![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Ammonite (400 - 65 mya) |
- went Extinct with dinosaurs at the same time ~ 65mya
- Lived in the sea
- excellent index fossil – a fossil that is associated with a particular span of geological time.
- can figure out the each layer of rock if an index fossil is found in embedded in it. |
|
|
How are fossils formed? |
- Rapid + permanent burial Oxygen deprivation No decay
- H 2 0 infused with minerals seeps into the bone ( chemical reaction occurs) Dissolving and replacement of the original minerals in the bone with other minerals (rock - like minerals)
|
|
|
What are the two types of dating methods used to interpret earths history? |
Numerical dating -what is radioactivity, and how are radioactive isotopes used in dating
- actual ages of rocks through radioactive decay
- numerical value
- A.k.a. absolutely
Relative dating - what are the laws, principles, and techniques used to establish relative dating?
- cannot establish
- can figure out rock sequence of formation - Which formed first, second, third and so forth through principles and techniques |
|
|
Rock cycle |
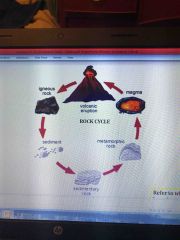
|
|
|
Three types of rock |
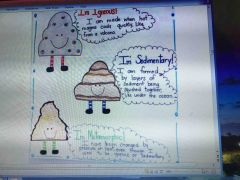
Metamorphic: I have been changed by pressure or heat, even though I used to be igneous or sedimentary .
All rocks breakdown to sediment. - All rocks begin from igneous rocks. (Introsive and extensive.) 🔽 Will be broken down to loose sediment. (Small sand.) 🔽 Will form into a sedimentary rock
|
|
|
Principles of relative dating |
Developed by Nicolaus steno 1.) law of superposition
2.) principle of original horizontality
3.) Prince a bowl of lateral continuity
4.) principle of cross-cutting relationships
5.) principle of inclusions |
|
|
Law of superposition |
In an undeformed sequence of sedimentary rocks, old is rock base; youngest at top.
Strata- A bed or layar of sedimentary rock that is visually distinguishable from adjacent beds or layers. |
|
|
Superposition: Grande Canyon |
- Kaibab Limestone: 250 mya ✔️fossils found are corals, sea lilies, and fish teeth
✔️ Was once covered by an ancient sea
- Supai Group: 285 mya ✔️ fossils found are amphibians, reptiles, and plants
✔️ Was once a muddy River Delta that fit into an ancient sea |
|
|
Grand Canyon is not a rift valley |
1.) Hey Mountain building 2.) formation of a sea 3.) Then sea retreats 4.) about 20 mya The Colorado river is formed and starts to carve rocks to form the canyon. |
|
|
Principles of original horizontality |
- Layers of sediment are deposited in a horizontal position; flate strata - no crustal disturbances.
- Layers of sediment are deposited in a horizontal position; folded or tilted strata - crustal disturbances occurred after their disposition.
|
|
|
Principle of lateral continuity |
Sedimentary beds originate as continuously layers That extend all directions until they eventually grade into different type of sediment or until they been out at the edge of the basin of disposition.
|
|
|
Principle of cross-cutting relationships |
When I fault cuts through other rocks, or when magma intrudes and crystallizes, but the faults or intrusions is younger than the rocks affected.
Principles of crosscutting relationships tells Aspect of the light colored granite must be older than the darker Basalt dike intruding the granite.
Dike: is a sheet of rock that formed in a fracture in a pre-existing rock body. |
|
|
Principle of inclusions |
Inclusions - Are fragments of minerals or rock contained within another rock.
States that a rock mass adjacent to the one containing the inclusions must have been there first in order to provide the rock fragments.
These inclusions of igneous rocks contained in the adjacent sedimentary layer indicate the sediments were deposited atop the weathered igneous mass and thus are younger. |
|
|
Unconformities |
- loss of rock record. Produced by long period of erosion and/or non-disposition.
3 types: 1.) Angular unconformity 2.) Disconformity 3.) Nonconformity |
|
|
Angular Unconformity |
Tilted or folded sedimentary rocks that are overlain by younger, more flat - lying strata.
- all are bended upwards or tilted layers of sedimentary rock with overlying horizontal sedimentary layers. |
|
|
Disconformity |
- the beds above and the below are parallel but time is lost.
- after erosion, continued horizontal disposition.
- all are parallel layers of sedimentary rock. |
|
|
Nonconformity |
- younger sedimentary rocks deposited above older metaphoric or igneous rocks with time lost.
- basement rocks exposed to erosion then sedimentation. |
|
|
Fossils and correlation |
✔️marching rocks layers from one geographic area with those of another area.
✔️ fossils are important time indicators and help in correlating rocks from difference places.
✔️note: layers were originally continuous across the canyons (principle of lateral Continuity) |
|
|
Geological time scale earths history in units |
1.) Era - when major life form changes
- Precambrian - Paleozoic - Mesozoic - Cenozoic |
|
|
Precambrian |
- before 550 mya - about 89% of all earths history - Little rock on surface (late.) |
|
|
Paleozoic |
550 - 250 mya -1st visible shells (fossils.) - early Paleozoic = shelled animals in sea: nothing land. - late Paleozoic = land plants, fish. |
|
|
Mesozoic |
250 - 65 mya - dinosaur fossils, conifer trees - metour collision — mass extinction |
|
|
Cenozoic |
65 - 0 mya - mammals, birds, flowering plants - ice Age - humans (modern human 200,000 years ago.) |
|
|
Ffff |

|
|
|
Why are some isotopes radioactive |
✔️ isotope that have the right amount of neutrons are called stable. They always stay the same.
✔️ some isotopes have too many neutrons or not enough - this makes them unstable and radioactive.
✔️ radioactive Atoms change or decay by giving off radiation until the Adam reaches a stable state.
✔️ The decay rate of radioactive Adams are used to determine numerical age. |
|
|
How long does a radioactive decay take |
✔️ Half-life — the time it takes for half a radioactive or parent isotope to decay to more stable daughters isotopes.
✔️ once known: on parent/ daughter ratio and number of half life that have occurred since the sample was formed, can calculate numerical age! |
|
|
Using various isotopes |

|
|
|
Tectonic settings for volcanoes 🌋 |
Convergent boundaries ✔️ subduction seductions zone ✔️oceanic - continental subduction ✔️oceanic - oceanic subduction
Divergent boundaries ✔️ spreading center volcanism occurring at the size of mid oceanic ridges, where two plates diverge from one another. As the plates are pulled apart hot asthenosphere rises upward to fill void of the extended lithosphere.
Introplate (Hot Spots) ✔️ although most volcanic rock auto generated at plate boundaries, there are few exceptionally active sites of volcanism within the plate interiors. Has nothing to do with subduction zones. (Ex. Yellowstone and Hawaii.) |
|
|
Where do volcanoes occur in California |
✔️Mount Saint Helen - 1980 in Washington
✔️Lassen peak - 1915 in Northern California
✔️Yellowstone - 640,000 years ago in the Wyoming was very devastating! |
|
|
1700 Cascadia Earthquake |
✔️ Occurred along the Cascadia subduction zone.
✔️Magnitude of 9.2!
✔️The mega thrust earthquake involved the Juan de focal plate (Canada ▶️ North Cali) caused a tsunami.
✔️Waves were about 50 feet high
✔️ due for another Mediplast earthquake. |
|
|
What is a volcano |
✔️ in mountain or hill, been through which melted rocks (magma), rock fragments, hot paper, and gas are or have been a wrapped it from the earths crust.
✔️the volcano includes the surrounding corner of a ruptured material. |
|
|
What causes the magma to escape the mantle and come up through the crust of earth |
✔️ subduction zone volcanoes - remember that seduction happens at convergent plate.
✔️ divergent zone volcanoes - this results in the mid-oceanic ridges
✔️ hotspots - please come pop up everywhere were crossed, even in the middle of plates.
- not caused by subduction zones - Yellowstone: 640,000 years ago |
|
|
What are hot spots volcanoes |
✔️ A hotspot is a location on the earths surface that have experienced active volcanism for a long period of time.
✔️ important to know: a hotspot can form into a cone shaped or flat in shape for Pinot at the surface of land. |
|
|
Pyroclastic flow |
✔️ A dence, destructive mass of very hot ash, lava fragments, and gases ejected explosively from a volcano, flowing down slap at great speed.
✔️ most hazardous of all volcanic processes.
✔️ causes of death are: - Asphyxiation by hot ash + dust.
- burning, boiling + dehydration during brief period of high temperature (400 - 1500F)
✔️ gravity- driven clouds that travel at great spirits.
✔️ speed are typically 20Dash70 MPH, but speeds up to 300 mph have been recorded (Mount Saint Helens – 1980) |
|
|
How and why do volcanoes erupt |
✔️Hot, molten rock (magma) is buoyant (has a lower density at the surrounding rocks) and will rise up through the crust to erupt on the surface. - same principle as hot air rising, example how a hot air balloon works
✔️ when magma reaches the surface it depends on how easily it flows (viscosity) and the amount of gas H2O, CO2, sulfur gas) in it.
Viscosity= State of thickness and stickiness. Honey has a higher viscosity then water.
✔️Large amounts of gas and a high viscosity (sticky) magma will form an explosive eruption. - Think about shaking a carbonated drink and then releasing the cap.
✔️ small amounts of gas and for no viscosity(runny) magma or form and effusive eruption. - where lava steadily flows out of a volcano onto the ground. |
|
|
Types of volcanoes |
✔️In active volcano is a volcano that has had a least one eruption during the past 10,000 years. An active volcano might be erupting or dormant.
- An erupting volcano is an active volcano that is having an eruption...
- A dormant volcano is an active volcano that is not erupting, but supposed to irrupt again. Yellowstone!
✔️ in extinct volcano has not had an eruption for at least 10,000 years and it’s not expected to erupt again.
|
|
|
Why do volcanoes stop erupting !? |
✔️All the trapped volatile gases have the gas and there is no longer sufficient pressure to drive the magma out of the earth. Or ✔️ enough heat is lost so that the magma cools and is no longer buoyant. |
|
|
Ring of fire 🔥 |
🔥 The ring of fire has 452 volcanoes and is home to over 75% of the world active and dormant volcanoes
🔥 The ring of fire is a direct result of play tectonics and the movement and collisions of crustal plates |
|
|
Four types of volcanoes |
1.) Composite Volcanoes 2.) shield Volcanoes 3.)cinder cone 4.) hotspots |
|
|
Composite Volcanoes |
🌋AKA: strata Volcano
🌋 cone-shaped volcanoes composed of layers of lava, ash and rock debris
🌋 can’t grow up to 8000 feet high
🌋Example Mount Saint Helens
🌋Very steep
🌋Errupt in explosive matter
🌋 Mount Versuvius: buried Roman city of Pompeii (Italy) up to 20 feet of volcanic ash in 79 A.D.
🌋 explosiveness of the eruption is due to the fact, Holly vicious lava and higher amount of gas.
🌋 The fish is lava has a lot to do with the way composite volcanoes are shaped.
🌋Take lava can I travel far down the slope of the volcano before it cools
🌋 this makes the sides of the volcanoes steep
🌋 this explosive volcano expel large quantities of rock and Ash, which gets Deposited on the sides of the volcano.
Therefore, we see the alternating layers of thehardened lava, volcanic ash and rock fragments. |
|
|
Shield volcanoes |
🌋 are board shaped volcanoes with long, gentle slope sides.
🌋How many large area but never grow very tall. Reasons: flatten out due to the composition of lava that flows from them.
🌋Very fluid lava and less gas
🌋 this more fluid lava spreads out in all directions but cannot pile up in the steep Mounds.
🌋Les explosive then a Composite volcanoes
🌋 Love a chance to pour out of the event, creating low-profile layers of lava.
🌋 The Hawaiian islands were formed by hotspots volcanoes I’m in the middle of the Pacific plate; then once the sound of magma reach above sea level is after many of options. Period...It formed into a shield volcano! |
|
|
Cinder Cone |
🌋 rise up one 1200 feet
🌋Explosive
🌋Short – lived volcanoes
🌋 form quickly in just a few years during one active., Afterwards they are extinct.
🌋paricutin formed in a corn filed. |
|
|
Hotspots |
🌋Within the plate interiors
🌋 has nothing to do with subduction zones |
|
|
Yellowstone |
Hotespot |
|
|
Rock |
It’s composed of 2 or more minerals |
|
|
Minerals |
Has a specific chemical composition (simple def.) example of some common minerals: Quarts SiO2, Calcite CaCO3 |
|
|
What is a minimal |
Mineral characteristics shared by all minerals: 1.) Naturally - occurs naturally - NOT manmade
2 ways minerals can form - crystallization of melted materials (magma or lava cools)
- crystallization of material dissolved in water (evaporation) |
|
|
Crystallization |
✔️Magma (melted rock from earths mantle) cools with a regularly repeating (lattice) structure to form igneous rocks
✔️Intrusive: underground ✔️Extrusive: above ground
✔️ crystallization: is the (natural or artificial) process where the solid forms where the Atoms or molecules are highly organized in a structure known as a crystal. |
|
|
What is the mineral |
2.) inorganic - is not alive - was never alive
-table salt (halite) is inorganic
Sugar is organic and comes from a sugar cane or sugar beets
Organic- comes from living matter
|
|
|
What is a mineral |
3.) Crystalline - atoms Are arranged in an orderly pattern |
|
|
What is a mineral |
4.) Definite chemical composition - Chemical formula - SiO2 is quarts |
|
|
What is a Manneral |
5.) Solid - Not a gas, not a liquid |
|
|
What is a mineral |
1.) natural 2.) inorganic 3.) Crystalline 4.) Definite chemical composition 5.) solid |
|
|
Matter |
Anything that takes up solid space |

