![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What structure is formed where the endoderm (hindgut) meets the ectoderm?
|
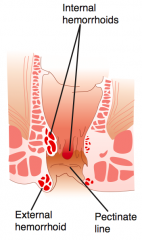
Pectinate (Dentate) Line
|
|
|
What is the location of the Pectinate line?
|
Formed between where endoderm (hindgut) ends and ectoderm begins
|
|
|
What pathology occurs above the pectinate line?
|
- Internal hemorrhoids
- Adenocarcinoma |
|
|
What is the arterial and venous supply to the area above the pectinate line?
|
- Arterial supply: superior rectal artery (branch of IMA)
- Venous drainage: superior rectal vein → inferior mesenteric vein → portal system |
|
|
What pathology occurs below the pectinate line?
|
- External hemorrhoids
- Anal fissures - Squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
What is the arterial and venous supply to the area below the pectinate line?
|
- Arterial supply: inferior rectal artery (branch of internal pudendal artery)
- Venous drainage: inferior rectal vein → internal pudendal vein → internal iliac vein → IVC |
|
|
How does the area above and below the pectinate line compare in terms of the pathology that occurs there? |
Above pectinate line:
- Internal hemorrhoids - Adenocarcinoma Below pectinate line: - External hemorrhoids - Anal fissures - Squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
How does the area above and below the pectinate line compare in terms of the arterial supply?
|
Above pectinate line:
- Superior rectal artery (branch of IMA) Below pectinate line: - Inferior rectal artery (branch of internal pudendal artery) |
|
|
How does the area above and below the pectinate line compare in terms of the venous drainage?
|
Above pectinate line:
- Superior rectal vein → inferior mesenteric vein → portal system Below pectinate line: - Inferior rectal vein → internal pudendal vein → internal iliac vein → IVC |
|
|
How do internal and external hemorrhoids compare?
|
Internal hemorrhoids:
- Above pectinate line - Visceral innervation → not painful External hemorrhoids: - Below pectinate line - Somatic innervation (inferior rectal branch of pudendal nerve) → painful |
|
|
What causes an anal fissure? Symptoms?
|
- Tear in the anal mucosa below the pectinate line
- Pain while Pooping: blood on "toilet" paper - Located Posteriorly since this area is Poorly Perfused |
|
|
What surface of the hepatocytes faces the bile canaliculi?
|
Apical surface of hepatocytes
|
|
|
What surface of the hepatocyte faces the sinusoids? |
Basolateral surface of hepatocytes
|
|
|
What are the zones of the liver?
|
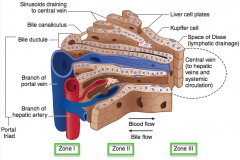
- Zone I: periportal zone
- Zone II: intermediate zone - Zone III: pericentral vein (centrilobular) zone |
|
|
What is the name of Zone I? Characteristics?
|
Periportal Zone:
- Affected first by viral hepatitis - Ingested toxins (eg, cocaine) |
|
|
What is the name of Zone II?
|
Intermediate Zone
|
|
|
What is the name of Zone III? Characteristics?
|
Pericentral Vein (Centrilobular) Zone
- Affected first by ischemia - Contains cytochrome P-450 system - Most sensitive to metabolic toxins - Site of alcoholic hepatitis |
|
|
Which type of hepatitis affects the different zones of the liver?
|
- Viral: zone I
- Alcoholic: zone III |
|
|
Which type of toxins affects the different zones of the liver?
|
- Ingested toxins (eg, cocaine): zone I
- Metabolic toxins: zone III |
|
|
Where are the cytochrome P-450 enzymes located in the liver?
|
Zone III (pericentral vein zone)
|
|
|
Which part of the liver is affected first by ischemia?
|
Zone III
|
|
|
What is the branching pattern of the biliary structures?
|
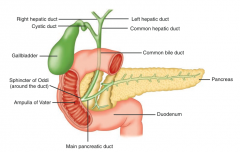
- L & R Hepatic Ducts drain bile from liver into Common Hepatic Duct
- Common Hepatic Duct takes bile to be stored in gallbladder via Cystic Duct or to drain into Duodenum via Common Bile Duct |
|
|
Which duct drains the gallbladder?
|
Cystic duct → Common Bile duct → Sphincter of Oddi / Ampulla of Vater → Duodenum
|
|
|
What happens if a gallstone reaches the common channel at the Ampulla of Vater?
|
Can block both the bile and the pancreatic ducts
|
|
|
What are the potential implications of tumors that arise in the head of the pancreas?
|
Can cause obstruction of the common bile duct (preventing bile from entering the duodenum)
|

