![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
96 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Unique eye anatomical structures of the bovine
|
-upper and lower lacrimal puncta
-horizontal pupil -dorsal and ventral pupillary ruff -tapetum w/ "stars of Winslow" -holangiotic fundus with tapetum |
|
|
Anophthalmia/Microphthalmia
-causes |
-congenital
-generally unknown cause -BVDV major concern**** -Infection, Toxin, Nutrition, environment, inherited |
|
|
Anophthalmia/Microphthalmia
-other ocular anomalies likely present |
-microcornea
-corneal opacity -cataracts -aniridia -retinal changes/detachment |
|
|
Most common maternal infection causing ophthalmic defects
|
-BVDV
|
|
|
When does BVDV usually cause ocular defects during gestation?
|
-76-150 days
|
|
|
BVDV
-ocular defects caused |
-wide range of defects
|
|
|
Coloboma
-define |
-tissue absence
|
|
|
Dermoid
-define |
-plaque of differentiated skin in an abnormal location
|
|
|
Dermoid
-type of condition |
-congenital
|
|
|
Dermoid
-most common location |
-temporal limbus
|
|
|
Dermoid
-breed predilection |
-inherited in herefords
|
|
|
Dermoid
-treatment |
-none if small, hair-free
-superficial keratectomy if painful or impairs vision |
|
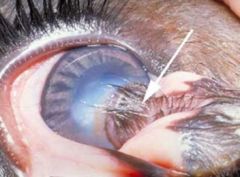
Diagnose
|
-dermoid
|
|
|
Diseases of globe position and movement
|
-Esotropia
-Exotropia |
|
|
Esotropia
-define |
-convergent strabismus
|
|
|
Exotropia
-define |
-divergent strabismus
|
|
|
Estropia
-causes |
-Bilateral Convergent Strabismus and Exophthalmia (BCSE)
-Polioencephalomalacia (PEM) -Listeriosis |
|
|
Bilateral Convergent Strabismus and Exophthalmia (BCSE)
-cause |
-inherited
|
|
|
Bilateral Convergent Strabismus and Exophthalmia (BCSE)
-effects |
-blinding
-abducent nerve (V) motor nucleus defect |
|
|
Polioencephalomalacia
-effects |
-dorsomedial direction
-blind and exhibiting episthotonus |
|
|
Listeriosis
-effects |
-Ipsilateral neurologic signs
-brain stem inflammation impinging on abducens nerve |
|
|
Exotropia
-causes |
-hydrocephalus when bilateral
-anomaly when unilateral |
|
|
Orbital disease
-most common clinical sign |
-exopthalmia
|
|
|
Orbital disease
-prognosis |
-depends on etiology (neoplasm, inflammatory)
|
|
|
Orbital disease
-most common neoplastic cause |
-Bovine Lymphosarcoma Virus (BLV)
-Squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
Orbital disease
-effects of neoplasia |
-unilateral or bilateral exophthalmos +/- strabismus
|
|
|
Orbital disease
-physical exam findings with a neoplastic cause |
Systemic abnormalities
-lymph nodes -melena -cardiac |
|
|
Orbital disease
-effects of cellulitis/abscess |
-exophthalmus
|
|
|
Orbital disease
-cause of cellulitis/abscess |
-trauma
-foreign body -chronic frontal sinusitis |
|
|
Chronic frontal sinusitis
-caused by |
-Dehorning (Actinomyces pyogenes)
-Respiratory dz (Pasteurella multocida) |
|
|
Orbital disease
-treatment for cellulitis/abscess |
-treat underlying cause
|
|
|
Entropion
-define |
-inward rolling of the eyelids
|
|
|
Entropion
-effect |
-skin/hairs irritate the eye
-squinting, tearing, ulceration -can lead to blindness |
|
|
Entropion
-lid normally affected |
-lower lid
|
|
|
Blepharitis
-bacterial cause |
-Dermatophilus congolensis (rain scald)
|
|
|
Blepharitis
-D. congoliensis initial areas affected |
-distal extremities
-muzzle -dorsum |
|
|
Dermatophilus congoliensis
-treatment |
-dry environment
-bathe with iodine/chlorhexidine shampoo (except head) -bathe head with dilute betadine solution -Penicillin +/- Streptomycin (IM) 3-5 days or -Long acting oxytetracycline injection |
|
|
Why not bathe the head in chlorhexidine shampoo?
|
-toxic to the corneal epithelium
|
|
|
Blepharitis
-fungal cause |
-Trichophyton sp. (all animals)
-Candida albicans (Jersey cattle) |
|
|
Blepharitis due to fungal
-treatment |
-infection self-limiting
-treat to affect spread to other animals and humans -topical/systemic antifungal -iodine shampoo -dry environment -good nutrition -Vaccination |
|
|
Blepharitis
-parasitic cause |
-Sarcoptes scabiei (reportable)
-Demodex sp. |
|
|
Differentiate between Demodex sp. and Sarcoptes scabiei
|
Sarcoptes scabiei
-pruritis -papules -erythema Demodex sp. -invade hair follicles and sebaceous glands of face, limbs, back -skin gets thick |
|
|
Blepharitis due to parasitic infection
-treatment |
-lime sulfur dip
-amitraz dip -ivermectin SQ |
|
|
Blepharitis
-Photosensitization causes |
Primary
-ingestion of photodynamic pigments Secondary -hepatitis -colicystitis |
|
|
/major sites for important ophthalmic disease in food-producing animals
|
-conjunctiva
-cornea |
|
|
Conjunctivitis/Keratitis
-causes |
-Infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis (IBK)
-Squamous Cell Carcinoma (Cancer eye) -Malignant Catarrhal fever -IBR, Chlamydophila sp., M. bovoculi -Thelazia spp. -Environment (pollen, dust, fumes) |
|
|
Infectious Bovine Keratoconjunctivitis (IBK)
-aka |
-Pink Eye
|
|
|
IBK
-etiology |
Moraxella bovis
-gram (-) -multiple serotypes |
|
|
Moraxella bovis
-transmission |
-fomites, contact, handlers
-vectors: face fly (Musca autumnalis) |
|
|
IBK
-contributing factors |
-sunlight
-dry environment -shipping stress -face flys |
|
|
IBK
-susceptibility |
-Bos Taurus > Bos indicus
-Herefords/Hereford crosses -Young animals |
|
|
IBK
-pathophysiology |
Moraxella bovis
-pathogenic strains are pilated (Q pili bind to cornea) -release proteolytic enzymes (beta-hemolysin) -proteases --> progression of ulcer |
|
|
Moraxella bovis
-effect of beta-hemolysin |
-damage corneal epithelium
-allow access to corneal stroma |
|
|
IBK
-epidemiology |
-acute dz (rapid spreading)
-occurs in summer (M. bovis, face flies, UV radiation) -dec in fall (less calves, less vectors) |
|
|
IBK
-clinical findings |
-unilateral/bilateral
-photophobia, blepharospasm, epiphora -conjunctivitis -central corneal lesion -corneal vascularization -secondary uveitis -corneal rupture w/ continued ulceration -anorexia due to blindness --> can't compete with herd for food |
|
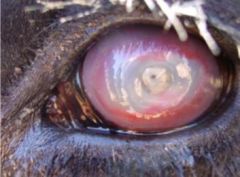
What is occurring?
|
-neovascularization to repair ulcerated region
|
|
|
IBK
-treatment |
-self-limiting but takes 4-6 wks (lose $$$)
Minimize production loss -prevent spread (isolation, vector control) -reduce exposure to enhancing factors -antibiotic -Pain control with atropine and NSAIDs Cover affected eyes -some king of patch |
|
|
IBK
-why should the affected eye be covered |
-provides shade
-protects from flys -NO ulcer healing |
|
|
IBK
-medicinal therapy |
Antibiotics
-Topical ointment (not practical) -Subconjunctival penicillin/ampicillin injection -Systemic oxytetracyclin Topical atropine for uveitis Systemic NSAIDs for discomfort/uveitis |
|
|
IBK
-strategies for prevention |
-fly control
-shade -temporary isolation of new animals -vaccination protocol (question efficacy) |
|
|
Most economically important neoplasm of large animals
-why |
-bovine ocular squamous cell carcinoma
-large part of slaughterhouse condemnations |
|
|
Bovine ocular squamous cell carcinoma
-aka |
-cancer eye
|
|
|
Bovine ocular squamous cell carcinoma
-associated with |
-bovine papilloma virus
|
|
|
Bovine OSCC
-risk factors |
-periocular depigmentation (Hereford, Ayrshire, Simmental)
-UV radiation (latitude, altitude, season) -Age -Genetics (bos Taurus; Herefords) |
|
|
Breeds with periocular depigmentation
|
-Hereford
-ayrshire -simmental |
|
|
Bovine OSCC
-clinical findings |
-ocular/periocular location (bulbar conjunctiva & cornea with most on the limbus)
-single or multiple lesions -unilateral/bilateral |
|
|
Bovine OSCC
-lesion progression |
-hyperplastic plaque
--papilloma noninvasive carcinoma (in situ) ---invasive carcinoma -extensive keratosis (keratoma) |
|
|
In situ
-definition |
-has not penetrated the basement epithelial membrane
|
|
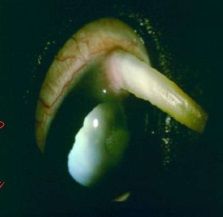
Diagnose
Disease associated with |
-keratosis (keratoma)
-Bovine OSCC |
|
|
Bovine OSCC
-pathophysiology |
-progression of premalignant stages to invasive
-rare metastasis -common local invasion with eyelid and nictitating membrane tumors |
|
|
Bovine OSCC
-diagnosis |
-appearance
-biopsy (histopath) |
|
|
Bovine OSCC
-treatment |
Practicality important
-surgical excision -Cryotherapy/laser therapy -enucleation -euthanasia *When there are multiple possible treatment, it means none are very good |
|
|
Bovine OSCC
-recurrence rate |
-30-40%
-culling is probably most effective option |
|
|
Bovine OSCC
-prevention |
-genetic selection for pigment around eyes
-select agains animals with high dz incidence |
|
|
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis
-etiology |
-Bovine herpes virus - 1
|
|
|
IBR
-Ocular signs linked with |
-shipping fever
-conjunctivitis: MC ocular manifestation -keratitis -discharge (mucopurulent) -+/- anterior uveitis |
|
|
IBR
-possible concurrent with what other ocular disease |
-IBK
|
|
|
IBR
-treatment |
-course 2-4 wks
-vaccines available |
|
|
Malignant Catarrhal Fever
-etiology |
-herpes virus
|
|
|
Malignant Catarrhal Fever
-clinical signs |
-"head-and-eye"
-pyrexia -profuse ocular/nasal discharge -hyperventilation -death |
|
|
Malignant Catarrhal Fever
-ocular signs |
-photophobia
-excessive lacrimation -episcleral injection and scleritis -keratitis (perilimbal edema, bullous keratopathy, corneal erosions) -anterior uveitis (if cornea clear) |
|
|
Malignant Catarrhal Fever
-diagnosis |
-PCR
|
|
|
MCF
-Prognosis |
-poor
|
|
|
MCF
-prevention |
-no vaccines or treatment
-keep cattle away from sheep |
|
|
Uveitis
-Cause |
Septicemic neonates
-umbilical infection -pneumonia -scours Systemic adults -mastitis -metritis -traumatic reticuloperitonitis -MCF -IBK -listeriosis -neoplasia -trauma |
|
|
Uveitis
-clinical signs |
-pain
-photophobia -flare -hypopyon -miosis -swollen iris -peripheral corneal edema -Glaucoma -cataract -phthisis bulbi |
|
|
Uveitis
-treatment |
-topical steroids
-topical atropine -flunixin -address underlying cause |
|
|
Ocular surgeries in cattle
|
-Enucleation (blind/painful eyes)
-Exenteration (neoplasia) |
|
|
Ocular surgery in cattle
-procedure |
-standing sedation with adequate restraint
-periocular nerve blocks -transpalpebral |
|
|
Cattle ocular surgery
-how long do sutures stay in |
-2-3 wks
|
|
|
Auriculopalpebral nerve block
-purpose |
-ocular exam/surgery
-eyelid akinesia |
|
|
Articulopalpebral nerve block
-procedure |
-inject lidocaine SQ where nerve crosses zygomatic arch (caudal to supraorbital process)
|
|
|
Local lidocaine block
-purpose |
-eyelid anesthesia during surgery
|
|
|
Four-point block
-purpose |
-enucleation
-retrobulbar block |
|
|
Four-point nerve block
-procedure |
-insert needle transconjunctivally adjacent to the globe
-inject lidocaine |
|
|
Peterson nerve block
-purpose |
-enucleation
-retrobulbar injection -block nerves II, III, IV, V, VI |

