![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
CONTROLLED SUBSTANCES ACT
|
Passed in 1970, federally regulated drugs. Divides drugs into schedules. Included "designer drugs" when the Anti-Drug Abuse Act got passed in 1986.
|
|
|
SCHEDULE 1 DRUGS
|
High potential for abuse/ no medical use.
Examples: heroin, LSD, pot, and methaqualone |
|
|
SCHEDULE 2 DRUGS
|
High potential for abuse/currently accepted medical use with severe restrictions.
Examples: cocaine, methadone, PCP, and amphetamines. |
|
|
SCHEDULE 3 DRUGS
|
Less potential for abuse/currently accepted medical use in the United States/ a potential for low or moderate physical/psychological dependence
Examples: anabolic steroids, codeine |
|
|
SCHEDULE 4 DRUGS
|
Low potential for abuse/currently medical use in the United States/ potential for limited dependence.
Examples: valium, librium, and darvon |
|
|
SCHEDULE 5 DRUGS
|
Low potential for abuse/currently accepted medical use/ lower potential for limited dependence.
Example: certain opiate drug mixtures |
|
|
THE FIVE P's
|
powders, plant matter, pills, precursors, paraphernalia
|
|
|
QUALITATIVE DETERMINATION
|
The identity of the material
|
|
|
QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION
|
percent composition of components of a mixture.
|
|
|
SCREENING TESTS
|
Presumptive test that is nonspecific and preliminary in nature.
|
|
|
MARQUIS TEST
|
Reagent turns purple in the presence of heroin and morphine. Turns orange-brown when amphetamines are present.
|
|
|
DILLIE-KOPPANYI TEST
|
Screens for barbiturates, turns violet blue.
|
|
|
DUQUENOIS-LEVINE
|
Tests for the presence of marijuana, turns purple.
|
|
|
VAN URK
|
Tests for the presence of LSD, turns blue-purple when present.
|
|
|
SCOTT TEST
|
Tests for cocaine
|
|
|
CHROMATOGRAPHY
|
a way to separate and identify components of a mixture.
|
|
|
SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
|
the study of the absorption of light by chemical substances. Used in both quantification and identification of organic substances.
|
|
|
MOBILE PHASE
|
a liquid or gas
|
|
|
STATIONARY PHASE
|
solid or liquid
|
|
|
GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
|
Mobile Phase: carrier gas
Stationary Phase: thin film of contained liquid Written record is called a chromatogram |
|
|
WHY USE HPLC INSTEAD OF GC?
|
HPLC takes place at room temperature, and GC does not.
|
|
|
MICROCRYSTALLINE TEST
|
A drop of a chemical reagent is added to a small quantity of the drug on the microscope slide.
|
|
|
HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY (HPLC)
|
separates compounds using stationary phase with solid particles and a liquid mobile phase. Different components are retarded to different degrees depending on their interaction with the stationary phase.
|
|
|
THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY (TLC)
|
uses solid stationary phase on a glass plate to separate the components of the mixture. Can be visualized with UV light.
|
|
|
THE TYLENOL MURDERS
|
Who: 7 people
What: potassium cyanide laced tylenol capsules Where: Chicago When: September and October 1982 |
|
|
ELEMENTS vs. COMPOUNDS
|
An element is a substance that is made up of the same type of atoms. A compound is made of different elements in definite proportions.
|
|
|
ORGANIC vs. INORGANIC COMPOUNDS
|
Organic compounds contain carbon in addition to other elements. Inorganic compounds are all the other known chemical substances.
|
|
|
GAS CHROMATOGRAPH (image)
|
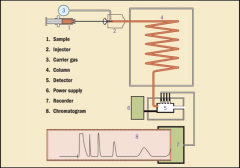
shows the separation of mixture being analyzed.
|
|
|
GAS CHROMATOGRAM
|
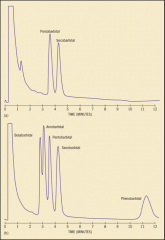
shows the compounds present in a mixture.
|
|
|
RETENTION TIME
|
the time required for a component to emerge from a GC column.
|
|
|
Rf VALUE
|
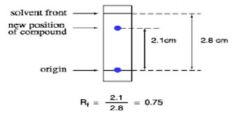
the ratio of the distance traveled by the center of a spot to the distance traveled by the solvent.
|
|
|
ELECTROPHORESIS
|
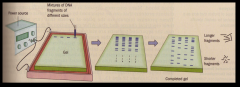
materials are forced to move across a gel-coated plate under the influence of an electrical potential. Proteins and DNA can be separated.
|
|
|
THEORY OF LIGHT
|
color is a visual indication that objects absorb certain portions of visible light and transmit or reflect others.
|
|
|
FREQUENCY AND WAVELENGTH
|
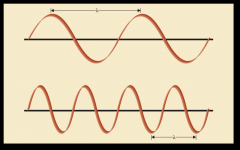
wavelength is the distance between two successive crests, frequency is the number of crests that pass any one given point per unit of time. Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional to one another.
|
|
|
PHOTON
|
a small packet of electromagnetic radiation energy.
Equation: E=hf |
|
|
BEER'S LAW
|
the quantity of light absorbed at any frequency is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species.
|
|
|
SPECTROPHOTOMETER
|
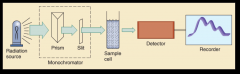
used to measure and record the absorption spectrum of a chemical substance.
|
|
|
UV SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
|
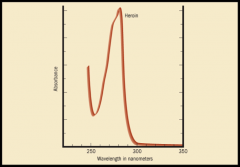
the pattern of UV spectrophotometry is less complex that Infrared spectrophotometry.
|
|
|
INFRARED SPECTROPHOTOMETRY
|
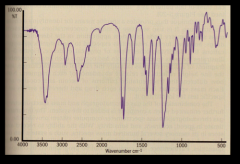
the pattern for IR spectrophotometry is more complex and shows the "fingerprint" of the substance.
|
|
|
MASS SPECTROMETRY
|
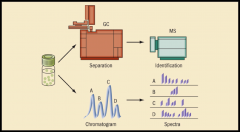
a high-energy electron beam collides with a material to make positively charged ions. No two substances make the same fragmentation pattern.
|

