![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
5 Basic Characteristics of living Organisms
|
1. Energy utilization
2. Cells 3. Information 4. Growth and Reproduction 5. Evolutionary adaptation |
|
|
Pop. Sizes stay relatively constant over the b/c
|
Resources are limiting
|
|
|
Req. For Evo. by Natural selection
|
1. Heritable trait variation within a pop.
2. survival and reproduction of indv. w/ specific heritable traits |
|
|
Classifying life Forms
|
1. Does it move? - Linnaeus, Animals + Plants
2. Nucleus?-Eukaryotes, prokaryotes. Mod. Linnaeus scheme-animals, fungi, plants, protists, monera 3. Sim. of molecular seq.? Carl Woese's phylogenetic tree 3 domains: Bacteria, Archaean, Eukarya |
|
|
Taxa (divisions)
|
kingdom (animalia)
Phylum (chordata) Class (mammalia) Order (primates) Family (Hominidae) Genus (homo) species (sapiens) |
|
|
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
|
Prokaryotes : do not have membrane- bound nucleus
Eukaryotes: have membrane-bound nucleus |
|
|
What is an atom?
|
•dense nucleus formed of protons and neutrons
•Orbiting cloud of electrons • # of protons = chemical Character b/c is # of elections available for chemical activity • chemistry mediated by electrons |
|
|
Atomic #
|
# of protons (seen on periodic table)
|
|
|
Atomic Mass
|
Sum of the masses of its protons and neutrons
|
|
|
Structure of Atoms
|
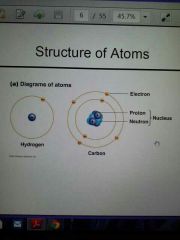
|
|
|
Isotopes
|
Atoms of an element (same # protons) that possess a dif. # neutrons
|
|
|
Molecule
|
group of atoms held together by energy (chemical bonds) in a stable association
|
|
|
Types of Bonds
|
-ionic bonds
-covalent bonds -hydrogen bonds (van der Waals forces) |
|
|
The formation of molecules depends on the tendency of elections to...
|
1) Occur in pairs
2) Balance + and - charges 3) Fill the outermost energy shell (satisfy "octet" rule) |
|
|
Covalent Bonds
|
• 2 atoms share 1 or more pairs of electrons
• covalently bonded atoms form a molecule, b/c covalent bonds are strong |
|
|
Theory
|
an expectation of what would happen
|
|
|
Hypothesis
|
Tentative explanation that maybe tested or answered by further investigation or experiment
|
|
|
Prediction
|
making an educated guess as to the outcome of a situation
|
|
|
Cell Theory
|
all living things are made of and came from cells
|
|
|
Microscope
|
lab equipment used to magnify small things that are too small to be seen by the naked eye
|
|
|
Cell
|
the stwchval, functional, ad biological unit of all organisms
|
|
|
Spontaneous generation
|
previously popular idea that living organisms develop from nonliving matter
|
|
|
Descent w/ modification |
passing of traits from parent organisms to offspring
|
|
|
Heritable Trait
|
traits that are caused by genes
|
|
|
Speciation
|
The process in which new genetically distinct species evolve, often by genetic isolation
|
|
|
rRNA
|
Sits in the ribosome, decoding mRNA into dif. amino acids and helping in translation
|
|
|
Tree of life
|
metaphor expressing the idea that all life is related by common descent
|
|
|
Chemical Evolution
|
Formation of complex organic molecules from simpler inorganic molecules through chemical reactions in early oceas
|
|
|
Carbon
|
Valence 4 ( 4 unpaired electrons) can make 4 bonds, 3 isotopes, 6 protons
|
|
|
Non-polar covalent
|
electrons spend copal time W/ both nuclei in bond
|
|
|
Polar Covalent
|
1 nuclei is more electronegative, elections spend more wme near that nucleus, giving it partial negative charge
|
|
|
Nitrogen
|
atomic #:7
|
|
|
Hydrogen
|
Atomic #: 1
|
|
|
Dalton
|
Unit of mass =~weight of hydrogen atom 1.657 x 10^-24g
|
|
|
Electron shell
|
outside par of an atom around the atomic nucleus
|
|
|
Valence electron
|
an election which is associated with on atom
|
|
|
Electro negativity
|
the tendency to attract electrons
O>> N>C ~=H |
|
|
what determines the strength of covalent bonds?
|

Depends on # shared electron pairs
|
|
|
Atoms and ions
|
• Neutral atoms- sane # protons and electrons
• ions-atoms where protons and elections aren't equal • cation- net positive charge • anion-net neg. charge |
|
|
Ionic bonds
|
• weak
• dissociate in water • form when atoms of opp. electrical charges attract each other |
|
|
Mole
|

|
|
|
Cohesion vs. Adhesion
|
Cohesion :like molecules sticking to each other due to mutual attraction
Adhesion: diff molecules or surfaces clinging to each other |
|

|
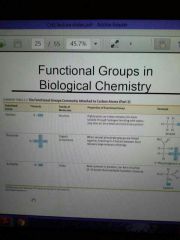
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bonds
|
• polar molecules interact w/ each other b/c of charge separation
• pariah negative side of one molecule is attracted to the partial positive side of another molecule |
|
|
Solvent + Solute
|

|
|
|
Properties of H20
|

|
|
|
pH
|
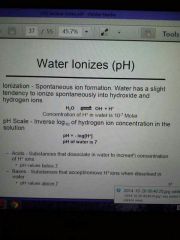
A change of 1 pH unit translates into 10 -fold difference, 2 → 100-fold, 3 →1000-fold
|
|
|
Buffer
|
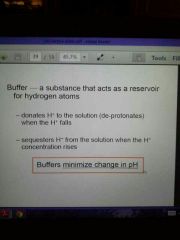
|
|
|
Chemical Reactions
|

|
|
|
Energy in Chemical Reactions
|

|
|
|
Energy Types
|

|
|
|
1st Law Thermodynamics
|
|
|
|
Entropy
|
thermodynamic quantity representing the unavailability of a system's thermal energy for conversion into mechanical work
|
|
|
Spontaneous and Non spontaneous Chem. reactions
|
Processes that proceed in a definite direction on their own are spontaneous , those that require energy are the latter
|
|
|
2nd law thermodynamics
|

|
|
|
Gibbs free energy
|
|
|
|
Free radicals
|
atom, molecule, or ion that has unpaired valence elections or on open electron shell
|
|
|
Organic vs. Inorganic molecules
|
• organic always contain carbon or almost all have C-H bonds
|
|
|
Disulfide Bond
|
a single covalent bond between 2 amino acids called cysteine
|
|
|
Chem. Evolution Hypothesis for Origin of life
|

|
|
|
Protein Functions
|

|

