![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
BRDC
-viruses |
-IBR (infectious bovine rhinotracheitis)
-BVD (bovine viral diarrhea) -PI3 (influenza) -BRSV (Bovine respiratory syncitial virus) |
|
|
IBR
-prevalence |
-very common
|
|
|
Virus that should be addressed every time you put a vaccine in a respiratory preventive program
|
-IBR
|
|
|
IBR
-vaccine to use |
-MLV (unless there are reproductive concerns)
|
|
|
Dominant antigen
-define |
-antigen that takes up the majority of the immune response when multiple antigens are administered at the same time
|
|
|
Bovine
-respiratory dominant antigen |
-IBR
|
|
|
IBR as a dominant antigen
-effect |
-if the animal has not been exposed, then IBR will negate the response to other antigens (Mannheimia, Trueperella)
|
|
|
IBR as a dominant antigen
-concurrent vaccination |
-wait to administer other antigens until after primary IBR exposure
or -don't include IBR at the time of initial exposure to other antigens |
|
|
IBR
-antemortem signs |
-"rednose"
-pustules in nares -high fever -watery eyes -excellent treatment response in uncomplicated IBR (no bacterial complication) |
|
|
IBR
-postmortem signs |
-Sewerpipe trachea
-possible no trachea signs |
|
|
Bovine
-how to autopsy an animal with respiratory disease |
-remove entire respiratory tract with the tongue
|
|
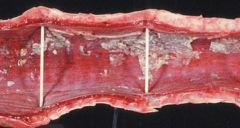
Describe
|
-sewerpipe trachea
*differentiate from respiratory debris by rubbing on trachea. Plaques stay on with sewerpipe trachea |
|
|
IBR
-poor therapeutic practices |
Vaccination in the face of disease
-MLV IBR vaccine given at the time of BRD therapy (no difference in outcome) Revaccinate entire pen -no data to support efficacy Trying revaccination on a pen before mass treatment -no evidence of benefit |
|
|
IBR
-proper therapy |
-address secondary bacterial infection with antimicrobials
|
|
|
IBR
-vaccine type use -why |
-MLV
-provide superior cellular immune response compared to killed vaccines |
|
|
IBR vaccine
-intranasal vs. instramuscular |
Intranasal
-immediate, local protection Intramuscular -systemic effect *suggest giving IM with intranasal unless there are reproductive concerns |
|
|
Chemically altered IBR vaccine
-when to use -name |
-only use where reproductive concerns are present
-DON'T use in feedlot -cattlemaster IV |
|
|
IBR
-Onset 5 IN problem (describe) |
-labeled for beef operations, branding and weaning, inducing a rapid immunological response in the face of high stress and as a measure against pre-shipment (high risk cattle)
-company response to not use with high risk cattle due to pulmonary infections |
|
|
BVD
-prevalence |
-very ubiquitous
|
|
|
BVD
-characteristics |
-Types I & II
-cytopathic and noncytopathic -antigenically diverse population |
|
|
BVD
-vaccination |
-never iintranasal
*not in the latest intranasal vaccine w/ IBR, PI3, BRSV |
|
|
Latest intranasal vaccine
|
-Inforce 3
|
|
|
BVD
-signs |
Presentation as a reproductive and respiratory disease (part of a severe respiratory outbreak)
+/- diarrhea +/- oral ulcers +/- hemorrhagic syndrome in a BRD calf (bleeding from mouth , nose, anus, pale mm, depressed, lungs look fine) -poor treatment response & chronics |
|
|
BVD
-effect of PI animals on morbidity in the feedlot pen |
-some studies show marked effect
-no significant changes in BRDC morbidity in single-source pens with a PI animal -increased morbidity if a PI animal is present in a comingled pen *most times should euthanize PI calves |
|
|
BVD
-diagnosis |
-ear notch
|
|
|
BVD
-postmortem lesions |
Erosions of the GIT
-mouth -esophageal linear erosions -abomasum (blood) -linear erosions in cecum Necrotic peyer's patches *erosions don't need to be present |
|
|
BVD
-therapy |
-Treat BRD
-euthanize chronics with oral ulcers (unethical to sell, shedding virus) |
|
|
BVD
-prognosis |
-many animals beat acute BVD
|
|
|
BVD
-vaccination |
-don't know the importance of cellular immunity because BVD wipes out leukocytes in test media
-concern over immunosuppression with MLV vaccines -use MLV BVD vaccine everywhere except where reproduction is a concern and intranasal |
|
|
Will MLV BVD vaccine kill persistently infected animals?
|
-only if it is a cytopathic match to the noncytopathic virus infecting the PI animal
|
|
|
Won't a previous killed vaccine block a subsequent MLV product?
|
marketing ploy by killed virus company (no data)
|
|
|
BVD
-MLV vs. Killed in the feedlot |
-some use Killed vaccines on arrival do to concern of immunosuppressive and stress effects
-some think superior protection by MLV is worth the risk -Dairys: KV can be used if vaccination isn't timed for when the cow is open |
|
|
MLV BVD in calves nursing the cow
|
-there are vaccines labeled for calves still nursing the cow
-vaccinated calves shed the vaccine virus for a short period |
|
|
MLV BVD use in cows
|
-not during the first trimester
-if needed,"", start up immunity the last month or so of pregnancy |
|
|
Parainfluenza type 3
-effect |
-unknown effects in vaccines
-probably no harm |
|
|
BRSV
-prevalence |
-geographical effect on occurance
|
|
|
BRSV
-signs |
-open mouth breathing
-severe dyspnea -high fever -bloody mucus in feedbunk |
|
|
BRSV
-signs often confused with |
-Acute interstitial pneumonia
|
|
|
BRSV
-possibly associated with |
-bacterial pneumonia complex presentation
|
|
|
BRSV
-postmortem |
-wet, heavy lungs
-possible interstitial edema -interstitial emphysema |
|
|
BRSV
-therapy |
-treat like BRD
*don't use anti-inflammatories or furosemide |
|
|
BRSV
-diagnostic tests |
-FA
-Immunohistochemistry -viral isolation -histopathology -PCR******** |
|
|
Is BRSV a hypersensitivity disease?
|
-no evidence of more severe clinical disease with vaccine
|
|
|
BRSV vaccination
-is it protective |
-no lasting immunity
-some economic benefit of vaccine after many attempts |
|
|
BRSV
-vaccination |
-give 2 shots immediately
|

