![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
193 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the dominant normal flora in the skin?
|
Staphylococcus epidermidis
|
|
|
What is the dominant normal flora in the nose?
|
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Colonized by Staphylococcus aureus |
|
|
What is the dominant normal flora in the oropharynx?
|
Viridans group Streptococci
|
|
|
What is the dominant normal flora in dental plaques?
|
Streptococcus mutans
|
|
|
What is the dominant normal flora in the colon?
|
Bacteroides fragilis > E. coli
|
|
|
What is the dominant normal flora in the vagina?
|
- Lactobacillus
- Colonized by E. coli and Group B Strep |
|
|
What is the normal flora in neonates delivered by C-section?
|
No flora, but rapidly colonized after birth
|
|
|
Which bugs cause food poisoning that starts quickly and ends quickly?
|
- Staphylococcus aureus (preformed toxin)
- Bacillus cereus |
|
|
Which microorganisms cause food poisoning?
|
- Bacillus cereus
- Clostridium botulinum - Clostridium perfringens - E. coli O157:H7 - Salmonella - S. aureus - Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus |
|
|
Which microorganism causes food poisoning after eating reheated rice?
|
Bacillus cereus ("Food poisoning from reheated rice, Be serious!")
|
|
|
Which microorganism causes food poisoning after eating improperly canned foods (sign is bulging cans)?
|
Clostridium botulinum
|
|
|
Which microorganism causes food poisoning after eating reheated meat dishes?
|
Clostridium perfringens
|
|
|
Which microorganism causes food poisoning after eating undercooked meat?
|
E. coli O157:H7
|
|
|
Which microorganism causes food poisoning after eating poultry, meat, or eggs?
|
Salmonella
|
|
|
Which microorganism causes food poisoning after eating meats, mayonnaise, or custard?
|
Staphylococcus aureus (preformed toxin)
|
|
|
Which microorganism causes food poisoning after eating contaminated seafood?
|
- Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- Vibrio vulnificus |
|
|
Which microorganism causes wound infections from contact with contaminated water or shellfish?
|
Vibrio vulnificus
|
|
|
Which bugs cause bloody diarrhea?
|
- Campylobacter
- Entamoeba histolytica - Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) - Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC) - Salmonella - Shigella - Yersinia enterocolitica |
|
|
Which bug that causes bloody diarrhea is comma- or S-shaped and grows at 42°C?
|
Campylobacter
|
|
|
Which bug that causes bloody diarrhea is a protozoan, causes amebic dysentery and liver abscesses?
|
Entamoeba histolytica
|
|
|
Which bug that causes bloody diarrhea can cause Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome and makes Shiga-like toxin?
|
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) - O157:H7
|
|
|
Which bug that causes bloody diarrhea invades colonic mucosa?
|
Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC)
|
|
|
Which bug that causes bloody diarrhea is lactose (-), has flagellar motility, animal reservoir, and especially found in poultry and eggs?
|
Salmonella (remember flagella because salmon swim)
|
|
|
Which bug that causes bloody diarrhea is lactose (-), has a very low ID50, produces Shiga toxin, only human reservoir, and causes bacillary dysentery?
|
Shigella
|
|
|
Which bug that causes bloody diarrhea is associated with day-care outbreaks and pseudoappendicitis?
|
Yersinia enterocolitica
|
|
|
Which bugs cause watery diarrhea?
|
- Clostridium difficile
- Clostridium perfringens - Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) - Giardia and Cryptosporidium in immunocompromised - Vibrio cholerae - Rotavirus, Norovirus |
|
|
Which bug that causes watery diarrhea causes pseudomembranous colitis, caused by antibiotics, and occasionally may be bloody?
|
Clostridium difficile
|
|
|
Which bug that causes watery diarrhea also causes gas gangrene?
|
Clostridium perfringens
|
|
|
Which bug that cause watery diarrhea is aka travelers' diarrhea and produces heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable (ST) toxins?
|
Enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC)
|
|
|
Which protozoa can cause watery diarrhea in healthy patients?
|
Giardia
|
|
|
Which protozoa can cause watery diarrhea in immunocompromised patients?
|
Cryptosporidium
|
|
|
Which bug that causes watery diarrhea is comma-shaped, associated with "rice-water" diarrhea, and often from infected seafood?
|
Vibrio cholerae
|
|
|
Which viruses cause watery diarrhea?
|
- Rotavirus
- Norovirus |
|
|
What are the common causes of pneumonia in neonates?
|
- Group B streptococci
- E. coli |
|
|
What are the common causes of pneumonia in children (4 weeks - 18 years)?
|
Runts May Cough Chunky Sputum
- Viruses (RSV) - Mycoplasma - Chlamydia trachomatis (infants - 3 years) - Chlamydophila pneumoniae (school-aged children) - S. pneumoniae |
|
|
What are the common causes of pneumonia in adults (18-40 years)?
|
- Mycoplasma
- Chlamydophila pneumoniae - S. pneumoniae |
|
|
What are the common causes of pneumonia in adults (40-65 years)?
|
- S. pneumoniae
- H. influenzae - Anaerobes - Viruses - Mycoplasma |
|
|
What are the common causes of pneumonia in elderly (>65)?
|
- S. pneumoniae
- Influenza virus - Anaerobes - H. influenzae - Gram negative rods |
|
|
Which bugs are common in alcoholics and IV drug users?
|
- S. pneumoniae
- Klebsiella - Staphylococcus |
|
|
Which bugs are common to aspirate?
|
Anaerobes
|
|
|
Which bugs are "atypical"?
|
- Mycoplasma
- Legionella - chlamydia |
|
|
Which bugs are associated with Cystic Fibrosis?
|
- Pseudomonas
- S. aureus - S. pneumoniae |
|
|
Which bugs are common in the immunocompromised?
|
- Staphylococcus
- Enteric G- rods - Fungi - Viruses - P. jirovecii (with HIV) |
|
|
What are the nosocomial (hospital acquired) infections?
|
- Staphylococcus
- Pseudomonas - Other enteric G- rods |
|
|
Which bacteria are common post-viral infection?
|
- Staphylococcus
- H. influenzae - S. pneumoniae |
|
|
What are the common causes of meningitis in newborns (0-6 months)?
|
* Group B streptococci
* E. coli - Listeria * = same as pneumonia |
|
|
What are the common causes of meningitis in children (6 months - 6 years)?
|
* S. pneumoniae
- N. meningitidis - H. influenzae type B - Enteroviruses * = same as pneumonia |
|
|
What are the common causes of meningitis in 6 to 60 year olds?
|
* S. pneumoniae
- N. meningitidis - Enteroviruses - HSV * = same as pneumonia |
|
|
What is the number one cause of meningitis in teens?
|
N. meningitidis
|
|
|
What are the common causes of meningitis in elderly (>60)?
|
* S. pneumoniae
* G- rods - Listeria * = same as pneumonia |
|
|
How should you treat suspected cases of meningitis?
|
Treat empirically with Ceftriaxone and Vancomycin
- Add Ampicillin if Listeria is suspected |
|
|
What are the viral causes of meningitis?
|
- Enteroviruses (especially coxsackievirus)
- HSV-2 (HSV-1 = encephalitis) - HIV - West Nile Virus - VZV |
|
|
What are the common causes of meningitis in HIV patients?
|
- Cryptococcus
- CMV - Toxoplasmosis (brain abscesses) - JC virus (PML) |
|
|
What are cases of meningitis due to H. influenzae more common?
|
In unimmunized children (rates have gone down significantly in last 10-15 years since introduction of the conjugate H. influenzae vaccine)
|
|
|
What are the CSF findings in bacterial meningitis?
|
- ↑ opening pressure
- ↑ PMNs - ↑ Protein - ↓ Glucose |
|
|
What are the CSF findings in fungal / TB meningitis?
|
- ↑ opening pressure
- ↑ lymphocytes - ↑ Protein - ↓ Glucose |
|
|
What are the CSF findings in viral meningitis?
|
- Nl/↑ opening pressure
- ↑ lymphocytes - Nl/↑ Protein - Nl Glucose |
|
|
What kind of infection is likely if there are increased PMNs in the CSF?
|
Bacterial meningitis
|
|
|
What kind of infection is likely if there are increased lymphocytes in the CSF?
|
Either fungal / TB meningitis or viral meningitis
|
|
|
What kind of infection is likely if there is a normal glucose?
|
Viral meningitis
(both bacterial and fungal/TB cause decreased glucose) |
|
|
What is the most common cause of Osteomyelitis?
|
Staphylococcus aureus
|
|
|
What should you suspect as the cause of osteomyelitis in a patient who is sexually active?
|
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (rare)
- Septic arthritis more common |
|
|
What should you suspect as the cause of osteomyelitis in a patient who is diabetic?
|
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Serratia (Same as IV drug users) |
|
|
What should you suspect as the cause of osteomyelitis in a patient who is an IV drug user?
|
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Serratia (Same as for diabetics) |
|
|
What should you suspect as the cause of osteomyelitis in a patient who has sickle cell disease?
|
Salmonella
|
|
|
What should you suspect as the cause of osteomyelitis in a patient who has a prosthetic joint replacement?
|
- S. aureus
- Staphylococcus epidermidis |
|
|
What should you suspect as the cause of osteomyelitis in a patient who has vertebral involvement?
|
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Pott disease)
|
|
|
What should you suspect as the cause of osteomyelitis in a patient who has cat and dog bites?
|
Pasteurella multocida
|
|
|
What should you suspect as the cause of osteomyelitis in a patient who has no other information available?
|
Staphylococcus aureus (most common overall)
|
|
|
When do most cases of Osteomyelitis occur?
|
Most in children
|
|
|
What are the lab tests in a patient with Osteomyelitis?
|
Elevated CRP and ESR (but non-specific)
|
|
|
What does osteomyelitis look like on radiographs? MRI?
|
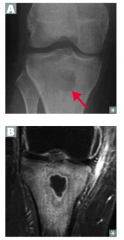
- Radiograph: more subtle (arrow in top picture)
- MRI: more easily seen |
|
|
What is the term for a bladder infection? Symptoms?
|
Cystitis
- Dysuria - Frequency - Urgency - Suprapubic pain - WBCs (but not WBC casts) in urine |
|
|
What is the method of infection that causes cystitis / UTI?
|
Ascension of microbes from urethra to bladder
- 10x more common in women because shorter urethra and urethra is colonized by fecal flora |
|
|
What are possible causes of UTIs in males?
|
- Infants with congenital defects
- Vesicoureteral reflex - Elderly with enlarged prostate |
|
|
What is the term for when a UTI / cystitis ascends to the kidney? Symptoms?
|
Pyelonephritis
- Fever - Chills - Flank pain - Costovertebral angle tenderness - Hematuria - WBC casts |
|
|
In what situations will you see WBC casts? When would you not see WBC casts?
|
- Cystitis (bladder infection): no WBC casts
- Pyelonephritis (kidney infection): WBC casts |
|
|
What are some predisposing factors for UTIs?
|
- 10x more common in females
- Obstruction - Kidney surgery - Catheterization - GU malformation - Diabetes (sugar in urine feeds bacteria) - Pregnancy |
|
|
What are the diagnostic markers for UTIs?
|
- Leukocyte esterase test (+) = bacterial UTI
- Nitrite test (+) = G- bacterial UTI - Urease test (+) = urease producing bugs (eg, Proteus, Klebsiella) - Urease test (-) = E. coli, Enterococcus |
|
|
What are the most common bugs that cause UTIs?
|
1. E. coli
2. Staphylococcus saprophyticus 3. Klebsiella pneumoniae - Serratia marcescens - Enterobacter cloacae - Proteus mirabilis - Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
Which bug that causes UTIs shows colonies with green metallic sheen on EMB agar?
|
Escherichia coli (leading cause of UTI)
- Negative urease test |
|
|
Which bug that causes UTIs is the 2nd leading cause of UTI in sexually active young women?
|
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
|
|
|
Which bug that causes UTIs has a large mucoid capsule and viscous colonies?
|
Klebsiella pneumoniae (3rd leading cause of UTI)
- Urease test positive |
|
|
Which bug that causes UTIs produces a red pigment?
|
Serratia marcescens (think maraschino cherry for red pigment)
- Usually nosocomial and drug resistant |
|
|
Which bugs that causes UTIs are often nosocomial and drug resistant?
|
- Serratia marcescens
- Enterobacter cloacae - Pseudomonas aeruginosa |
|
|
Which bug that causes UTIs has motility allowing it to "swarm" on agar and is associated with struvite stones?
|
Proteus mirabilis
- Produces urease |
|
|
Which bug that causes UTIs produces a blue-green pigment and fruity odor?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Usually nosocomial and drug resistant |
|
|
What marker will be positive if a UTI is positive?
|
Leukocyte esterase
|
|
|
What marker will be positive if a UTI is due to a gram negative bug?
|
Nitrite test
|
|
|
What are the common vaginal infections?
|
- Bacterial vaginosis
- Trichomoniasis - Candida vulvovaginitis |
|
|
Which vaginal infection causes no inflammation and a thin, white discharge with a fishy odor? Lab findings? Treatment?
|
Bacterial Vaginosis
- Clue cells - pH > 4.5 (elevated) - Treat with Metronidazole |
|
|
Which vaginal infection causes inflammation and a frothy, grey-green, foul-smelling discharge? Lab findings? Treatment?
|
Trichomoniasis
- Motile trichomonads - pH >4.5 (elevated) - Treat with Metronidazole and treat sexual partner |
|
|
Which vaginal infection causes inflammation and a thick, white, cottage cheese discharge? Lab findings? Treatment?
|
Candida vulvovaginitis
- Pseudohyphae - pH normal (4.0-4.5) - Treat with -azoles |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of Bacterial Vaginosis? Lab findings? Treatment?
|
- No inflammation
- Thin, white discharge with fishy odor - Clue cells - pH >4.5 (elevated) - Treat with Metronidazole |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of Trichomoniasis? Lab findings? Treatment?
|
- Inflammation
- Frothy, grey-green, foul-smelling discharge - Motile trichomonads - pH >4.5 (elevated) - Treat with Metronidazole and treat sexual partner(s) |
|
|
What are the signs/symptoms of Candida Vulvovaginitis? Lab findings? Treatment?
|
- Inflammation
- Thick, white, "cottage cheese" discharge - Pseudohyphae - pH normal (4.0-4.5) - Treat with -azoles |
|
|
What are the "ToRCHeS" infections?
|
Microbes that may pass from mother to fetus
- Transmission is transplacental and in most cases via delivery |
|
|
What are the non-specific signs common to many ToRCHeS infections?
|
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Jaundice - Thrombocytopenia - Growth retardation |
|
|
What are the infections that may pass from mother to fetus transplacentally or via delivery?
|
ToRCHeS:
- Toxoplasma gondii - Rubella - CMV - HIV - HSV-2 - Syphilis |
|
|
What are the non-ToRCHeS infections that all cause meningitis in neonates?
|
- Streptococcus agalactiae (group B streptococci)
- E. coli - Listeria monocytogenes |
|
|
What bug causes hydrops fetalis?
|
Parvovirus B19
|
|
|
Which infection presents with chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, and intracranial calcifications in neonates? Presentation in mother? Mode of transmission?
|
Toxoplasma gondii
- Usually asymptomatic in mom or lymphadenopathy (rarely) - Acquired via cat feces or ingestion of undercooked meat |
|
|
Which infection presents with PDA (or pulmonary artery hypoplasia), cataracts, and deafness ± blueberry muffin rash in neonates? Presentation in mother? Mode of transmission?
|
Rubella
- In mother: rash, lymphadenopathy, arthritis - Transmitted via respiratory droplets |
|
|
Which infection presents with hearing loss, seizures, petechial rash, and "blueberry muffin" rash in neonates? Presentation in mother? Mode of transmission?
|
CMV
- Usually asymptomatic in mom or mononucleosis like illness - Transmitted via sexual contact or organ transplants |
|
|
Which infection presents with recurrent infections and chronic diarrhea in neonates? Presentation in mother? Mode of transmission?
|
HIV
- Variable presentation in mom depending on CD4+ count - Transmitted via sexual contact or needlestick |
|
|
Which infection presents with encephalitis, herpetic (vesicular) lesions in neonates? Presentation in mother? Mode of transmission?
|
HSV-2
- Usually asymptomatic in mom or presence of herpetic (vesicular) lesions - Transmitted via skin or mucous membrane contact |
|
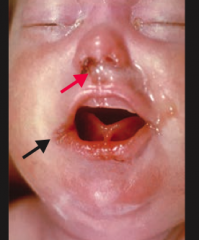
Which infection presents with stillbirth or hydrops fetalis in neonates; if the child survives presents with facial abnormalities (notched teeth, saddle nose, short maxilla), saber shins, and CN VIII deafness? Presentation in mother? Mode of transmission?
|
Syphilis
2 presentations in mom that are associated with fetal infection: - 1° chancre - 2° disseminated rash Spread via sexual contact |
|
|
Which neonatal infection is transmitted to the mom via cat feces or ingestion of undercooked meat? Neonatal manifestation? Maternal manifestation?
|
Toxoplasma gondii
- Neonatal: chorioretinitis, hydrocephalus, intracranial calcifications - Maternal: usually asymptomatic, lymphadenopathy (rare) |
|
|
Which neonatal infection is transmitted to the mom via respiratory droplets? Neonatal manifestation? Maternal manifestation?
|
Rubella
- Neonatal: PDA (or pulmonary artery hypoplasia), cataracts, and deafness ± blueberry muffin rash - Maternal: rash, lymphadenopathy, arthritis |
|
|
Which neonatal infection is transmitted to the mom via sexual contact or organ transplants? Neonatal manifestation? Maternal manifestation?
|
CMV
- Neonatal: hearing loss, seizures, petechial rash, blueberry muffin rash - Maternal: usually asymptomatic or mononucleosis-like illness |
|
|
Which neonatal infection is transmitted to the mom via sexual contact or needlestick? Neonatal manifestation? Maternal manifestation?
|
HIV
- Neonatal: recurrent infections and/or chronic diarrhea - Maternal: variable presentation depending on CD4+ count |
|
|
Which neonatal infection is transmitted to the mom via skin or mucous membrane contact? Neonatal manifestation? Maternal manifestation?
|
HSV-2
- Neonatal: encephalitis, herpetic (vesicular) lesions - Maternal: usually asymptomatic, herpetic (vesicular) lesions |
|
|
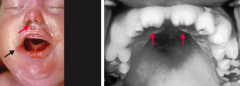
Which neonatal infection is transmitted to the mom via sexual contact but not organ transplant or needlesticks? Neonatal manifestation? Maternal manifestation?
|
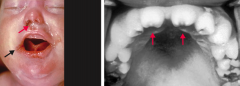
Syphilis
- Neonatal: often results in stillbirth, hydrops fetalis - Neonatal if child survives: facial abnormalities (notched teeth, saddle nose, short maxilla), saber shins, CN VIII deafness - Maternal: chancre (1°) and disseminated rash (2°) are the two stages likely to result in fetal infection |
|
|
Which neonatal infections can cause a blueberry muffin rash?
|
- Rubella
- CMV |
|
|
Which neonatal infections can cause deafness?
|
- Rubella
- Syphilis (CN VIII deafness) |
|
|
Which bugs cause red rashes in childhood?
|
- Coxsackievirus type A
- HHV-6 (Roseola) - Measles virus - Parvovirus B19 - Rubella virus - Streptococcus pyogenes - VZV |
|
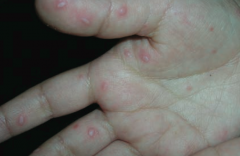
What bug is responsible for a vesicular rash on palms and soles as well as vesicles and ulcers in oral mucosa in children? Associated disease?
|
Coxsackievirus type A - hand-foot-mouth disease
|
|
|
What bug is responsible a macular rash over body that appears after several days of high fever, can present with febrile seizures, and usually affects infants? Associated disease?
|
HHV-6 - Roseola
|
|
|
What bug causes a rash that begins at the head and moves down, rash is preceded by cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, and blue-white (Koplik) spots on buccal mucosa in children? Associated disease?
|
Measles virus - Rubeola
(a paramyxovirus) |
|
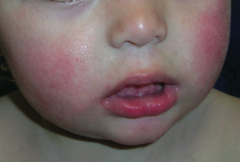
What bug causes "slapped cheek" rash on the face of children and can cause hydrops fetalis in pregnant women? Associated disease?
|
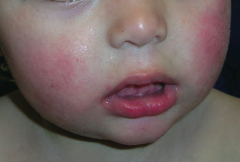
Parvovirus B19 - Erythema Infectiosum (fifth disease)
|
|
|
What bug causes a rash that begins at the head and moves down making a fine truncal rash and postauricular lymphadenopathy in children? Associated disease?
|
Rubella virus (Rubella)
|
|
|
What bug causes an erythamtous, sandpaper-like rash with fever and sore through in children? Associated disease?
|
Streptococcus pyogenes - Scarlet Fever
|
|
|
What bug causes a vesicular rash that begins on the trunk, spreads to the face and extremities with lesions of different ages in children? Associated disease?
|
VZV - Chickenpox
|
|
|
What disease is caused by Coxsackievirus Type A? Clinical presentation?
|
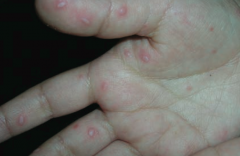
Hand-foot-mouth disease
- Vesicular rash on palms and soles - Vesicles and ulcers in oral mucosa |
|
|
What disease is caused by HHV-6? Clinical presentation?
|
Roseola
- Macular rash over body - Rash appears after several days of high fever - Can present with febrile seizures - Usually affects infants |
|
|
What disease is caused by Measles Virus? Clinical presentation?
|
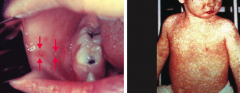
Measles / Rubeola
- Paramyxovirus - Rash begins at head and moves down - Rash is preceded by cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, and blue-white Koplik spots on buccal mucosa |
|
|
What disease is caused by Parvovirus B19? Clinical presentation?
|
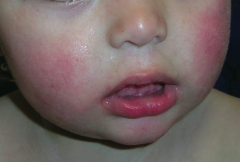
Erythema Infectiosum (Fifth Disease)
- "Slapped cheek" rash on face - Can cause hydrops fetalis in pregnant women |
|
|
What disease is caused by Rubella Virus? Clinical presentation?
|
Rubella
- Rash begins at head and moves down - Fine truncal rash - Postauricular lymphadenopathy |
|
|
What disease is caused by Streptococcus pyogenes? Clinical presentation?
|
Scarlet Fever
- Erythematous, sandpaper-like rash - Fever and sore throat |
|
|
What disease is caused by VZV? Clinical presentation?
|
Chickenpox
- Vesicular rash begins on trunk - Rash spreads to face and extremities with lesions of different ages |
|
|
What are the sexually transmitted diseases?
|
- AIDS
- Chancroid - Chlamydia - Condylomata acuminata - Genital herpes - Gonorrhea - Hepatitis B - Lymphogranuloma venereum - Syphilis (1°, 2°, and 3°) - Trichomoniasis |
|
|
Which STD is caused by HIV? Clinical features?
|
AIDS
- Opportunistic infections - Kaposi sarcoma (HHV-8) - Lymphoma |
|
|
Which STD is caused by Haemophilus ducreyi? Clinical features?
|
Chancroid
- Painful genital ulcer (ducreyi - "it's so painful you DO CRY") - Inguinal adenopathy |
|
|
Which STD is caused by Chlamydia trachomatis (D-K)? Clinical features?
|
Chlamydia
- Urethritis - Cervicitis - Conjunctivitis - Reactive arthritis - PID |
|
|
Which STD is caused by HPV 6 and 11? Clinical features?
|
Condylomata acuminata
- Genital warts - Koilocytes |
|
|
Which STD is caused by HSV-2 (less commonly HSV-1)? Clinical features?
|
Genital herpes
- Painful penile, vulvar, or cervical vesicles and ulcers - Can cause systemic symptoms such as fever, headache, myalgia |
|
|
Which STD is caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae? Clinical features?
|
Gonorrhea
- Urethritis - Cervicitis - PID - Prostatitis - Epididymitis - Arthritis - Creamy purulent discharge |
|
|
Which STD is caused by HBV? Clinical features?
|
Hepatitis B
- Jaundice |
|
|
Which STD is caused by Chlamydia trachomatis (L1-L3)? Clinical features?
|
Lymphogranuloma venereum
- Infection of lymphatics - Painless genital ulcers - Painful lymphadenopathy (ie, buboes) |
|
|
Which STD is caused by Treponema pallidum? Clinical features?
|
Syphilis
- 1° - painless chancre - 2° - fever, lymphadenopathy, skin rashes, condylomata lata - 3° - gummas, tabes dorsalis, general paresis, aortitis, Argyll Robertson pupil |
|
|
Which STD is caused by Trichomonas vaginalis? Clinical features?
|
Trichomoniasis
- Vaginitis - Strawberry cervix - Motile in wet prep |
|
|
Which STD presents with opportunistic infections, Kaposi Sarcoma, and lymphoma? Causative organism?
|
AIDS - HIV
|
|
|
Which STD presents with painful genital ulcers and inguinal adenopathy? Causative organism?
|
Chancroid - Haemophilus ducreyi (it's so painful you "do cry")
|
|
|
Which STD presents with urethritis, cervicitis, conjunctivitis, reactive arthritis, and PID? Causative organism?
|
Chlamydia - C. trachomatis (D-K)
|
|
|
Which STD presents with genital warts and koilocytes? Causative organism?
|
Condylomata acuminata - HPV-6 and -11
|
|
|
Which STD presents with painful penile, vulvar, or cervical vesicles and ulcers; can cause systemic symptoms such as fever, headache, and myalgia? Causative organism?
|
Genital herpes - HSV-2 (less commonly HSV-1)
|
|
|
Which STD presents with urethritis, cervicitis, PID, prostatitis, epididymitis, arthritis, and creamy purulent discharge? Causative organism?
|
Gonorrhea - Neisseria gonorrhoeae
|
|
|
Which STD presents with jaundice? Causative organism?
|
Hepatitis B - HBV
|
|
|
Which STD presents with infection of lymphatics, painless genital ulcers, and painful lymphadenopathy (buboes - armpit or groin)? Causative organism?
|
Lymphogranuloma venereum - Chlamydia trachomatis (L1-L3)
|
|
|
Which STD presents with a painless chancre? Causative organism?
|
1° Syphilis - Treponema pallidum
|
|
|
Which STD presents with fever, lymphadenopathy, skin rashes, and condylomata lata (wart-like lesions on genitals)? Causative organism?
|
2° Syphilis - Treponema pallidum
|
|
|
Which STD presents with gummas, tabes dorsalis, general paresis, aortitis, and Argyll Robertson pupil? Causative organism?
|
3° Syphilis - Treponema pallidum
|
|
|
Which STD presents with vaginitis, strawberry cervix, and motility in wet prep? Causative organism?
|
Trichomoniasis - Trichomonas vaginalis
|
|
|
Which bugs cause Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
|
- Chlamydia trachomatis (subacute, often undiagnosed)
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae (acute) |
|
|
What is the most common bacterial STD in the US?
|
Chlamydia trachomatis
|
|
|
What are the signs of Pelvic Inflammatory Disease?
|
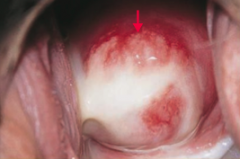
- Cervical motion tenderness (chandelier sign)
- Purulent cervical discharge (picture) - May include salpingitis (inflammation of fallopian tubes), endometritis, hydrosalpinx (distally blocked fallopian tube by clear or serous fluid), and tubo-ovarian abscess |
|
|
What can Pelvic Inflammatory Disease lead to?
|
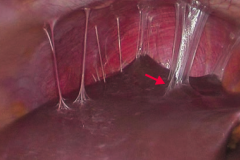
Fits-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
- Infection of the liver capsule - "Violin string" adhesions of peritoneum to liver |
|
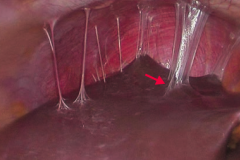
What is this a sign of?
|
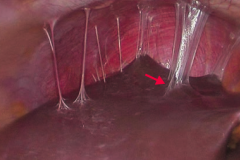
Fits-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
- Infection of the liver capsule - "Violin string" adhesions of peritoneum to liver This is caused by Pelvic Inflammatory Disease |
|
|
What are the nosocomial infections?
|
- Candida albicans
- CMV, RSV - E. coli, Proteus mirabilis - HBV - Legionella - Pseudomonas aeruginosa - S. aureus |
|
|
What nosocomial infection are you at risk for if you have hyperalimentation (tube feeding)?
|
Candida albicans
|
|
|
What nosocomial infection are you at risk for in the newborn nursery?
|
- CMV
- RSV |
|
|
What nosocomial infection are you at risk for if you have urinary catheterization?
|
- E. coli
- Proteus mirabilis |
|
|
What nosocomial infection are you at risk for if you have a wound infection?
|
S. aureus
|
|
|
What nosocomial infection are you at risk for if you work in the renal dialysis unit?
|
Hepatitis B Virus
|
|
|
What nosocomial infection are you at risk for if you are around water aerosols?
|
Legionella (think Legionella when a water source is involved)
|
|
|
What nosocomial infection are you at risk for if using respiratory therapy equipment?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
What nosocomial infection are you at risk for if burned?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
What are the two most common causes of nosocomial infections?
|
- E. coli (UTI)
- S. aureus (wound infection) |
|
|
What bugs most commonly affect unimmunized children?
|
- Rubella virus
- Measles virus - H. influenzae type B - Poliovirus - Corynebacterium diphtheriae |
|
|
An unimmunized child presents with a rash that begins at the head and moves down with postauricular lymphadenopathy. What do you suspect they have?
|
Rubella virus
|
|
|
An unimmunized child presents with a rash taht begins at the head and moves down with the rash preceeded by cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, and blue-white (Koplik) spots on buccal mucosa. What do you suspect they have?
|
Measles virus
|
|
|
An unimmunized child presents with meningitis caused by a microbe that colonizes the nasopharynx. What do you suspect they have?
|
H. influenzae type B
|
|
|
An unimmunized child presents with meningitis that leads to myalgia and paralysis. What do you suspect they have?
|
Poliovirus
|
|
|
An unimmunized child presents with fever with dysphagia, drooling, and difficulty breathing due to edematous "cherry red" epiglottis (thumbprint sign on x-ray). What do you suspect they have?
|
H. influenzae type B (also capable of causing epiglottitis in fully immunized children)
|
|
|
An unimmunized child presents with a grayish oropharyngeal exudate ("pseudomembranes" may obstruct airway) and a painful throat. What do you suspect they have?
|
Corynebacterium diphtheriae (elaborates toxin that causes necrosis in pharynx, cardiac, and CNS tissue)
|
|
|
If you have an asplenic patient (due to surgical splenectomy or autosplenectomy, eg, chronic sickle cell anemia), what organism are they at risk for?
|
Encapsulated microbes, espeically SHiN
- S. pneumoniae >> - H. influenzae type B >> - N. meningitidis |
|
|
What organism is branching rods in oral infection and has sulfur granules?
|
Actinomyces israelii
|
|
|
Which organisms produce chronic granulomatous disease?
|
Catalase (+) microbes, especially S. aureus
|
|
|
Which organism produces "currant jelly" sputum?
|
Klebsiella
|
|
|
Which organism is associated with a dog or cat bite?
|
Pasteurella multocida
|
|
|
Which organism is associated with facial nerve palsy?
|
Borrellia burgdorferi (Lyme disease)
|
|
|
Which fungal infection is associated with a diabetic or immunocompromised patient?
|
Mucor or Rhizopus species
|
|
|
What organism is associated with health care providers?
|
Hepatitis B Virus (from a needle stick)
|
|
|
Which organisms are associated with neutropenic patients?
|
- Candida albicans (systemic)
- Aspergillus |
|
|
Which organism is associated with organ transplant recipients?
|
Cytomegalovirus
|
|
|
Which organism is associated with PAS (+)?
|
Tropheryma whipplei (Whipple's disease)
|
|
|
Which organism is associated with pediatric infections?
|
Haemophilus influenzae (including epiglottitis)
|
|
|
Which organism is associated with pneumonia in cystic fibrosis?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
Which organism is associated with burn infections?
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
|
|
|
Which organisms are associated with rash on hands and feet?
|
- Coxsackie A virus
- Treponema pallidum - Rickettsia rickettsii |
|
|
Which organism is associated with sepsis / meningitis in a newborn?
|
Group B strep
|
|
|
Which organism is associated with surgical wounds?
|
S. aureus
|
|
|
Which organism is associated with a traumatic open wound?
|
Clostridium perfringens
|

