![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Factors contributing to mastitis
|
-cow factors
-people factors -environmental factors -bacteria factors |
|
|
Most important factor that contributes to mastitis
|
-people factors
|
|
|
How do bacteria move into the udder?
-exception |
via the streak canal
-bacterial located on the surface of the teat --moisture or injection carry bacteria up the teat canal ---colonization of milk producing tissue -cannot move from quarter to quarter -exception = Mycoplasma sp. |
|
|
Mastitis
-people causes |
Poor milking procedure
-dirty teats -poor lag time -poor teat dipping -poor milking unit management |
|
|
Mastitis
-animal causes |
Immunosuppression from calving
Conformation (udder depth) -deep udders carry more dirt -teats get injured |
|
|
Why is udder conformation not a big deal in today's herds?
|
-moderately heritable
|
|
|
Matitis
-environmental causes |
-dirty stalls
-heat stress (immunosuppression) -dirty alleyways |
|
|
Mastitis
-bacterial causes |
-environmental vs. contagious
|
|
|
For mastitis to occur, what must be present?
|
-bacteria
- + one of the epidemiological triad arms |
|
|
Arms of the epidemiological triad
|
-pathogen
-host -environment/management |
|
|
Mastitis
-Iceberg principle |
-for every clinical mastitis case there are 15-40 subclinical cases
|
|
|
How can subclinical mastitis cases be found?
|
-somatic cell count
|
|
|
Why is finding subclinical mastitis important?
|
-more costly than clinical mastitis
|
|
|
Clinical mastitis
-signs |
-swollen quarter
-abnormal appearing milk w/ clots, flakes, etc. |
|
|
Clinical mastitis
-severity score |
-1: abnormal milk only
-2: abnormal milk & swollen quarter -3: abnormal milk, swollen quarter, and systemic signs |
|
|
Mastitis
-purpose of severity score |
-monitor how quickly milkers are recognizing mastitis
-if 20% or more mastitis cases are score 3 then milkers are not recognizing the signs |
|
|
Contagious organisms
-characteristics |
-able to colonize and live in the udder
-Infection occurs during the milking process -Post-dip is key to prevent |
|
|
Environmental organisms
-characteristics |
-Eliminated rapidly once in the udder
-Infection occurs between milkings -Pre-dipping helps to control |
|
|
Environmental causes of mastitis
-how long for self-elimination |
-about 10 days
|
|
|
Bovine mastitis
-typical contagious infection etiological agents |
-S. aureus
-Mycoplasma sp. |
|
|
Main method for reducing new infection rate for contagious and environmental infections
|
-management changes
|
|
|
Contagious mastitis
-effect on BTSCC after management change |
-slow decrease
|
|
|
Environmental mastitis
-effect on BTSCC after management changes |
-quick decrease
|
|
|
What needs to always be kept in mind in order to prevent mastitis?
|
-Epidemiological triad
|
|
|
Preventing mastitis
-animal components that affect the epidemiological triad |
-udder conformation
-immunosuppression -age |
|
|
When is immunosuppression resulting in mastitis a problem in a cow?
-why? |
-right before and right after lactation
-all fresh cows suffer from immunosuppression |
|
|
Immunological suppression
-how to prevent |
-balanced diet concentrating on feed intake and the proper density of nutrients to maximize immunity that is present
-reduce environmental exposure |
|
|
Describe the relationship between the onset of mastitis and age
|
-young and old cows are more susceptible to mastitis infection
|
|
|
Why is controlling the environment so important to mastitis prevention?
|
-mastitis risk is directly related to the bacterial load on the teat
|
|
|
Ways to minimize bacterial load on the teats
|
-routine clip/flame of excess hair from the udder
-clean bedding and clean area to stand/walk -teat dip |
|
|
Why do some herds use barn lime?
-problem |
-thought to decrease the pH, providing an inhospitable environment for bacteria
-problem: needs to be reapplied every few hrs and doesn't really work too well |
|
|
Problem with environmental management for mastitis prevention in the southeast
|
-cooling pools are needed
-need to consider the health impacts of not having cooling pools and weight them against the SCC/bacterial load |
|
|
Pre-dip
-for control of |
-environmental mastitis
|
|
|
Pre-dip
-purpose |
-reduce the bacteria load on the teat at the time of milking
|
|
|
Post-dip
-for control of |
contagious mastitis
|
|
|
Post-dip
-purpose |
-remove milk film
-reduces the number of bacteria that can colonize the teat skin |
|
|
Why is removing the milk film from the teat important?
|
lessens the nutrients available for bacterial growth
|
|
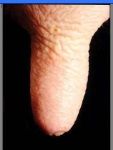
Describe
|
-normal teat
|
|
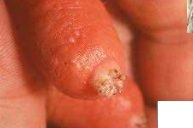
Describe
|
-hyperkeratosis
-bacteria able to live in cracks |
|
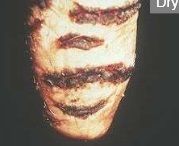
Describe
|
-dry, cracked teat
-due to cold/winter conditions -bacteria con colonize in cracks |
|
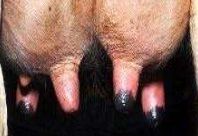
Describe
|
-overmilked teat
-red -edematous |
|
|
Mastitis
-infection rate is directly related to? |
-amount of bacteria on the teat
|
|
|
Key to excellent udder health
|
-clean cows
-milking procedures that reduce the number of bacteria present on the test (if cows are extremely dirty, no milking procedure can effectively reduce the bacterial numbers on the teat) |
|
|
Keys to mastitis prevention
|
-clean cows
-proper milking procedure -culture all cows before practice -train and monitor milker performance -review DHI and other records monthly -proper milking equipment maintenance |
|
|
Most of the money lost in milk production is due to_____
|
sub-clinical mastitis
|

