![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
100 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is associated with an epispadias? ...
|
Exstrophy of the bladder
|
|
|
What is Meckel's diverticulum? ...
|
Persistence of the vitelline duct or yolk sac
|
|
|
What is oligohydramnios associated with? ...
|
Bilateral renal agenesis or posterior urethral valves (in males)
|
|
|
What is oligohydramnios? ...
|
< 0.5 L of amniotic fluid
|
|
|
What is polyhydramnios associated with? ...
|
Esophageal/duodenal atresia, anencephaly
|
|
|
What is polyhydramnios? ...
|
> 1.5-2 L of amniotic fluid
|
|
|
What is Potter's syndrome? ...
|
Bilateral renal agenesis, that results in ologohydramnios causing limb and facial deformities and pulmonary hypoplasia (Babies with Potter's can’t pee in utero)
|
|
|
What is the acrosome of sperm derived from? ...
|
Golgi apparatus
|
|
|
What is the female homologue to the corpus spongiosum in the male? ...
|
Vestibular bulbs
|
|
|
What is the female homologue to the prostate gland in the male? ...
|
Urethral and paraurethral glands (of Skene)
|
|
|
What is the female homologue to the scrotum in the male? ...
|
Labia majora
|
|
|
What is the female homologue to the ventral shaft of the penis in the male? ...
|
Labia minora
|
|
|
What is the flagellum (tail) derived from? ...
|
One of the centrioles
|
|
|
What is the food supply of sperm? ...
|
Fructose
|
|
|
What is the male homologue to the glans clitoris in the female? ...
|
Glans Penis
|
|
|
What is the male homologue to the greater vestibular glands (of Bartholin) in the female? ...
|
Bulbourethral glands (of Cowper)
|
|
|
What is the most common congenital anomaly of the GI tract?
|
Meckel's Diverticulum
|
|
|
What is the most common ectopic thyroid tissue site? ...
|
The Tounge
|
|
|
What is the normal remnant of the thyroglossal duct?
|
Foramen cecum
|
|
|
What is the postnatal derivative of the notochord? ...
|
The nucleus pulposus of the intervertebral disc
|
|
|
What is the site of T-cell maturation? ...
|
Thymus
|
|
|
What part of the gut is the pancreas derived? ...
|
Foregut
|
|
|
What suppresses the development of the paramesonephric ducts in males? ...
|
Mullerian inhibiting substance (secreted by the testes)
|
|
|
What teratogenic agent causes limb defects ('flipper' limbs)? ...
|
Thalidomide
|
|
|
What three structures does the 3rd pharyngeal pouch develop into? ...
|
- Thymus - Left inferior parathyroid - Right inferior parathyroid
|
|
|
What three things does the 1st pharyngeal pouch develop into? ...
|
- Middle ear cavity - Eustachian tube - Mastoid air cells
|
|
|
What three things does the paramesonephric (mullerian) duct develop into? ...
|
Fallopian tube - Uterus - Part of the vagina
|
|
|
What three things does the ventral pancreatic bud become?
|
- Pancreatic head - uncinate process - main pancreatic duct
|
|
|
What two things occur during week 4 of fetal development? ...
|
Heart begins to beat, upper and lower limb buds begin to form
|
|
|
What type of bone formation is spontaneous without preexisting cartilage? ...
|
Intramembranous
|
|
|
What type of twins would have 1 placenta, 2 amniotic sacs, and 1 chorion? ...
|
Monozygotic twins
|
|
|
What type of twins would have 2 amniotic sacs and 2 placentas? ...
|
Monozygotic or dizygotic twins
|
|
|
What will DiGeorge's syndrome lead to? ...
|
T cell deficiency & hypocalcemia
|
|
|
When do primary oocytes begin meiosis I? ...
|
During fetal life
|
|
|
When do primary oocytes complete meiosis I? ...
|
Just prior to ovulation
|
|
|
When does fetal erythropoiesis occur in the bone marrow? ...
|
Week 28 and onward
|
|
|
When does fetal erythropoiesis occur in the liver? ...
|
Weeks 6-30
|
|
|
When does fetal erythropoiesis occur in the spleen? ...
|
Weeks 9-28
|
|
|
When does organogenesis occur in the fetus? ...
|
Weeks 3-8
|
|
|
Where does positive and negative selection occur in the thymus? ...
|
At the corticomedullary junction
|
|
|
Where does spermatogenesis take place? ...
|
Seminferous tubules
|
|
|
Where is the first place fetal erythropoiesis occurs and when does this take place? ...
|
Yolk sac (3-8 wk)
|
|
|
Which aortic arch does the stapedial artery and the hyoid artery come from? ...
|
2nd aortic arch
|
|
|
Which branchial arch are the greater horn of hyoid and the stylopharyngeus muscle derived from? ...
|
3rd branchial arch
|
|
|
Which branchial arch does Meckel's cartilage develop from? ...
|
1st arch
|
|
|
Which branchial arch forms the anterior 2/3 of the tongue? ...
|
1st arch
|
|
|
Which branchial arch forms the incus and malleus of the ear? ...
|
1st arch
|
|
|
Which ear bone(s) does the 2nd branchial arch form? ...
|
Stapes
|
|
|
Which embryonic tissue are branchial clefts derived from? ...
|
Ectoderm
|
|
|
Which embryonic tissue are branchial pouches derived from? ...
|
Endoderm
|
|
|
Which is more common a hypospadias or epispadias? ...
|
Hypospadias
|
|
|
Which muscles (3) are derivatives of the 4th branchial arch? ...
|
- Most pharyngeal constrictors - Cricothyroid - Levator veli palatini
|
|
|
Which muscles (4) are derivatives of the 2nd branchial arch? ...
|
- Muscles of facial expression - Stapedius - Stylohyoid - Posterior belly of digastric
|
|
|
Which muscles (8) are derivatives of the 1st branchial arch? ...
|
- Temporalis - Masseter - Lateral pterygoid - Medial pterygoid - Mylohyoid - Anterior belly of digastric - Tensor tympani - Tensor veli palatini
|
|
|
Which muscles are derivatives of the 6th branchial arch? ...
|
All intrinsic muscles of the larynx, except the cricothyroid
|
|
|
Which pharyngeal arch does Reichert's cartilage develop from? ...
|
2nd arch
|
|
|
Which teratogenic agent causes vaginal clear cell adenocarcinoma? ...
|
DES
|
|
|
Which two branchial arches form the posterior 1/3 of the tongue? ...
|
3rd and 4th arches
|
|
|
Which two embryonic tissues are branchial arches derived from? ...
|
Mesoderm and neural crests
|
|
|
Which week of fetal development have the genitalia taken on male/female characteristics? ...
|
Week 10
|
|
|
A common football injury caused by clipping from the lateral side will damage what structures (3 answers)? ...
|
--Medial collateral ligament --Medial meniscus --Anterior cruciate ligament
|
|
|
A lumbar puncture is performed at what landmark? ...
|
Iliac crest
|
|
|
A positive anterior drawer sign indicates damage to what structure? ...
|
Anterior cruciate ligament(ACL)
|
|
|
A pudendal nerve block is performed at what landmark? ...
|
Ischial spine
|
|
|
Abnormal passive abduction of the knee indicates damage to what structure? ...
|
Medial collateral ligament(MCL)
|
|
|
'Anterior' in ACL refers to what attachment? ...
|
Tibial
|
|
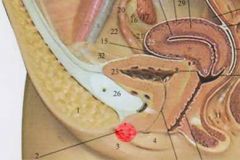
At what level is a lumbar puncture performed? ...
|
Between L3-L4 or L4-L5
|
|
|
Common peroneal nerve damage manifests what deficit? ...
|
Loss of dorsiflexion(Foot Drop)
|
|
|
Common peroneal, Tibial, Femoral, and Obturator nerves arise from what spinal cord segments (4 answers)? ...
|
--'L4-S2 (common peroneal) --L4-S3 (tibial) --L2-L4 (femoral) and (obturator)
|
|
|
Coronary artery occlusion usually occurs where? ...
|
Left anterior descending artery (LAD)
|
|
|
Do the coronary arteries fill during systole or diastole? ...
|
Diastole
|
|
|
Erection and sensation of the penis is in what dermatomes? ...
|
S2,3,4 penis off the floor
|
|
|
Femoral nerve damage manifests what deficit? ...
|
Loss of knee jerk
|
|
|
How does the course of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve differ from that of the right? ...
|
The left wraps around the arch of the aorta and the ligamentum arteriosum while the right wraps around the subclavian artery.
|
|
|
How is the appendix located? ...
|
2/3 of the way from the umbilicus to the anterior superior iliac spine
|
|
|
How many lobes are in the right and left lungs and what are their names? ...
|
--Right has three (superior,middle,inferior) --Left has two (superior and inferior) and the lingula
|
|
|
Name five portal-systemic anastomoses. ...
|
1.Left gastric-azygous vv. 2.Superior-Middle/Inferior rectal vv. 3.Paraumbilical-inferior epigastric 4.Retroperitoneal-renal vv. 5.Retroperitoneal-paravertebral vv.
|
|
|
Name the 4 ligaments of the uterus. ...
|
--Suspensory ligament of ovaries --Transverse cervical (cardinal) ligament --Round ligament of uterus --Broad ligament
|
|
|
Name the hypothenar muscles. ...
|
--Opponens digiti minimi --Abductor digiti minimi --Flexor digiti minimi
|
|
|
Name the retroperitoneal structures (9). ...
|
1.Duodenum(2nd-4th parts) 2.Descending colon 3.Ascending colon 4.Kidney & ureters 5.Pancreas 6.Aorta 7.Inferior vena cava 8.Adrenal glands 9.Rectum
|
|
|
Name the rotator cuff muscles. ...
|
--Supraspinatus --Infraspinatus --teres minor --Subscapularis
|
|
|
Name the thenar muscles ...
|
--Opponens pollicis --Abductor pollicis brevis --Flexor pollicis brevis
|
|
|
Obturator nerve damage manifests what deficit? ...
|
Loss of hip adduction
|
|
|
Pain from the diaphragm is usually referred where? ...
|
Shoulder
|
|
|
Subarachnoid space extends to what spinal level? ...
|
S2
|
|
|
The area of the body that contains the appendix is known as what? ...
|
McBurney's point
|
|
|
The femoral triangle contains what structures from lateral to medial? ...
|
--Femoral nerve --Femoral artery --Femoral vein --Femoral Canal (lymphatics)
|
|
|
The inguinal ligament exists in what dermatome?
|
L1
|
|
|
The kneecaps exist in what dermatome? ...
|
L4
|
|
|
The male sexual response of ejaculation is mediated by what part of the nervous system? ...
|
Visceral and somatic nerves
|
|
|
The male sexual response of emission is mediated by what part of the nervous system? ...
|
Sympathetic nervous system
|
|
|
The male sexual response of erection is mediated by what part of the nervous system? ...
|
Parasympathetic nervous system
|
|
|
The nipple exists in what dermatome? ...
|
T4
|
|
|
The recurrent laryngeal nerve arises from what cranial nerve and supplies what muscles?
|
1.CN X 2.All intrinsic muscles of the larynx except the cricothyroid muscle
|
|
|
The SA and AV nodes are usually supplied by what artery? ...
|
Right Coronary Artery (RCA)
|
|
|
The spinal cord ends at what level in adults? ...
|
L1-L2
|
|
|
The umbilicus exists in what dermatome? ...
|
T10
|
|
|
The xiphoid process exists in what dermatome? ...
|
T7
|
|
|
Tibial nerve damage manifests what deficit? ...
|
Loss of plantar flexion
|
|
|
What are hernias? ...
|
Protrusions of peritoneum through an opening, usually sites of weakness.
|

