![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
125 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Homeostatsis
|
The healthy internal balance of the human organism. The body will always try to return to homeostatis.
|
|
|
Feedback Systems
|
Maintains homeostasis.
|
|
|
Normal blood sugar
|
80 - 120mg/ml
|
|
|
Normal body temp range
|
36.5-38* C
97.7 - 100.4* F |
|
|
Sagittal Plane
|
Extends veritically (from head to toes) and divides body into left and right portions.
|
|
|
Parasagittal plane
|
Any sagittal plane that passes through the body to the left or right of the midline and divides the body into unequal left and right portions.
|
|
|
Frontal Coronal Plane
|
Vertical plane that divides the body into front (anterior) and back (posterior) portions.
|
|
|
Transverse plane
|
Horizontal (perpendicular) plane that divides body into top (superior) and bottom (inferior) portions.
|
|
|
Oblique plane
|
Passes through the body at an angle between transverse plane and either a sagittal or frontal plane.
|
|
|
Another name for Anterior
|
Ventral
|
|
|
Another name for Posterior
|
Dorsal
|
|
|
Medial
|
Toward the midline
|
|
|
Proximal
|
Closer to midline or point of attachment of a limb.
|
|
|
Distal
|
Farther away from the midline or point of attachment of a limb.
|
|
|
Superficial
|
Closer to the surface of the body.
|
|
|
Deep
|
Farther from the body surface.
|
|
|
Axial region
|
Area of body closest to midline or axis. (head, neck, and trunk)
|
|
|
Thoracle
|
Chest region above the diaphragm.
|
|
|
Abdominopelvic region
|
Region below the diaphragm.
|
|
|
Appendicular region
|
Region farthest away from the midline and consists of the appendages (extremities).
|
|
|
Brachium
|
Arm from the shoulder to elbow.
|
|
|
Antebrachium
|
Forearm from the elbow to the wrist.
|
|
|
Carpus
|
Wrist area
|
|
|
Metacarpus
|
Hand between carpus and phalanges.
|
|
|
Manus
|
Hand
|
|
|
Digits
|
Fingers
|
|
|
Thigh
|
Area from hip to knee
|
|
|
Crus
|
Area from knee to ankle (shank)
|
|
|
Tarsus
|
Ankle (between leg and metatarsus)
|
|
|
Pes
|
Foot
|
|
|
Phalanges
|
Toes
|
|
|
9 abdominal regions
|
1. Right hypochondriac region
2. Epigastric region 3. Left hypochondriac region 4. Right lateral (lumbar) region 5. Umbilical region 6. Left lateral (lumbar) region 7. Right inguinal (iliac) region 8. Hyprogastric region 9. Left inguinal (iliac) region |
|
|
Right hypochondriac region
|
Liver, Gall bladder
|
|
|
Epigastric region
|
Liver, Stomach, Pancreas
|
|
|
Left hypochrondriac region
|
Stomach, Spleen
|
|
|
Right lateral (lumbar) region
|
Ascending colon, gall bladder
|
|
|
Umbilical region
|
Stomach, transverse colon, small intestine, pancreas
|
|
|
Left lateral (lumbar) region
|
Small intestine, descending colon
|
|
|
Right inguinal (iliac) region
|
Cecum, small intestine
|
|
|
Hyprogastric region
|
Small intestine, rectum, urinary bladder, reproductive organs
|
|
|
Left inguinal (iliac) region
|
Small intestine, sigmoid colon
|
|
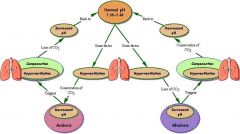
Homeostasis
|
Homeostatsis
|
|
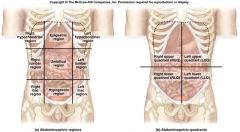
Abdomnopelvic region
|
Abdominopelvic region
|
|
|
Dorsal cavity
|
Cranial cavity
Vertebral or spinal cavity |
|
|
Ventral cavity
|
Thoracic cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity |
|
|
6 characteristic of living organisms
|
Metabolism, growth, differentiation, movement, responsiveness, reproduction
|
|
|
Negative feedback does what?
|
The body senses a change in a variable and activates mechanisms that reverse that change.
|
|
|
Positive feeback system does what?
|
Produces a self amplifying affect to orginal stimulus.
|
|
|
Hierachy of complexity
|
From simple to complex.
Chemical level > Cellular level > Tissue level > Organ level > System level > Oraganism level |
|
|
Chloride is the only
|
Anion
|
|
|
Inorganic chemistry (or General chemistry)
|
Deals with substances that DO NOT have CARBON as part of the structure
|
|
|
Organic molecules (4 categories)
|
Carbohydrates
Lipids Proteins Nucleic acids |
|
|
Element
|
Simplest form of matter to have unique chemical properties and cannot be broken down by oridinary chemical means.
|
|
|
Water can be broken down into...
|
Hydrogen and oxygen
|
|
|
The 6 elements:
|
Oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, calcium, phosphorus.
|
|
|
Atom
|
Smallest unit of matter
|
|
|
Ion
|
Electrically charged particle with unequal numbers of protons and electrons.
|
|
|
Cation
|
Particle that loses electrons and aquires a POSITIVE charge.
|
|
|
Anion
|
Particle that gains electrons and acquires a NEGATIVE charge.
|
|
|
Chloride is the only
|
Anion
|
|
|
Molecules
|
Chemical particles composed of 2 or more atoms.
|
|
|
Compound
|
Composed of atoms of 2 or more DIFFERENT elements.
|
|
|
Free radicals
|
Charged groups of atoms with an odd number of electrons. Produced by some normal metabolic reactions of the body as well as by radiation. They are unstable and combine quickly with fats, proteins, and DNA. They destroy nearby molecules.
|
|
|
3 types of bonds
|
Ionic, covalent, hydrogen
|
|
|
Ionic bond
|
Weak attraction between an anion and cation.
|
|
|
Covatlent bond
|
Shares one or more pairs of electrons between atoms.
|
|
|
Nonpolar bond
|
Atoms share the electrons equally.
|
|
|
Polar bond
|
Uneven sharing of electrons.
|
|
|
Hydrogen bond
|
Weak attactiion between a hydrogen atom with a partially positive charge, and a neighboring atom with a partially negative charge.
|
|
|
Compound with No carbon is what type?
|
Inorganic compound
|
|
|
Compound WITH carbon
|
Organic compound
|
|
|
4 properties of water
|
Solvency
Cohesion Chemical reactivity Thermal Stability |
|
|
Solvency
|
Ability to dissolve other chemicals. Water is the universal solvent.
|
|
|
Cohesion
|
Tendancy of molecules of the same substance to cling to each other.
|
|
|
Surface tension
|
The film held together by a force.
|
|
|
Chemical reactivity
|
Ability of water to participate in a wide variety of chemical reactions.
|
|
|
Hydrolysis reactions
|
Involve adding of water molecules to decompose or breakdown compounds.
|
|
|
Dehydration reactions
|
Involve the removal of water molecules to add small molecules together.
|
|
|
Thermal stability of water
|
Stabilizes the internal temp of the body. Water can absorb or release large amts of heat without a big change in its own temp.
|
|
|
3 types of Mixtures
|
Solutions
Colloids Suspensions |
|
|
Solution
|
Consists of dissolved particles (solute)
Solvent is clear Mixed with abundant substance Small particle size Ex: Sugar water |
|
|
Colloiid
|
Cloudy
Particles are < 100nm in size Particles are suspended (not dissolved) Particles are small enough to remain permanently mixed, but not dissolved. Ex: Milk |
|
|
Suspension
|
Suspended particles
Exceed 100 nm in size Particles are too heavy to remain permanently suspended. Suspensions will separate on standing Ex: Blood |
|
|
Normal pH
|
7.35-7.45
|
|
|
pH of blood depends on what ions?
|
H+ (hydrogen)
OH- (hydroxide) |
|
|
The higher the H+ ions, the more ____ the blood.
|
Acidic
|
|
|
Energy and work
|
Process of breaking old bonds (release energy) and forming new bonds (require energy).
|
|
|
Potential energy
|
Energy stored by matter because of its position or internal state, but which is not doing work at this time.
|
|
|
Kinetic energy
|
Energy of motion.
Ex: Heat |
|
|
Chemical energy
|
Potential energy stored in the chemical bonds of molecules.
|
|
|
Activation energy
|
Amt of energy needed to allow an atom/molecule to collide with another and cause a disturbance of their valence electrons. Increased temp and number of particles, the greater the chance of collision.
|
|
|
Catalysts
|
Substances that speed up the rate of chemical reactions in the body by lowering the amt of activation energy needed to start the reactions.
|
|
|
Metabolism
|
Sum of all the chemical reactions in the body.
2 divisions: anabolism and catabolism |
|
|
Anabolism
|
Energy requiring reactions where small molecules are joined together to form large ones. (synthesis or endergentic reactions)
|
|
|
Catabolism
|
Energy releasing reactions where large molecules are broken down into smaller ones Idecomposition, or exergonic reactions)
|
|
|
Carbohydrates
|
Hydrophyllic (water-loving) organic molecules. Main source of energy production for cells to perform chemical reactions (ATP)
|
|
|
Names of carbs usually contain the root ____-or the suffix ____.
|
Sacchar,
ose (both mean sweet) |
|
|
Carbohydrates contain..
|
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
|
|
|
Monosaccharides
|
Simple sugars that are composed of a single carbon containing molecule.
(Glucose, Fructose, Galactose) |
|
|
Disaccharides
|
Simple sugars composed of 2 monosaccharide molecules.
(Sucrose, Lactose, Maltose) |
|
|
Sucrose
|
Combination of glucose and fructose.
|
|
|
Lactose
|
Combination of glucose and galactose.
|
|
|
Maltose
|
Two glucose chains.
|
|
|
Polysaccharides
|
Complex sugars made of many monosaccharide molecules. (Ex. Glycogen)
|
|
|
Lipids (fats)
|
Hydrophobic organic molecules, composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Function as a source of stored energy.
|
|
|
4 primary categories of lipids
|
Triglycerides
Phospholipids Eicosanoids Steroids |
|
|
Triglycerides
|
Most common lipid in the body and diet. Stored as adipose tissue. Cosists of 3 fatty acids attached to glycerol.
|
|
|
Saturated fatty acid
|
Solid at room temp: Full of hydrogen and only a single bond between carbon atoms.
|
|
|
Unsaturated fatty acid
|
Liquid at room temp: Room for hydrogen and double bonds between carbon atoms.
|
|
|
Phospholipids
|
Lipids containing phosphorus. These are the major lipids in cell membranes.
|
|
|
Eicosanoids
|
Physiologically active substances derived from arachidonic acid. Plays a major role in blood clotting, hormone action, labor, control of BP, imflammation.
|
|
|
Steroids
|
Lipids that are composed of 4 rings of carbon atoms and include cholesterol.
|
|
|
Cholesterol
|
A basic building block molecule for all sex hormones, adrenaline, and part of cell membrane.
|
|
|
Proteins
|
Polymers (large molecules) of building blocks called amino acids joined by a tougher peptide.
Composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen,and nitrogen. |
|
|
Enzymes
|
Proteins that function as biological catalysts.
|
|
|
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
|
Most important energy-transfer molecule. Much of its energy comes from glucose oxidation.
|
|
|
Glycolysis
|
First stage of glucose oxidation.
Literally means "sugar splitting" 2 molecules of ATP is produced at this stage Splits glucose into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid. |
|
|
Anaerobic metabolism
|
Absence of oxygen.
Little or no ATP produced Produces lactic acid |
|
|
Aerobic metabolism
|
Breaks pyruvic acid down to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O)
Generates a total of 38 molecules of ATP |
|
|
Nucleic acid
|
Huge organic molecules that contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
|
|
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
|
Largest nucleic acid
Composed of a double stranded helix |
|
|
DNA contains
|
4 nitrogenous bases: adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine.
Composed of a double stranded helix |
|
|
RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
|
Translates the genetic information from DNA into specific proteins.
-Single stranded molecule |
|
|
Kreb cycle
|
Aerobic metabolism
|
|
|
Genetic code
|
Carry instructions for protein synthesis.
|

