![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
General functions of respiratory system |
Provide large respiratory surface for gas exchange between air and blood Smell incoming air Produce sound |
|
|
Nervous system |
Uses electricity, hard wired, info moves quickly but short lived |
|
|
Name 2 control and communication systems |
Nervous system and Endocrine system |
|
|
Central nervous system consists of? Peripheral nervous system consists of? |
Brain and spinal cord Everything else |
|
|
Endocrine system |
Uses hormones, from integrator to effector via blood |
|
|
Visceral sensory |
Receives sensory info from viscera(guts) |
|
|
Somatic sensory |
Afferent-receives sensory info from skin, fascia, Joints etc |
|
|
Sensory nervous system (afferent) |
transmits info from receptors to the CNS |
|
|
Motor nervous system (efferent) |
Transmits info from CNS to rest of body |
|
|
Autonomic motor |
"Involuntary" nervous system-innervates cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, glands |
|
|
Reflex Arc |
Arrival of stimulus Activation of sensory neuron Info processing in CNS Activation of motor neuron Response by effector |
|
|
Signal flow |
Afferent➡Through PNS to CNS ➡efferent somatic or efferent autonomic➡skeletal muscle➡sympathetic or para sympathetic |
|
|
What does the Autonomic nervous system consists of? |
Sympathetic and parasympathetic |
|
|
Sympathetic |
Doesn't go to brain Fight or flight response Thoraco-lumbar spinal nerves, no cranial |
|
|
Parasympathetic |
Goes to the brain Rest, digestion, lumbosacral spinal nerves, cranial 3,7, 9, 10 |
|
|
Somatic motor |
"Voluntary"-innervates skeletal muscle |
|
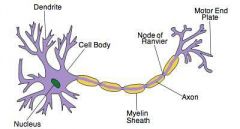
Parts of a neuron and there function |
Cell body w/ organelles Dendrites- collect info Axon- transmits info to the next cell Synapse- point of communication (usually chemical) between neuron and another cell |
|
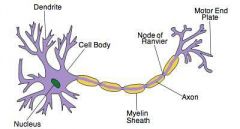
Anatomy of neuron |
Dendrites- signal towards nucleus Axon- signal away from nucleus Schwann cell- wraps around axon, made from lipids and protein called myelin
Schwann cells found in PNS |
|

Nodes of Ranvier |
Divets between schwann cells where the signal jumps |
|
|
What is it called when the signal jumps between schwann cells? |
Saltatory conduction |
|
|
Autoimmune disease -multiple sclerosis |
Demyelinating disease that attacks the myelin around axon or immune cells attack white matter Genetic history or toxin exposure |
|
|
Glial cells(neuroglia) |
assistants to the neuron, clean up brain waste, provide nutrients, protection, energy |
|
|
Oligodendrocytes |
produce the myelin sheath insulating CNS axons. Function is maintenance and protection of the neurons. |
|
|
Motor neuron consists of? |

|
|
|
What are the 5 steps to respiration? |
1. Ventilation- air in 2. External respiration- oxygen into blood 3. Transport- move around 4. Internal respiration- deliver to cells 5. Cell respiration- use oxygen to make ATP. Usually between 34-38 |
|
|
External respiration |
Exchange of gases between air and blood at the aveoli |
|
|
What does the lymphatic system do? |
Drains ECF into circulatory system and immunity |
|
|
Nasopharynx |
To warm and humidify the air To smell |
|
|
Pharynx |
Back of throat, for swallowing |
|
|
Name the 2 parts of the larynx |
Epiglottis, vocal chords |
|
|
Epiglottis |
A flap of elastic cartilage, closes trachea so food & liquid doesn't go into lungs |
|
|
Trachea |
Cartilaginous rings, prevents collapse Made of hyaline cartilage |
|
|
Primary bronchi Secondary bronchi |
One on left and one on the right. 2 on the left and 3 on the right. |
|
|
Why is the bronchi Asymmetrical? |
Because the left lung has 2 lobes and right lung has 3. |
|
|
Why does the left lung only have 2 lobes? |
The left lung has the cardiac notch which makes room for the heart |
|
|
What binds to oxygen and carbon dioxide to transport it? |
Hemoglobin |
|
|
5 Functions of blood |
Transports gas Regulation of pH Defense against clotting & immunity Filtered to make body fluids Provides turgidity to erectile tissues |
|
|
What is the composition of blood? |
Plasma Red and white Cells, platelets |
|
|
What is Plasma composed of? |
92% water Plasma proteins-antibodies, lipoprotein, albumin, fibrinogen Dissolved solutes- electrolytes, nutrients, gases, hormones, wastes |
|
|
What is Erythrocyte(red blood cells) composed of? And there function? |
Bioconcave disc- increases surface area Enucleate- has no nucleus- 120 day lifespan Carry oxygen to body and carbon dioxide to the lungs |
|
|
What is Hematocrit |
Percentage of blood that is cells |
|
|
What is Anemia |
Low oxygen carrying capacity. Either low hematocrit or low hemoglobin |
|
|
Blood types |
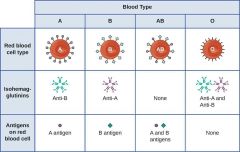
|
|
|
Antigens |
Surface proteins on red blood cells |
|
|
What are antibodies and there function |
A protein made by immune system. Antibodies bind to foreign substances and destroy them |
|
|
What is Systole |
Contraction |
|
|
What is diastole |
Relaxation |
|
|
What is the functions of cardiovascular system? |
Moves blood Transport oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, hormones Regulate pH, temp Protection against clotting and immunity |
|
|
What is the heart |
Double muscular pump |
|
|
What is pulmonary circuit |
Right part of the heart collects deoxygenated blood & goes into the lungs |
|
|
What is Systemic circuit |
Left side of heart goes to body |
|
|
Why is the myocardium muscle larger in the left ventricle than the right? |
to pump blood into the systemic circulation |
|
|
Lymphatic vessels |
Drain into veins |
|
|
ECF or Lymph |
Lymphatic fluid; flows through vessels and nodes |
|
|
Lymphocytes |
Immune cells |
|
|
Lymphatic function |
Return fluid from tissues to blood Production, maintenance, distribution of lymphocytes |
|
|
Alveoli cell types |
Simple squamous- diffusion Septal cells- surfactant to reduce surface tension Alveolar macrophages- ingest particulara |

