![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which enzyme converts membrane lipids (eg, phosphatidylinositol) to arachidonic acid? What drugs inhibit this? |
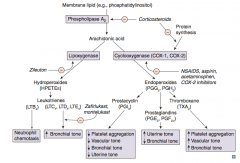
Phospholipase A2 |
|
|
What enzyme converts arachidonic acid to leukotrienes? Which drug inhibits this?
|
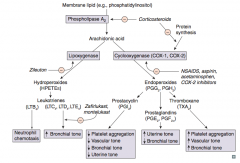
Lipoxygenase
- Inhibited by Zileuton ("E" in Zileuton for enzyme") |
|
|
Which leukotriene(s) is/are a neutrophil chemotactic agent?
|
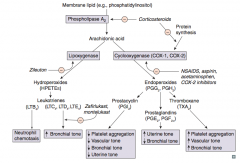
LTB4: neutrophils arrive "B4" others
|
|
|
Which leukotriene(s) function in bronchoconstriction, vasoconstriction, contraction of smooth muscle, and ↑ vascular permeability? Which drugs inhibit this?
|
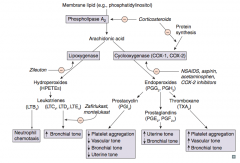
LTC4, LTD4, LTE4
- Inhibited by Zafirlukast and Montelukast |
|
|
Which enzyme converts arachidonic acid to prostaglandins? Which drugs inhibit this?
|
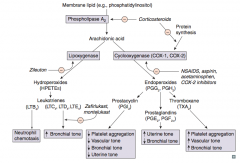
Cyclooxgenase (COX-1 and COX-2)
- Inhibited by NSAIDs, aspirin, acetaminophen, and COX-2 inhibitors - Inhibited by corticosteroids by inhibiting protein synthesis |
|
|
Which prostaglandin inhibits platelet aggregation, promotes vasodilation (↓ vascular tone), ↓ bronchial tone, and ↓ uterine tone?
|
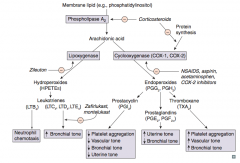
PGI2 = Platelet Gathering Inhibitor
|
|
|
Which prostaglandin ↑ uterine tone and ↓ bronchial tone?
|
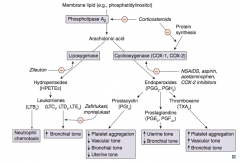
PGE2 and PGF2α
|
|
|
Which arachidonic acid product ↑ platelet aggregation, ↑ vascular tone, and ↑ bronchial tone?
|
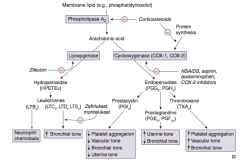
TXA2 (Thromboxane)
|
|
|
What is the function of LTB4?
|
Neutrophil chemotaxis (Neutrophils arrive B4 others)
|
|
|
What is the function of LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4?
|
- ↑ Bronchial tone (bronchoconstriction)
- Vasoconstriction - Contraction of smooth muscle - ↑ Vascular permeability |
|
|
What is the function of PGI2 (Prostacyclin)?
|
- ↓ Platelet aggregation (PGI = platelet gathering inhibitor)
- ↓ Vascular tone - ↓ Bronchial tone - ↓ Uterine tone |
|
|
What is the function of PGE2 and PGF2α (prostaglandins)?
|
- ↑ Uterine tone
- ↓ Bronchial tone |
|
|
What is the function of Thromboxane (TXA2)?
|
- ↑ Platelet aggregation
- ↑ Vascular tone - ↑ Bronchial tone |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Aspirin?
|
- Irreversible inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2) by covalent acetylation
- Decreases synthesis of Thromboxane A2 (TXA2) and Prostaglandins |
|
|
What is the effect of aspirin on bleeding?
|
- ↑ Bleeding time until new platelets are produced (~7 days)
- No effect on PT or PTT |
|
|
What are the clinical uses of Aspirin?
|
- Low dose (<300 mg/day): ↓ platelet aggregation
- Intermediate dose (300-2400 mg/day): antipyretic and analgesic - High dose (2400-4000 mg/day): anti-inflammatory |
|
|
What are the toxic side effects of Aspirin?
|
- Gastric ulceration
- Tinnitus (CN VIII) - Chronic use can lead to: acute renal failure, interstitial nephritis, upper GI bleeding - Reye syndrome in children treated for viral infection - Stimulates respiratory centers: hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis |
|
|
What causes Reye Syndrome?
|
Occurs in children treated with aspirin for a viral infection
|
|
|
What are the types of NSAIDs?
|
- Ibuprofen
- Naproxen - Indomethacin - Ketorolac - Diclofenac |
|
|
What is the mechanism of NSAIDs?
|
- Reversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2)
- Blocks prostaglandin synthesis |
|
|
How are NSAIDs used clinically?
|
- Anti-pyretic
- Analgesic - Anti-inflammatory - Indomethacin is used to close a PDA |
|
|
What drug can be used to close a patent ductus arteriosus? Mechanism?
|
Indomethacin (NSAID) - reversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase, blocking prostaglandin synthesis
|
|
|
What are the toxic side effects of NSAIDs?
|
- Interstitial nephritis
- Gastric ulcer (PGs protect gastric mucosa) - Renal ischemia (PGs vasodilate afferent arteriole) |
|
|
How do NSAIDs affect the kidney?
|
- Can cause interstitial nephritis
- Can cause renal ischemia (PGs vasodilate afferent arteriole) |
|
|
What drug is a specific COX-2 inhibitor?
|
Celecoxib
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Celecoxib?
|
Reversibly inhibits COX-2, which is found in inflammatory cells and vascular endothelium and mediates pain
|
|
|
How is Celecoxib hypothetically better than NSAIDs?
|
- Spares COX-1, which helps maintain gastric mucosa
- Should not have the corrosive effects of other NSAIDs on GI lining - Spares platelet function as TXA2 production is dependent on COX-1 |
|
|
What are the uses of Celecoxib?
|
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Osteoarthritis - Patients with gastritis or ulcers |
|
|
What are the toxic side effects of Celecoxib?
|
- Increased risk of thrombosis
- Sulfa allergy |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Acetaminophen?
|
- Reversibly inhibits cyclooxygenase, mostly in CNS
- Inactivated peripherally |
|
|
What are the clinical uses of Acetaminophen?
|
- Anti-pyretic
- Analgesic - NOT anti-inflammatory - Used instead of aspirin to avoid Reye syndrome in children with a viral infection |
|
|
How do NSAIDs compare to Acetaminophen?
|
Both have anti-pyretic and analgesic action, but only NSAIDs are anti-inflammatory
|
|
|
What are the toxic side effects of Acetaminophen?
|
- Overdose produces hepatic necrosis
- Acetaminophen metabolite (NAPQI) depletes glutathione and forms toxic tissue adducts in liver |
|
|
What is the antidote for an Acetaminophen overdose? Mechanism?
|
N-acetylcysteine - regenerates glutathione
Remember: Acetaminophen metabolite (NAPQI) depletes glutathione and forms toxic tissue adducts in liver |
|
|
What are the names of bisphosphonate drugs?
|
- Alendronate
- Other -dronates |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Bisphosphonates (Alendronate)?
|
Pyrophosphate analogs
- Binds hydroxyapatite in bone - Inhibits osteoclast activity |
|
|
What are the clinical uses of Bisphosphonates (Alendronate)?
|
- Osteoporosis
- Hypercalcemia - Paget disease of the bone |
|
|
What are the toxic side effects of Bisphosphonates (Alendronate)?
|
- Corrosive esophagitis (patients are advised to take with water and remain upright for 30 minutes)
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw |
|
|
What drugs can be used to prevent gout flares (chronic)?
|
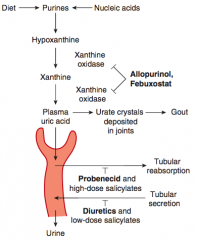
- Allopurinol
- Febuxostat - Probenecid |
|
|
What drugs can be used to treat gout flares (acute)?
|
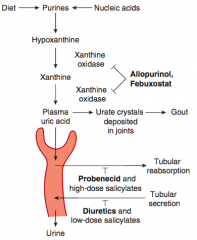
- NSAIDs
- Glucocorticoids - Colchicine |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Allopurinol?
|
Inhibits Xanthine Oxidase
- ↓ Conversion of xanthine to uric acid |
|
|
What are the uses of Allopurinol?
|
- Chronic gout drug (preventive)
- Lymphoma and leukemia to prevent tumor lysis-associated urate nephropathy |
|
|
What drugs should not be given with Allopurinol? Why?
|
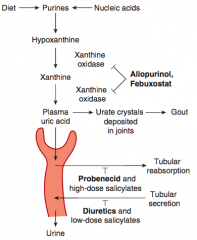
- Azathioprine and 6-Mercaptopurine (both normally metabolized by xanthine oxidase, which Allopurinol inhibits)
- Salicylates - all but the highest doses depress uric acid clearance |
|
|
What is the mechanism and use of Febuxostat?
|
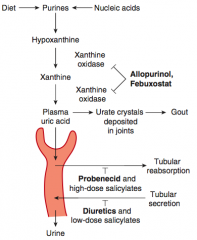
- Inhibits xanthine oxidase
- Chronic gout drug (preventive) |
|
|
What is the mechanism and use of Probenecid?
|
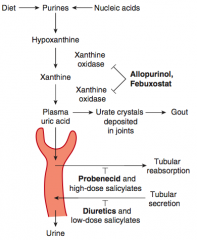
- Inhibits reabsorption of uric acid in proximal convoluted tubule (also inhibits secretion of penicillin)
- Chronic gout drug (preventive) |
|
|
What NSAIDs can be used to treat gout? In what circumstance?
|
- Naproxen and Indomethacin
- Acute gout flares |
|
|
How can glucocorticoids be administered? In what circumstance?
|
- Oral or intra-articular (into the joint)
- Acute gout flares |
|
|
What is the mechanism and use of Colchicine? Side effects?
|
- Binds and stabilizes tubulin to inhibit microtubule polymerization, impairing leukocyte chemotaxis and degranulation
- Acute and prophylactic value for gout - GI side effects |
|
|
What are the types of TNF-α inhibitors?
|
- Etanercept
- Infliximab - Adalimumab |
|
|
What are the characteristics of all TNF-α inhibitors? Why?
|
Predispose to infection, including reactivation of latent TB, since TNF blockade prevents activation of macrophages and destruction of phagocytosed microbes |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Etanercept?
|
- Fusion protein (receptor for TNF-α + IgG1 Fc portion) produced by recombinant DNA
- Etaner"CEPT" is a TNF decoy reCEPTor |
|
|
What are the clinical uses of Etanercept?
|
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Psoriasis - Ankylosing Spondylitis |
|
|
What is the mechanism of Infliximab?
|
Anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody
|
|
|
What is the mechanism of Adalimumab?
|
Anti-TNF-α monoclonal antibody
|
|
|
What are the clinical uses of Infliximab and Adalimumab?
|
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Rheumatoid Arthritis - Ankylosing Spondylitis - Psoriasis |

