![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
132 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Normal range temperature
|
97 to 99.6
|
|
|
Radiation
|
Transfer of heat between two objects without touching
|
|
|
Conduction
|
Transfer of heat with direct contact
|
|
|
Control Center of temperature
|
Hypothalamus
|
|
|
Convection
|
Transfer of heat by fan source
|
|
|
Evaporation
|
600 to 900 each day output breath and sweat
|
|
|
Diaphoresis
|
Visible prespiration on skin
|
|
|
Insensible loss
|
Unmeasurable fluid loss
|
|
|
Sensible loss
|
Urine output measurable wound drainage
|
|
|
Behavioral control of temperature
|
Removing clothing changing thermostat putting on a jacket
|
|
|
Factors affecting temperature
|
Age activity hormones time of day emotions stress disease drugs
|
|
|
Temperature sites
|
Oral rectal auxiliary tympanic temporal artery
|
|
|
Types of thermometers
|
Electronic infrared tympanic temporal artery and chemical
|
|
|
What do you do if abnormal
|
Always recheck abnormal and assess patient
|
|
|
Hyper thermia
|
Patient has a fever
|
|
|
Pyrexia
|
Means temperature fever
|
|
|
Hypothermic patients at risk
|
Elderly prolonged exposure alcoholics post op patience newborns
death below 93.2 |
|
|
Signs of hypothermia
|
Shivering pale skin lifeless body slow heart rate slow respirations decrease thinking
|
|
|
Pulse
|
Rhythmic breathing sensation produced by waves of pressure resulting from ejection of blood during heart contraction
|
|
|
Peripheral pulse
|
Extremities
|
|
|
Central pulse apical pulse
|
5tj intercostal space true heartbeat
|
|
|
Pulse ranges
|
Adult 60 to 100 child 80 to110 infant 100 to140 newborn 120 to 160
|
|
|
Assessing pulse
|
Palpitation= touch
ausculation= stethoscope -apical doppler |
|
|
pulse sites
|
Carotid in the neck
Brachial in the elbow Radial in the wrist Femoral in the groin Popliteal behind the knee Dorsalis pedis top of foot Posterior tibial back of ankle |
|
|
Apical pulse
|
Central poles actual beating of the heart listening at the chest angle of Louis
|
|
|
Apical radial pulse
|
2 Rns
1 full minute Compare findings pulse deficit subtract the difference radial never greater than apical |
|
|
Stethoscope
|
Diaphragm high sounds vital signs bowel and heart
Bell lower sounds heart sounds sounds within the vessels |
|
|
Pulse strength
|
0 = absent
1+= thready/barely there 2+= normal 3+= full strong 4+ = bounding |
|
|
Tachycardia
|
Heart rate above 100
|
|
|
Bradycardia
|
Heart rate below 60
|
|
|
Dysrhythmias or arrhythmia
|
Irregular pulse
|
|
|
Pulse deficit
|
Difference between apical and radial pulse
|
|
|
Ventilation
|
Movement of gases in and out of lungs
|
|
|
Diffusion
|
Movement of o2 and co2 between in the aveoli and red blood cells
|
|
|
eupnea
|
Even regular quiet and effortless normal respiration
|
|
|
Respiration assessment
|
Rate
Depth rhythm and quality |
|
|
Tachypnea
|
Respirations over 20 per minute
|
|
|
Brady Pena
|
Respirations below 12 per minute
|
|
|
Apnea
|
Without respirations
|
|
|
Dyspnea
|
Difficulty breathing
|
|
|
Orthopnea
|
Positioning can only breathe with in certain positions
|
|
|
Cheyne Stokes
|
Dying patients apnea then breathing apnea again
|
|
|
kussmauls
|
Rapid respirations happens in DKA patience
|
|
|
Hyperventilation
|
Rapid breathing patients will pass out
|
|
|
Respiratory distress signs and symptoms
|
Cyanosis restlessness irritability confusion difficulty breathing using accessory muscles nasal flaring
|
|
|
Definition of blood pressure
|
Pressure exerted on the blood vessel walls with each heartbeat normal range 120 over 80
|
|
|
Why obtain blood pressure
|
Reflects cardiac output contractibility of the heart blood volume peripheral resistance
give a base |
|
|
Pulse pressure
|
Difference between systolic and diastolic
ex 120/80 difference = 40 normal range 30-50 |
|
|
How many phases of blood pressure
|
5
|
|
|
How do pressure ulcers begin
|
There is no circulation where there is pressure sores develop
|
|
|
Halitosis
|
Bad breath
|
|
|
glossitis
|
Inflamed tongue
|
|
|
Stomatitis
|
Inflamed oral mucosa
|
|
|
cheilosis
|
Cracked lips
|
|
|
sordes
|
Collection of mucus secretions
|
|
|
hirutism
|
Excessive body hair growth
|
|
|
pediculosis capitis
|
Head lice
|
|
|
alopecia
|
hair loss
|
|
|
effleurage
|
massage associated with reducing anxiety
|
|
|
acne
|
inflammation of skin involving bacterial breakdown of sebum
appears on face shoulders back |
|
|
edentulous
|
lacking teeth
|
|
|
enucleation
|
removal of the eye due to trama infection ect
|
|
|
hygiene
|
conditions and practices that help in maintaining health and preventing disease
|
|
|
scabies
|
easily speak skin diseases caused by a mite
|
|
|
tinea pedis
|
Athletics foot
infection of the foot causes by fungus |
|
|
xerostomia
|
dry mouth
|
|
|
feet and hands care of a diabetic
|
never ever soak due to low vascular feeling.
|
|
|
oral care on unconscious pt
|
turn lateral head turned to side
place head on pillow for secretions to run down place bulb syringe and yanked close by |
|
|
denture care
|
use gauze to prevent slipping
place washcloth in sink tepid water close to bottom of sink ( incase you drop) |
|
|
showers/bath assessment
|
check patient for moles, warts, rashes, skin lesions
|
|
|
shaving patients
|
caution if on aspirin or anticoagulant
use electric razor |
|
|
assessing tube and lines
|
o2 stays on during bath
IV don't open lines, use special gowns cath- draining? unkinked, bag below bladder |
|
|
posture
|
maintains bodies alignment
|
|
|
joint mobility
|
able to move limb through full range of motion with control
|
|
|
balance
|
balance of low center gravity over a wide stable base
|
|
|
coordinated body movement
|
Center of gravity is located at exact center and force of weight is directed downward
|
|
|
effects of immobility
|
muscle atrophy
contracture |
|
|
body mechanics
|
the way a person uses bones, muscles, and joints to create movement
|
|
|
active ROM
|
able to move joints freely and on thier own
|
|
|
passive ROM
|
needs help with ROM and joints have limits
|
|
|
ROM guidelines
|
3-4 daily
move slow, smooth, gentle If client is in pain stop |
|
|
Fowlers
|

45-60 degrees
|
|
|
high fowlers
|
HOB 90 degrees
|
|
|
semi fowlers
|
HOB 30 degrees
|
|
|
supine
|
on back
|
|
|
prone
|
face down
|
|
|
lateral
|
side lying position
|
|
|
SIMS POSITION (semi prone)
|

semi prone
|
|
|
transferring bed to chair
|
bed lowest position
HOB sitting position non skid footwear gait belt allow dangling brace patients weak leg against knee stand and pivot |
|
|
ROM neck
|
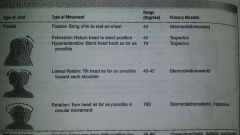
|
|
|
shoulder ROM
|

|
|
|
shoulder abd and adduction
|

|
|
|
ROM
|

|
|
|
ROM joint hinge/pivotal
|

|
|
|
condyloid hinge
|

|
|
|
saddle ROM
|
thumb
|
|
|
ball and socket
|

|
|
|
ROM
|

|
|
|
safety/falls/restrainst
|
psychological ( happiness) needs come first!
|
|
|
TJC (JACHO)
|
improves hospital care, correct patients, communication, prevent Healthcare infections, identifies safety risks, ect
|
|
|
National Quality Forum
|
wrong procedute, wrong patient, wromg site
SREs ( serious reportable events) surgical, product or device, care managment, criminal |
|
|
CMS list of never events
|
medical and Medicaid refuses to pay for hospital acquired issues
falls, infections, bed sores, pneumonia, urosepsis ect |
|
|
QSEN quality and safety for nurses
|
QSEN minimizes risks for patients but education nurses
co pentcies to perform your role as a nurse. |
|
|
hazards of infant toddler
|
mvc, burns, poison, chocking, drowning, child abuse
|
|
|
hazards for school aged kids
|
mvc, drowning, injury, falls, child abuse, homicides firearms
|
|
|
hazards for teens
|
mvc, sports, homicides, suicides, drugs and alcohol
|
|
|
hazards for adults
|
falls, mvc, homicides, suicides, over exertion
|
|
|
hazards for elderly
|
falls, mvc, polypharmacy, fires, burns, brain injuries, suicide
|
|
|
Msds
|
chemical data sheet
|
|
|
health care risks
|
#1 med errors
infection bed sores failure to diagnose and treat in time |
|
|
4 inherent risks in health care
|
#1 falls
#2 patient inherent accidents ( patient is primary reason) #3 procedure related caused by provider ( meds errors) #4 equipment related errors |
|
|
fire safety
|
RACE
rescue, activate, confine, extinguish PASS pull, aim, squeeze, sweep |
|
|
fire extinguishers
|
class A paper, wood, rags, ordinary rubbish
class B flammable liquids and gases class C electrical |
|
|
restraint
|
any method of physical restrictions a person freedom of movement activity or access to thier body
|
|
|
2 types of restraints
|
behavioral (ER)
medical/ surgical |
|
|
nutrients
|
elements in food that are necessary for the body to function
|
|
|
macronutrients
|
carbs proteins fats
|
|
|
micronutrients
|
minerals vitamins water
|
|
|
basal metabolic rate
|
energy needed to maintain life sustaining activities for a specific period of time at rest
|
|
|
resting energy expenditure aka REE ( rest metibolic rate)
|
the amount of energy the individual needs to consume over 24 hours for the body to maintain internal working activities at rest
|
|
|
carbs
|
45-60% total cals
|
|
|
protien
|
10-35 % total cals 4k/cal
helps healing |
|
|
fats
|
20-35% total cals
poly and mono |
|
|
fat soluble vitamins
|
stores in the body
A D E And K vitamin toxic |
|
|
water soluble vitamins
|
C and B complex
doesn't get stores urine output can be toxic |
|
|
minerals
|
inorganic sub used to regulate body processes
|
|
|
water
|
needed to Cary out cellular processes
helps digestion and process fluids |
|
|
digestion
|
process broken down where the process starts
|
|
|
absorption
|
where enters blood stream or where it needs to go
|
|
|
metabolism
|
chemical reaction
|
|
|
hospital diets
|

|
|
|
cholesterol levels
|

|

