![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
4 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are ocular presentations of gonococcal conjunctivitis (6)?
|
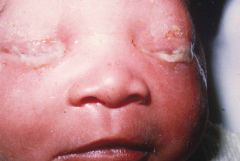
1. Severe purulent discharge
2. Hyperacute onset (within 2 days after exposure) 3. Preauricular lymph node swelling 4. Conjunctival papillae 5. Marked chemosis 6. Eyelid swelling / redness (picture from Online Atlas of Ophthalmology) |
|
|
What connective tissue diseases may cause dry eye (4)?
|
1. Sjogren's syndrome
2. Rheumatoid arthritis 3. Systemic lupus erythematosus 4. Wegener granulomatosis |
|
|
What is the difference between herpes simplex virus (HSV) corneal lesions and herpes zoster virus (HZV) corneal lesions?
|
HSV: dendritic lesions stain well with fluorescein.
HZV: pseudodendrites are actually raised mucous plaques that do not have true terminal bulbs and do not stain well with fluorescein. |
|
|
How do you treat HSV eyelid lesions?
|
1. Antibiotic ointment (erythromycin or bacitracin) bid
2. Warm or cool soaks to skin tid 3. Topical acyclovir is an option but has not been proven effective. 4. Continue for 7-14 days or until resolution. (WEM p. 61) |

