![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
12 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three types of muscle and their four possible functions?
|
1. Skeletal 2. Smooth 3. Cardiac
1. Body mvmt 2. Stabilization of body position 3. Mvmt of substances through body 4. Generating heat to maintain body temp |
|
|
Difference between a tendon and a ligament
In reference to muscle, what is an agonist, antagonist, and synergistic muscle? |
A tendon connects muscle to bone and a ligament connects bone to bone
The agonist, muscle responsible for mvmt, contracts, while the antagonist, stretches The synergistic muscle assists the agonist by stabilizing the origin bone or by positioning the insertion bone during the mvmt |
|
|
Describe how physics (leverage, F) can be applied to a muscle
|
The elbow can function s a fulcrum, the ulna/radius as a lever, the weight in the hand as the resistance and the muscle in the upper arm as the force applied
-A greater force than mg is required to lift a mass m -If the muscle has a shorter lever arm, it is closer to the body, and thus creates less bulk |
|
|
Explain what happens during a muscle contraction:
-A band, H zone, I band, Actin, Myosin |
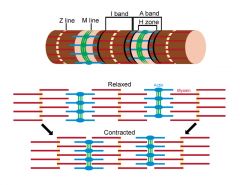
The H zone and I band get smaller. The A band does not change size.
A sarcomere is the smallest functional unit of skeletal muscle and is made up of a thin filament (actin) and a thick filament (myosin). Attached to actin are the proteins troponin and tropomyosin. Tropomyosin covers the active site on actin so that the myosin head cannot bind, but in the presence of Ca2+, troponin pulls tropomyosin back |
|
|
Describe the function of a T-tubule and the sarcoplasmic reticulum in contraction
|
T-tubule: when an AP occurs, it flows through the T-tubule in order to allow for a uniform contraction by allowing the AP to spread through the muscle more rapidly. The AP is then transferred to the SR, which suddenly becomes permeable to Ca2+ ions - releasing them so that they can bind to troponin. At the end of a 5-stage cycle, Ca2+ is actively pumped into the SR
|
|
|
1. Myoglobin
2. Can muscle cells replicate? |
1.Myoglobin looks like one subunit of Hb. It is only capable of storing one O2 molecule. It stores O2 inside muscle cells.
2. Muscle cells are so specialized that they have lost their ability to undergo mitosis. It is rare for them to split into 2 cells |
|
|
Describe the structure of cardiac muscle cells
|
They are striated like skeletal muscle, which means they have sarcomeres. They only have one nucleus per cell. They are separated by intercalated disks, which contain gap junctions and allows AP's to spread from one cell to the next. Cardiac muscle is involuntary unlike voluntary skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Describe the structure of smooth muscle
|
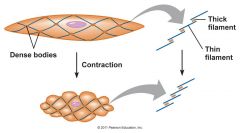
Smooth muscle has one nucleus like cardiac muscle. It also has thick and thin filaments, but they are not organized into sarcomeres, so the cells aren't striated.
Upon contraction, the thin filaments pull the dense bodies together and the cell shrinks length-wise |
|
|
What are the functions of bone?
|
Bone is not just for support, mvmt, and protection. It also stores Ca2+ and phosphate, helping to maintain a balance of these ions in the blood. Bone stores energy in the form of fat. Bone is the site of blood cell formation
|
|
|
1. Osteoblasts?
2. Osteocytes? 3. Osteoclasts? |
1. secrete collagen and organic compounds to help form bone
2. exchange nutrients and waste materials with the blood 3. resorb bone matrix, releasing materials back into the blood |
|
|
1. Most of the Ca2+ in the body is stored in the bone matrix as?
|
1. Hydroxyapatite
|
|
|
What are 7 functions of the skin?
|
1. Protection
2. Excretion 3. Vitamin D 4. Immunity 5. Thermoregulation 6. Environmental sensory input 7. Blood reservoir |

