![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Frontal Bone |
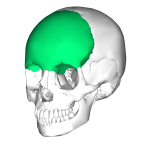
3 parts: squamous, orbital and nasal |
|
|
Parietal bones |
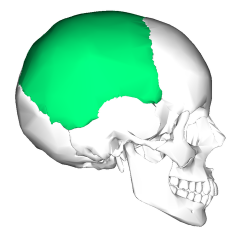
2 bones separated by sagittal suture |
|
|
Occipital bone |
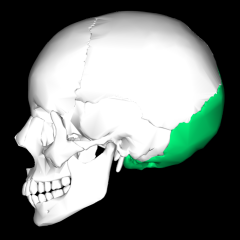
Foramen magnum: medulla oblongata passes through it Occipital condyles: function in articulation with superior facets of atlas vertebrae External occipital protuberance Nuchal lines |
|
|
Temporal bones |
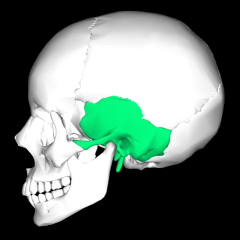
External acoustic meatus Mandibular fossa Styloid process Mastoid process Zygomatic process |
|
|
Coronal suture |
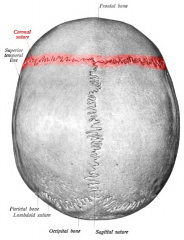
|
|
|
Sagittal suture |
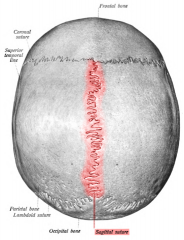
|
|
|
Lambdoid suture |
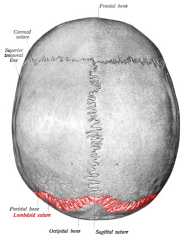
|
|
|
Squamosal suture |
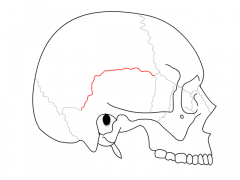
|
|
|
Ethmoid bone |
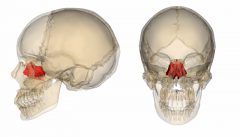
Crista galli Cribiform plate Perpendicular plate Superior nasal conchae Middle nasal conchae |
|
|
Sphenoid bone |
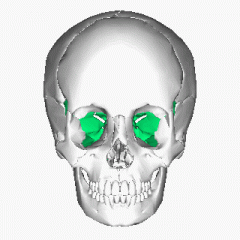
Sella turcica: saddle-shaped depression in body of sphenoid bone |
|
|
Zygomatic bones |
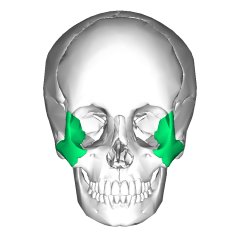
Temporal process: |
|
|
Nasal bones |
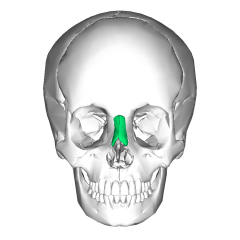
|
|
|
Lacrimal bones |
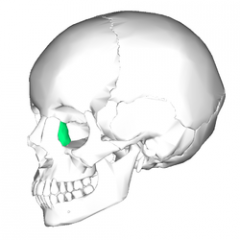
|
|
|
Vomer bone |
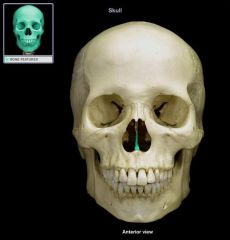
|
|
|
Maxillae |
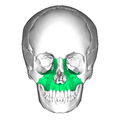
|
|
|
Inferior nasal conchae |
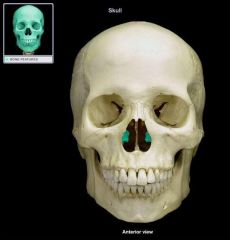
|
|
|
Palatine bones |
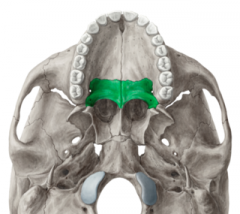
|
|
|
Mandible |
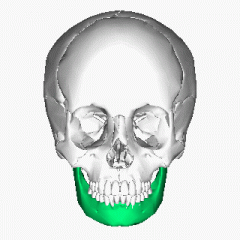
Ramus Coronoid process Angle Mandibular condyle Mental foramen |
|
|
Which bones make up the nasal cavity? |
|
|
|
Which bones contain paranasal sinuses? |
|
|
|
What is the function of the conchae? |
|
|
|
What is the function of the paranasal sinuses? |
|
|
|
Describe key structural differences between the skulls of infants, children and adults |
Anterior (bregmoid) fontanel
Posterior (lambdoid) fontanel Anterolateral (sphenoid) fontanel Posterolateral (mastoid) fontanel |
|
|
Lacrimal foramen |
|
|
|
Optic foramen |
|
|
|
Olfactory foramina |
|
|
|
Cervical vertebrae |
|
|
|
Thoracic vertebrae |
|
|
|
Lumbar vertebrae |
|
|
|
Sacral vertebrae |
|
|
|
Coccygeal vertebrae |
|
|
|
Structures of general vertebrae |
Body Vertebral arch Pedicles Laminae Spinous Process Articular processes (superior and inferior) Articular facets (superior and inferior) Transverse process Vertebral foramen Intervertebral foramen Intervertebral disc |
|
|
Structures of cervical vertebrae |
Transverse foramen Atlas Axis Odontoid process (dens) |
|
|
Curvatures of spinal column |
*Describe + Function Primary (cervical and lumbar) Secondary (thoracic and sacral) Kyphosis Lordosis Scoliosis |
|
|
Hyoid bone |
|
|
|
Sternum |
Manubrium Body Xiphoid process |
|
|
Vertebrosternal ribs
|
|
|
|
Thoracic cage |
*Function of thoracic cage Sternum (manubrium, body, xiphoid process) Costal cartilage Vertebrosternal ribs Vertebrochondral ribs Vertebral ribs |
|
|
Vertebrochondral ribs |
|
|
|
Vertebral ribs |
|
|
|
Clavicle |
Acromial end Sternal end |
|
|
Scapula |
Superior angle Lateral angle Inferior angle Superior border Lateral border Medial border Subscapular fossa Coracoid process Acromion Spine Supraspinous fossa Infraspinous fossa Glenoid cavity |
|
|
Humerus |
*Function of humerus Head GreaterTubercle LesserTubercle Bicipitalgroove Surgicalneck Anatomicalneck Deltoidtuberosity Lateralepicondyle Medialepicondyle Capitulum Trochlea Olecranonfossa Coronoid fossa Radialfossa |
|
|
Ulna |
Coranoid process of ulna Olecranon process Trochlear notch Radial notch Styloid process of ulna |
|
|
Radius |
Head Neck Radial tuberosity Ulnar notch Styloid process of radius Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges |
|
|
Carpals |
Scaphoid Lunate Triquetrium Pisiform Trapezium Trapezoid Capitate Hamate |
|
|
Pelvic girdle |
Illium Ischium Pubis Acetabulum Obturator foramen |
|
|
Illium |
Anterior Superior Iliac Spine Iliac crest Auricular surface Greater sciatic notch |
|
|
Ischium |
Ischial spine Lesser sciatic notch Ischial tuberosity Ischial ramus |
|
|
Pubis |
Pubic ramus (superior and inferior) Pubic symphysis Pubic angle |
|
|
Femur |
Head Fovea capitis Neck Greater trochanter Lesser trochanter Linea aspera Lateral condyle Medial condyle Intercondylar fossa Lateral epicondyle Medial epicondyle |
|
|
Patella |
|
|
|
Tibia |
Medial condyle Lateral condyle Tibial tuberosity Anterior crest Medial malleolus |
|
|
Fibula |
Head Lateral malleolus |
|
|
Tarsals |
Calcaneous Talus Navicular Cuboid Lateral cuneiform Intermediate cuneiform Medial cuneiform |
|
|
Types of Joints |
Synostosis Fibrous Cartilagenous Synovial |
|
|
Synostosis |
*Definition and Examples |
|
|
Fibrous |
*Definition and Examples Sutures Gomphoses Syndemoses |
|
|
Cartilagenous |
*Definition and Examples Synchondroses Symphyses |
|
|
Synovial |
*Definition and Examples Articular capsule Synovial cavity Synovial fluid Articular cartilages Menisci Fat pads Bursae Tendon sheath |
|
|
Intervertebral discs |
Anulus fibrosus Nucleus pulposus Protruding disc Herniated disc |
|
|
Shoulder joint |
Glenoid labrum Coraco-acromial ligament Acromioclavicular ligament Coracoclavicular ligament |
|
|
Elbow joint |
Annular ligament Radial collateral ligament Ulnar collateral ligament |
|
|
Hip joint |
Acetabular labrum Ligamentum teres Pubofemoral ligament Ischiofemoral ligament Iliofemoral ligament |
|
|
Knee joint |
Patellar ligament Quadriceps tendon Fibular collateral ligament Tibial collateral ligament Medial meniscus Lateral meniscus Anterior cruciate ligament Posterior cruciate ligament |
|
|
6 functions of skeletal muscle |
|
|
|
Skeletal muscle |
Striation Fiber organization Location of nucleus |
|
|
Cardiac muscle |
Striation Fiber organization Location of nucleus Intercalated disc |
|
|
Smooth muscle |
Striation Fiber organization Location of nucleus |
|
|
Epidermis |
Keratinocyte Melanocyte Stratum basale/germinativum Stratum spinosum Stratum granulosum Stratum lucidum Stratum corneum |
|
|
Dermis |
Papillary layer Dermal papilla Meissner's corpuscle Reticular layer Pacinian corpuscle Cleavage lines of skin |
|
|
Sebaceous gland |
secretes sebum |
|
|
Sudoriferous gland |
Merocrine gland Apocrine gland |
|
|
Hypodermis |
Subcutaneous Hair follicle Arrector pili muscle |
|
|
Fingernail |
Nail body Free edge Nail bed Cuticle (eponychium) |
|
|
Melanin |
Effects of pigmentation UV radiation Malignant melanoma ABCDE rule |

