![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
231 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is ORM?
|
Operational Risk Management. It is a decision making tool used by personnel at all levels to increase operational effectiveness by identifying, assessing and managing risk.
|
|
|
What are the three ORM process levels?
|
1. Time Critical
2. Deliberate 3. In-Depth |
|
|
What are the 4 principles to ORM?
|
1. Accept risk when the benefit outweighs the cost.
2. Accept no unnecessary risk. 3. Anticipate and manage risk by planning. 4. Make risk decisions at the right level. |
|
|
What are the 5 steps to ORM?
|
1. Identify hazards
2. Assess hazards 3. Make risk decisions 4. Implement controls 5. Supervise. |
|
|
What are the 3 types of ORM controls?
|
1. Engineering
2. Administrative 3. PPE |
|
|
What does PPE stand for?
|
Personal Protective Equipment
|
|
|
OPNAVINST 3500.39B
|
Operational Risk Management instruction
|
|
|
OPNAVINST 5100.19E
|
NAVOSH for Forces Afloat
|
|
|
OPNAVINST 5100.23G
|
NAVOSH for Forces Ashore
|
|
|
Who is the head of the Safety Council and Committee?
|
Commanding Officer.
|
|
|
What are the three basic functions of the Safety Council and Committee?
|
1. Create and maintain an active interest in safety.
2. Serve as a means of communications regarding safety. 3. Provide program assistance to the Commanding Officer, including proposing policy and program objectives. |
|
|
What is the purpose of mishap investigations?
|
They are to determine how and why the event occurred and to prevent future occurrences from happening.
|
|
|
When does a mishap investigation occur?
|
When there is damage to Navy facilities and equipment or occupational injuries, illnesses, or deaths to Navy personnel that degrade operational readiness and increase operational costs.
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of mishap investigations?
|
1. Safety
2. JAGMAN 3. Criminal and Security |
|
|
What are the three basic functions of the Safety Council and Committee?
|
1. Create and maintain an active interest in safety.
2. Serve as a means of communications regarding safety. 3. Provide program assistance to the Commanding Officer, including proposing policy and program objectives. |
|
|
What are the three basic functions of the Safety Council and Committee?
|
1. Create and maintain an active interest in safety.
2. Serve as a means of communications regarding safety. 3. Provide program assistance to the Commanding Officer, including proposing policy and program objectives. |
|
|
What form is used for a mishap report?
|
SF 91
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a Safety Stand Down?
|
To promote safety by covering various topics like mishaps, compensation, MSDSs, work procedures, smoking, stress, plans and goals, radiation, etc.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of mishap investigations?
|
They are to determine how and why the event occurred and to prevent future occurrences from happening.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of mishap investigations?
|
They are to determine how and why the event occurred and to prevent future occurrences from happening.
|
|
|
What is ergonomics?
|
Is the field of study that involves the application of knowledge about physiological, psychological, and biomechanical capacities and limitations of the human body.
|
|
|
When does a mishap investigation occur?
|
When there is damage to Navy facilities and equipment or occupational injuries, illnesses, or deaths to Navy personnel that degrade operational readiness and increase operational costs.
|
|
|
When does a mishap investigation occur?
|
When there is damage to Navy facilities and equipment or occupational injuries, illnesses, or deaths to Navy personnel that degrade operational readiness and increase operational costs.
|
|
|
Commander in Chief (President)
|
President Barack Obama
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of mishap investigations?
|
1. Safety
2. JAGMAN 3. Criminal and Security |
|
|
Vice President
|
Vice President Joseph Biden
|
|
|
What form is used for a mishap report?
|
SF 91
|
|
|
What are the 3 types of mishap investigations?
|
1. Safety
2. JAGMAN 3. Criminal and Security |
|
|
SECDEF
|
Honorable Robert Gates
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a Safety Stand Down?
|
To promote safety by covering various topics like mishaps, compensation, MSDSs, work procedures, smoking, stress, plans and goals, radiation, etc.
|
|
|
What form is used for a mishap report?
|
SF 91
|
|
|
What is ergonomics?
|
Is the field of study that involves the application of knowledge about physiological, psychological, and biomechanical capacities and limitations of the human body.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a Safety Stand Down?
|
To promote safety by covering various topics like mishaps, compensation, MSDSs, work procedures, smoking, stress, plans and goals, radiation, etc.
|
|
|
Commander in Chief (President)
|
President Barack Obama
|
|
|
What is ergonomics?
|
Is the field of study that involves the application of knowledge about physiological, psychological, and biomechanical capacities and limitations of the human body.
|
|
|
Vice President
|
Vice President Joseph Biden
|
|
|
Commander in Chief (President)
|
President Barack Obama
|
|
|
SECDEF
|
Honorable Robert Gates
|
|
|
Vice President
|
Vice President Joseph Biden
|
|
|
SECDEF
|
Honorable Robert Gates
|
|
|
Commander, Fleet Forces Command
|
ADM John Harvey
|
|
|
Fleet Master Chief, CFFC
|
FLTCM Mike Stevens
|
|
|
Commander, Navy Expeditionary Combat Command
|
RADM Michael Tillotson
|
|
|
Force Master Chief, NECC
|
FORCM Farris Foresman
|
|
|
Commander, Maritime Expeditionary Security Group ONE
|
CAPT Richard Daniel
|
|
|
Command Master Chief, MESG1
|
CMDCM Jacob Grgurich
|
|
|
Commanding Officer, Maritime Expeditionary Security Squadron THREE
|
CDR Thomas F. Murphy, III
|
|
|
Executive Officer, Maritime Expeditionary Security Squadron THREE
|
CDR Jeremy P. Jurkoic
|
|
|
Command Master Chief, MSRON THREE
|
CMDCM James R. Lindemann
|
|
|
What is an OPLAN?
|
OPerational PLAN. It is a detailed statement of a course of action to be followed to accomplish a future mission.
|
|
|
What is an OPORD?
|
OPerational ORDer. It puts an OPLAN into effect. It is a formal statement issued by the senior commander to subordinate commanders that outlines the coordinated execution of a future operation in the field.
|
|
|
What does TPFDD stand for?
|
Time Phased Force Deployment Data.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of a TPFDD?
|
It contains the forces and supplies in an OPLAN that are required to execute the combatant commander's strategic concept and a movement schedule of these resources to the theatre of operations.
|
|
|
What are the three stages of a TPFDD?
|
1. Concept
2. Plan 3. Review |
|
|
What is a Warning Order?
|
A planning directive that describes the situation, allocates forces and resources, establishes command relationships, provides other initial planning guidance, and initiates subordinate unit mission planning.
|
|
|
What does EDVR stand for?
|
Enlisted Distribution Verification Report
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the EDVR?
|
It is a monthly statement of an activity's enlisted personnel for manning accountability.
|
|
|
How many sections are there in the EDVR?
|
12.
|
|
|
List ten things you can find in the EDVR?
|
1. Name
2. SSN 3. NECs 4. ADSD 5. EAOS 6. PRD 7. Time in Rate 8. Date of Rate 9. Security Clearance 10. Special Duty Assignment Pay |
|
|
What is a Naval message?
|
A formal means of communication.
|
|
|
What is in a Naval message?
|
- Date/Timegroup
- Precedence - Originator - Addresses - Text - Office Codes - Point of Contact |
|
|
What are the 4 precedences of a Naval Message?
|
R - Routine (within 6 hours)
P - Priority (within 3 hours) I - Immediate (within 30 minutes) F - Flash (ASAP with an objective of 10 minutes) |
|
|
What does MINIMIZE mean in regards to Naval messages?
|
Reduce the normal amount of message traffic so that vital messages will not be delayed.
|
|
|
What are the 3 categories of message users and their responsibilities?
|
Originator: The command or activity from which the message is sent. The originator is presumed to be the Commanding Officer.
Drafter: The person who actually composes the message. Releaser: The properly designated individual authorized to release messages for transmission in the name of the command or activity. |
|
|
E-mail is what kind of communication?
|
Informal means of communication.
|
|
|
What is NAVPERS 1070/600?
|
Enlisted Field Service Record Jacket.
|
|
|
What is NAVPERS 1070/602?
|
Record of Emergency Data (Page 2)
|
|
|
What is NAVPERS 1070/604?
|
Record of Qualifications and Awards (Page 4)
|
|
|
What is NAVPERS 1070/613?
|
Administrative Remarks (Page 13)
|
|
|
What does LOGREQ stand for and its purpose?
|
LOGistics REQuirement report. The CO lets the port know what requirements are needed for the ship 72 hours prior to pulling in port. (stores, brows, transport, water, waste, etc.)
|
|
|
What does SORTS stand for and what is its purpose?
|
Status Of Resources/Training-Systems. It provides command readiness data.
|
|
|
What does SITREP stand for and what is its purpose?
|
SITuational REPort. It is a multi-purpose narrative report that keeps addressees informed and enables commands and Services concerned to expect and prepare for potential effects.
|
|
|
What does CASREP stand for and what is its purpose?
|
CASualty REPort. It is a message submitted to document a significant casualty affecting equipment essential for the performance of designated mission areas.
|
|
|
What does LOAC stand for and what is its purpose?
|
Laws Of Armed Conflict. It tells you what you can and can not do in combat situations.
|
|
|
Who are Combatants?
|
- Persons in Uniform
- Carrying a weapon - Participating in military operations or activities |
|
|
Who are non-Combatants?
|
- Civilians
- Medical - Chaplains |
|
|
How do you treat non-Combatants?
|
- Humanely
|
|
|
What led to the formation of the US Navy?
|
GEN George Washington initiated America's first sea-based offensive to cut off the English resupply lines during the Revolutionary War.
|
|
|
What is the US Navy's birthday?
|
13 October 1775
|
|
|
What date was the rank of Chief Petty Officer established?
|
1 April 1893
|
|
|
What date was the rank of SCPO/MCPO established?
|
1 June 1958
|
|
|
What date was the first MCPON instated?
|
13 January 1967
|
|
|
Who was the first MCPON and what was his former rating?
|
MCPON Delbert Black, Gunner's Mate.
|
|
|
Who is the Father of the US Navy?
|
John Paul Jones.
|
|
|
What are the 3 Maritime Services?
|
1. US Navy
2. US Marine Corps 3. US Coast Guard |
|
|
In what year did Congress authorize 6 frigates to be built, establishing the first US Navy warships?
|
1794.
|
|
|
What are the 4 qualities and characteristics of the Navy/Marine Corps team?
|
1. Readiness
2. Flexibility 3. Self-Sustainability 4. Mobility |
|
|
What are the three levels of war?
|
1. Tactical
2. Operational 3. Strategic |
|
|
What led to the creation of the Seabees?
|
Before 1942, under international law civilians were not permitted to resist enemy military attack. Resistance meant summary execution as guerrillas. The need for a militarized Naval Construction Force to build advance bases in the war zone was self-evident. On 5 January 1942, RADM Ben Moreell gained authority from the Bureau of Navigation to recruit men from the construction trades for assignment to a Naval Construction Regiment composed of three Naval Construction Battalions.
|
|
|
What is the birthday of the Seabees?
|
5 March 1942
|
|
|
What is the significance of Pearl Harbor?
|
It caused the US to enter World War II.
|
|
|
What US battleships were sunk during the battle of Pearl Harbor?
|
- USS ARIZONA (BB 39)
- USS CALIFORNIA (BB 44) - USS OKLAHOMA (BB 37) - USS WEST VA (BB 48) - USS UTAH was redesignated (AG 16 in 1931, formerly BB 31) |
|
|
Who was the Japanese commander at Pearl Harbor?
|
VADM Chuichi Nagamo
|
|
|
What Japanese carriers were involved at Pearl Harbor?
|
- Akagi
- Soryu - Shokaku - Kaga - Hiryu - Zuikaku |
|
|
What date was the Battle of the Coral Sea?
|
8 May 1942
|
|
|
What was the significance of the Battle of the Coral Sea?
|
Both surface fleets never saw each other visually, the battle was fought with aircraft launched from carriers. It also prevented the Japanese invasion of Northern Australia.
|
|
|
What US Navy carriers were present at Coral Sea?
|
USS Yorktown, USS Lexington
|
|
|
What was the significance of the Battle of Midway?
|
It was the turning point in the War of the Pacific. The Japanese could not reach Hawaii or mainland US without a forward base.
|
|
|
What US Navy carriers were involved at the Battle of Midway?
|
- USS Yorktown
- USS Hornet - USS Enterprise |
|
|
When did the invasion of Normandy take place?
|
6 June 1944
|
|
|
What is the significance of the Invasion of Normandy?
|
It was the largest expeditionary operation in recorded history.
|
|
|
What was the codename for the Invasion of Normandy?
|
OPERATION OVERLORD.
|
|
|
What beaches were involved in the Invasion of Normandy?
|
- GOLD
- SWORD - OMAHA - JUNO - UTAH - Pointe du Hoc |
|
|
What does EOD stand for?
|
Explosive Ordnance Disposal.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of EOD?
|
They handle, defuse and dispose of munitions and other explosives.
|
|
|
What does UDT stand for?
|
Underwater Demolition Team.
|
|
|
What was the purpose of creating the UDT?
|
In 1942, the Army and Navy jointly established the Amphibious Scout and Raider School at Ft. Pierce, Florida. LCDR Phil Bucklew, the "Father of Naval Special Warfare", helped organize and train what became the Navy's 'first group' to specialize in amphibious raids and tactics. This "Scouts and Raiders" unit was first employed in Operation Torch, the invasion of North Africa in November 1942.
|
|
|
What does NCW stand for?
|
Naval Coastal Warfare.
|
|
|
What are the two mission of NCW?
|
1. Expeditionary Operations.
2. Support US Coast Guard in Homeland Security and Homeland Defense. |
|
|
What does SLOC stand for?
|
Sea Lines Of Communication.
|
|
|
What does MRF stand for?
|
Mobile Riverine Force
|
|
|
What are the two type of Riverine Operations?
|
- Assualt
- Surveillance, Interdiction, Security |
|
|
Name all of the "N" codes.
|
N1 - Admin
N2 - Intelligence N3 - Operations N4 - Supply N43- CESE N5- Future Operations N6- Communications N7- Training |
|
|
What does NECC stand for?
|
Navy Expeditionary Combat Command
|
|
|
What is the purpose of NECC?
|
To provide oversight and Command and Control of Anti-terrorism/Force Protection and Expeditionary-type forces within the Navy
|
|
|
Name all 11 NECC Command types.
|
1. MESF
2. MDSU 3. EOD 4. RIVRON 5. Seabees 6. Combat Camera 7. Expeditionary Logisitics Support 8. Expeditionary Training 9. Expeditionary Combat Readiness 10. Expeditionary Intelligence 11. Maritime Civil Affairs |
|
|
What is the definition of "embarkation"?
|
The process of loading military personnel, vehicles, CONEX boxes, etc. into ships or aircraft.
|
|
|
What does UIC stand for?
|
Unit Identification Code.
|
|
|
What does a unit use the UIC for during embarkation/debarkation?
|
For labeling of vehicles, containers and equipment.
|
|
|
What does AMC stand for?
|
Air Mobility Command
|
|
|
What is the purpose of Air Mobility Command?
|
To provide operational support aircraft for the deployment of troops and cargo in support of in-theatre operations.
|
|
|
What does MPF stand for?
|
Maritime Prepositioning Force
|
|
|
What is the purpose of MPF?
|
Protect key Naval chokepoints and Sea Lines of Communication.
|
|
|
What does MAGTF stand for?
|
Marine Air-Ground Task Force
|
|
|
What does MEU stand for?
|
Marine Expeditionary Unit
|
|
|
What does MSC stand for?
|
Military Sealift Command
|
|
|
What is the purpose of MSC?
|
To provide strategic, common-user sealift transportation services to US forces to deploy, employ, sustain and redeploy those forces on a global basis.
|
|
|
What does APF stand for?
|
Afloat Prepositioning Force.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of APF?
|
It is an alternative to land-based storage. The strategy of afloat prepositioning is to position ships preloaded with equipment and supplies, (including ammo and gas) at various strategic locations.
|
|
|
How many ships are in the MPF and what 2 categories do they fall into?
|
Over 30.
- Maritime Prepositioning Ships - Afloat Prepositioning Ships |
|
|
What does MPSRON stand for?
|
Maritime Prepositioning Ship Squadron
|
|
|
Where are all the MPSRONs located?
|
MPSRON 1 - Med/Atlantic: No homeport
MPSRON 2 - Indian Ocean: Diego Garcia MPSRON 3 - Pacific Ocean: Guam/Saipan |
|
|
What does HAZMAT stand for?
|
HAZardous MATerials.
|
|
|
What kinds of HAZMAT can be shipped?
|
- Flammables (liquid/solid)
- Explosives - Lithium batteries - Compressed gases - Corrosive materials - Oxidizers - Cleaning agents |
|
|
When shipping HAZMAT, what must be done?
|
Proper HAZMAT ID labels placed on three sides of the container. The ID label is used to assign the stowage location onboard the transportation asset.
|
|
|
What Code of Federal Regulations Title provides specific requirements and shows label examples for shipping HAZMAT?
|
Title 49
|
|
|
What are PROWORDS?
|
Words that have authorized meanings
|
|
|
What does WAIT OUT mean?
|
I must pause for longer than a few seconds.
|
|
|
What are the three types of non-oral communications?
|
- Whistle signals
- Arm and Hand Signals - Special Signals (practiced beforehand) |
|
|
What factors affect the capabilities of radio communications?
|
BLEW TAG P
- Buildings - Location of radio - Enemy jamming - Weather - Terrain - Antenna power - Generators - Power lines |
|
|
What is Command and Control (C2)?
|
The process and the system by which the commander decides what must be done and sees that his decisions are carried out.
|
|
|
What is the process of C2?
|
- Planning
- Coordinating - Directing - Controlling of forces and operations |
|
|
What does OODA stand for?
|
- Observe
- Orient - Decide - Act |
|
|
What are the three levels of Naval Intelligence?
|
- Strategic Intel: oriented toward national objectives and supports the formulation of policies and determination of priorities
- Operational Intel: concentrates on intelligence collection, identification, location, and analysis to support the operational level of warfare, which includes identifying an adversary's operational critical vulnerabilities. - Tactical Intel: Focuses on potential adversary's capabilities, immediate intentions, and the environment. |
|
|
What are the principles of Naval Intelligence?
|
KEPUTU
- Know the Adversary - Ensure Unity of Intelligence Effort - Plan for Combat - Use an All-resource Approach - Timeliness - Usability |
|
|
What are the key attributes to Naval Intelligence?
|
TAU TAR
- Timeliness - Availability - Usability - Thoroughness - Accuracy - Relevance |
|
|
Name the Intelligence Cycle.
|
PCPPD
- Planning and Direction - Collection - Processing - Production - Dissemination |
|
|
What are the ranges for radio voice transmission?
|
- LO: 200m-400m
- M: 400m-5km -HI: 5km-10km -PA: 10km-40km |
|
|
What does CMS stand for?
|
Communication security Material System
|
|
|
What does EKMS stand for?
|
Electronic Key Management System
|
|
|
What is the responsibility of the CMS/EKMS custodian?
|
- Managing the CMS account
- Physical security and Handling of CMS - Stowage, drawing, correcting and destruction of CMS. |
|
|
What is TPI and what is its purpose?
|
TPI: Two Person Integrity
It prevents single access to CMS materials. |
|
|
What does DTD stand for?
|
Data Transfer Device
|
|
|
What are the two DTDs that are used to load crypto?
|
KYK-13 (Kick 13): holds 6 lines.
AN/CZY-10 (Crazy 10): holds 1000 lines. |
|
|
What is meant by Access?
|
The ability and opportunity to obtain knowledge to classified information.
|
|
|
What is meant by Classification?
|
A specific degree of protection against unauthorized disclosure.
|
|
|
What is meant by Compromise?
|
A security violation of classified information or material to an unauthorized person.
|
|
|
What is meant by Need to Know?
|
A determination that a recipient needs to gain access to classified information.
|
|
|
What is meant by Clearance?
|
Eligibility for access to classified information.
|
|
|
Four types of clearance and the colors associated.
|
UNCLAS: green
CONFIDENTIAL: blue SECRET: red TS: orange |
|
|
What does EEFI stand for?
|
Essential Elements of Friendly Information
|
|
|
Why is keeping EEFI safe important?
|
They are specific items, that if revealed and correlated with other information, would degrade the security of military operations.
|
|
|
What is BEADWINDOW?
|
A procedure that is used to alert circuit operators that an unauthorized disclosure has occurred over a non-secure circuit.
|
|
|
Name all BEADWINDOWS.
|
1- Position
2- Capabilities 3- Operations 4- EW 5- Personnel 6- COMSEC 7- Wrong circuit |
|
|
What is the only authorized reply to BEADWINDOW?
|
Roger, out.
|
|
|
What does GINGERBREAD mean?
|
Intruder on the Net.
|
|
|
Name all Frequencies and ranges.
|
HF: 3Mhz-30Mhz
VHF: 30Mhz-300Mhz UHF: 300Mhz-3Ghz |
|
|
What is the most frequently used frequency range used in the Navy?
|
UHF.
|
|
|
What are the three types of comms gear used on the boats?
|
AN/PRC 117 (Prick 117)
AN/PRC 150 (Prick 150) Marine Band Radio (MARBAND) |
|
|
What are the four factors in a camp site selection?
|
1. Mission Convenience
2. Security 3. Safety of Camp 4. Geographical Terrain |
|
|
What are the five factors in camp setup?
|
1. Planning
2. Site survey 3. Camp Establishment 4. Camp Maintenance 5. Tear Down |
|
|
In the camp, what is the distance between roads and anything?
|
15 feet
|
|
|
In the camp, what is the distance between berthing and berthing?
|
15 feet
|
|
|
In the camp, what is the distance between potable water and latrines?
|
50 feet
|
|
|
In the camp, what is the distance between berthing and latrines?
|
200 feet
|
|
|
In the camp, what is the distance between garbage and potable water?
|
300 feet
|
|
|
In the camp, what is the distance between the galley and latrines?
|
300 feet
|
|
|
In the camp, what is the distance between the galley and fuel
|
300 feet
|
|
|
In the camp, what is the distance between berthings and the helo pad?
|
500 feet
|
|
|
What is a leach field and what other names are there for it?
|
It is a sewage disposal system of grey water.
AKA Tile Field/Absorption Trench |
|
|
What is the camp Trouble Desk for?
|
They receive all customer trouble calls.
|
|
|
What are the four priority work classifications?
|
1. Safety
2. Function 3. Preventative 4. Appearance |
|
|
What are the three levels of importance for each work classification?
|
1. High
2. Routine 3. Low |
|
|
What does an Operation Inspection consist of?
|
- Examining
- Lubricating - Minor Adjustments |
|
|
What is Potable Water?
|
Water that is safe to drink, free from foul odor and disease.
|
|
|
What does ROWPU stand for?
|
Reverse Osmosis Water Purification Unit
|
|
|
What does ROWPU do?
|
Produces raw/brackish/sea water into potable water. It can also treat water contaminated by CBR.
|
|
|
What is the purpose of chlorination?
|
To disinfect a water supply.
|
|
|
What is 782 gear?
|
It is the standard issue of gear.
|
|
|
What are 10 examples of 782 gear?
|
1. Pistol belt
2. Suspenders 3. Canteen 4. Poncho 5. Bayonet 6. Combat Pack 7. Ammo Pouches 8. Blow-out Kit 9. Entrenching tool 10. Kevlar Helmet |
|
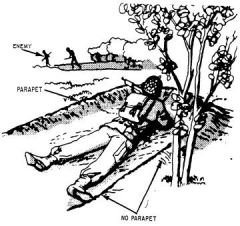
What kind of emplacement is this?
|
Hasty/Skirmisher's
|
|
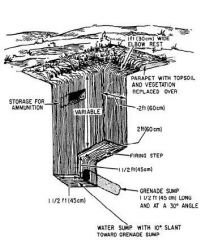
What fighting position is this?
|
Improved 1 Man
|
|
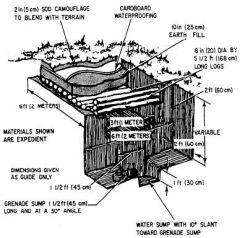
What fighting position is this?
|
Improved 2 Man
|
|
|
What is Camouflaging?
|
Measures taken to conceal yourself from enemy observation.
|
|
|
What are three general rules to camouflaging?
|
1. Take advantage of all natural concealment.
2. Camouflage by altering form, shadow, texture, and color of objects. 3. Camouflage against both ground and air observation. |
|
|
What are 7 things we camouflage?
|
1. Fighting positions
2. Personal equipment 3. Persons 4. Vehicles 5. Buildings 6. Supply Points 7. Water Points |
|
|
What do you do if you are caught in an overhead flare?
|
Immediately hit the deck, resume movement as soon as the flare burns out.
|
|
|
What do you do if you are caught in the light of a ground flare?
|
Move out of the area of light as quickly and quietly as possible.
|
|
|
What does KOCOA stand for?
|
Key terrain
Observation and fields of fire Cover and concealment Obstacles to movement Avenues of approach |
|
|
What does BAMCIS stand for?
|
Begin planning
Arrange for reconnaissance Make reconnaissance Complete the plan Issue the order Supervise |
|
|
What does METT-T stand for?
|
Mission analysis
Enemy forces Terrain/weather analysis Troops and support available Time |
|
|
What does SMEAC stand for?
|
Situation
Mission Execution Admin and logistics Command and signal |
|
|
What does SALUTE stand for?
|
Size
Activity Location Uniform Time Equipment |
|
|
What is a SPOT report?
|
A hastily modified SALUTE report.
|
|
|
What is a Security Patrol?
|
A detachment of troops sent out from a larger body on a mission of combat, reconnaissance, security or contact with friendly units.
|
|
|
What is a Reconnaissance Patrol?
|
A detachment sent out to gain information about the enemy or the terrain.
|
|
|
How many steps are there in patrol planning?
|
12.
|
|
|
1st step in patrol planning
|
Establish security
|
|
|
2nd step in patrol planning
|
Hastily set up COMMS
|
|
|
3rd step in patrol planning
|
Position weapons
|
|
|
4th step in patrol planning
|
Clear fields of fire
|
|
|
5th step in patrol planning
|
Assign sectors of fire
|
|
|
6th step in patrol planning
|
Prepare fighting positions
|
|
|
7th step in patrol planning
|
Plan, coordinate and plot fire support
|
|
|
8th step in patrol planning
|
Install tactical and supplementary wire
|
|
|
9th step in patrol planning
|
Lay wire for final COMMS network
|
|
|
10th step in patrol planning
|
Prepare obstacles, claymores and protective wire
|
|
|
11th step in patrol planning
|
Prepare alternative fighting positions
|
|
|
12th step in patrol planning
|
Prepare supplementary fighting positions
|
|
|
What does BDA stand for?
|
Battalion Defense Area
|
|
|
What does FEBA stand for?
|
Forward Edge of Battle Area
|
|
|
What are the three BDAs and their parameters?
|
Security Area: Starts at FEBA and extends 500m to the front and flanks of the battalion
Forward Defense Area: Extends rearward from the FEBA to the rear boundaries of the frontline companies. Reserve Area: Extends from the rear boundary of the frontline companies to the rear boundary of the battalion. |
|
|
What is a Fire Plan Sketch?
|
A plan to cover the entire sector of fire with the heaviest volume of fire possible.
|
|
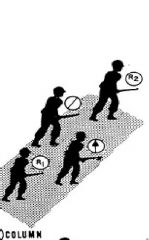
Column
|
Used when speed and control are governing factors, such as moving through woods, fog, smoke, and long roads and trails.
|
|
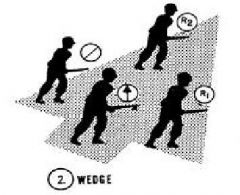
Wedge
|
Is used when the enemy situation is unknown but contact is possible.
|
|
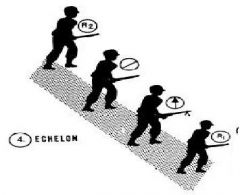
Echelon
|
Is to protect an exposed flank.
|
|
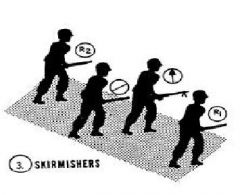
Skirmishers
|
Most effective when you are assaulting a known enemy position.
|
|
|
What are Immediate Actions?
|
Pre-drilled, pre-rehearsed reactions to contact or anticipated contact with the enemy to reduce losses to personnel and neutralize the enemy.
|
|
|
What is a sector of fire?
|
An area of responsibility assigned to a squad, platoon, or a CSW to be covered by fire.
|
|
|
What are Lateral Limits?
|
Readily identifiable terrain features selected to show the line of sight along each sector.
|
|
|
What are Forward Limits?
|
An established range at which the weapon will open fire.
|

