuterol, Salmeterol, and Terbutaline on the adrenergic receptors? Applications of use?
|
β2 > β1
- Albuterol for acute asthma - Salmeterol for long-term asthma or COPD control - Terbutaline to reduce premature uterine contractions |
|
|
What are the indirect sympathomimetics?
|
- Amphetamine
- Ephedrine - Cocaine |
|
|
What are the effects of Amphetamines? Uses?
|
- Indirect general agonist, reuptake inhibitor, also releases stored catecholamines
- Used for narcolepsy, obesity, attention deficit disorder |
|
|
What are the effects of Ephedrine? Uses?
|
- Indirect general agonist, releases stored catecholamines
- Used for nasal decongestion, urinary incontinence, and hypotension |
|
|
What are the effects of Cocaine? Uses?
|
- Indirect general agonist, reuptake inhibitor
- Causes vasoconstriction and local anesthesia - Never give β-blockers if cocaine intoxication is suspected (can lead to unopposed α1 activation and extreme hypertension) |

