![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Why care about udder health?
|
-mastitis is the most frequent and costly disease of the dairy industry
|
|
|
Mastitis
-economic effects |
-Inc. amount of non-saleable milk
-Dec. milk production -Dec. milk quality (reduced quality bonus, reduced shelf life and cheese yield) -Inc. treatments -Inc. culling $2.8 billion |
|
|
Mastitis
-largest economic losses due to |
-reduced production*
-culling (replacement cost) |
|
|
US dairy industry facts
|
-Avg. herd = 115 cows
-97% family owned -rising in the western US |
|
|
Days in milk
-define |
-days since calving
|
|
|
Freshened
-define |
-calved
|
|
|
Dry cow
-define |
-cow that is not milking and waiting to calve
|
|
|
Dry/Dried/Dry-off
-define |
-cease milking
|
|
|
Lactation
-define |
-from calving to calving
|
|
|
Parlor
-define |
-where cows are milked
|
|
|
Pit
-define |
-where the milker stands to milk cows
|
|
|
Cow prep or Prep
-define |
-procedure carried out at the udder just prior to milk harvest at each milking
|
|
|
Pre-dip
-define |
-antimicrobial dip applied to every teat on every cow before milking
|
|
|
Post-dip
-define |
-antimicrobial dip applied to every teat on every cow after milking
|
|

|
Ayrshire
|
|

|
Black and white holstein
|
|

|
Brown swiss
|
|

|
Danish red
|
|

|
Guernsey
|
|

|
Jersey
|
|

|
Jersey x Holstein
|
|

|
Montbeliarde
|
|

|
Normandy
|
|
|
Dairy production cycle
|
-Birth
-Weaned (5-6 wks) -Breed (13-15 mo) -Calve (22-24 mo) --> 1st lactation -Breed (50 days post calving) -Dry-off (305 days post calving) -Calve (45-60 days post dry off) -Breed (50 days post calving) |
|
|
Approximately how many lactations are there per cow
|
-3
|
|
|
When is peak milk production
|
-approx. 60 days post-calving
|
|
|
Dairy cattle
-types of housing |
-dry lot
-tie stall (colder climates) -free stall |
|
|
Milking system types
|
Small Farms
-Flat barn/Stanchion barn -Tie-stall barn Larger Farms -Tandem parlor -Herringbone parlor -Parallel parlor -Rotary parlor Robotic |
|
|
Most cows are milked in what kind of milking facility
|
-parlors
|
|
|
Problem with rotary/carousel parlor
|
-milkers don't get to interact
-each person has a specific job |
|
|
Robotic milking system
-benefit |
-reduction in labor
|
|
|
Robotic milking system
-negatives |
-requires 3 months of training
-high up front costs -life expectancy about 10 yrs |
|
|
Bulk tank
-define |
-where the milk is collected to be transported to the milk company
-where samples for milk cultures can be collected |
|
|
Bulk tank
-what milk can be collected |
-milk from cows > 3 days fresh (colostrum)
-not on antibiotics/anti-inflammatories |
|
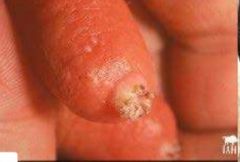
-diagnosis
-cause |
hyperkeratosis
-overmilking cow |
|

|
-A: teat cup
-B: vacuum tube -C: Claw -D: milk line/hose |
|
|
Automatic Detacher/Takeoff
-function |
-prevents overmilking
|
|
|
Key performance indicators for milking equipment
|
-mean claw vacuum (10.5-12.5"Hg)
-max claw vacuum fluctuation (<3"Hg) -% use of manual mode when automatic takeoffs are used (<5%) -D phase of pulsation cycle (>150-200 ms) |
|
|
In addition to a properly functioning milking system, what else is needed to optimize production and prevent mastitis?
|
-optimal milk letdown
|
|
|
Milk letdown
-define |
-the process where the muscles surrounding the alveoli contract to move the milk into the ducts and cistern for efficient milk harvest
|
|
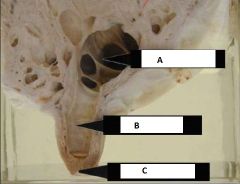
|
-A: Gland sinus
-B: Teat sinus -C: Papillary duct |
|
|
Alveoli
-function |
-milk production
-60% of milk storage in cows (differs between spp.) |
|
|
Alveoli
-surrounded by |
-myoepithelial cells
|
|
|
Pathway of milk letdown
|
-teat stimulation by milker, sound/smell of milking area, presence of milking unit
--nerve impulse to hypothalamus then to posterior pituitary ---post pituitary releases oxytocin ----oxytocin reaches myoepithelial cells in mammary gland -----myoepithelial cells constrict causing milk to be secreted into the ducts ------milking unit removes milk from ducts and cisterns |
|
|
What is important to get milk letdown on first lactation?
|
-human stimulation
|
|
|
Why don't you want the cows to become excited when getting milked?
|
-epinephrine can over-ride oxytocin
|
|
|
To achieve optimal milk letdown we must have _______
|
-proper milking procedures
|
|
|
What is important to know about milking procedures?
|
-timing is key
|
|
|
Pre-dip contact time (kill time)
|
-30 sec
|
|
|
Milking unit attached how long after pre-dip
|
-90-120 sec
|
|
|
Why is attachment of the milking machine from 90-120 sec after pre-dip important?
|
-time of highest oxytocin concentration
-considered overmilking if on either side of the window |
|
|
Strip
-define |
-remove 2-3 streams of milk from each teat
|
|
|
Wipe
-define |
-remove dip and bacteria
|
|
|
Why is stripping important?
|
-the first 2-3 streams of milk contain the highest somatic cell count, therefore milk quality is enhanced
-allows milker to look for clinical mastitis -most powerful stimulation for oxytocin release |
|
|
Why is stimulation of the teats important?
|
-inc. milk letdown --> dec. amount of time the milking unit is on the teats
-detrimental to teat health to leave the milking machine on the teats too long -extended unit on times are additive and accumulative |
|
|
Milking routines
-types |
-sequential
-territorial (most popular) |
|
|
Is there one procedure for optimal milk letdown?
|
-No
-different herds use different procedures that suit their needs |
|
|
Ways to monitor milking procedure?
|
-cameras
-electronic monitoring systems to monitor milking efficiency |

