![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pyrimidine |
Cytosine or thymine |
|
|
Purine |
Adenine or guanine |
|
|
4 DNA bases |
Adenine + thymine // Cytosine + guanine |
|
|
The genetic code is... |
Degenerate, since multiple codons code for the same amino acid |
|
|
Transcription |
DNA to mRNA |
|
|
Translation |
mRNA to protein |
|
|
Mendel's Law of Segregation |
Allele pairs separate or segregate during gamete formation, and randomly unite at fertilization. |
|
|
Mendels' Law of Independent Assortment |
When two or more characteristics are inherited, individual factors assor independently during gamete production, given different traits an equal opportunity of occurring together (unless linked) |
|
|
Blending inheritance |
The theory that inheritance of traits from two parents produces offspring with characteristics that are intermediate between those of the parents |
|
|
Particulate inheritance |
The pattern of inheritance discovered in part from Mendel; shows that phenotypic traits can be passed down through "discrete particles" we now know to be genes |
|
|
Epigenetic changes |
Changes in the mother can be passed down through DNA methylation; Very Lamarckian! |
|
|
DNA Transition |
When a purine is replaced with a purine or a pyrimidine is replaced with a pyrimidine |
|
|
DNA Transversion |
When a purine is replaced with a pyrimidine, or vice versa |
|
|
Convergent evolution |
Was not able to be well detected until we developed genetics |
|
|
Synonymous mutations |
A point mutation that results in the codon encoding the same amino acid |
|
|
Nonsynonymous Mutation |
Also known as a missense mutation; causes a new codon to encode for a new amino acid. This is usually deleterious |
|
|
Nonsense Mutation |
The new codon is a stop codon; deleterious |
|
|
In frame mutation |
Three nucleotides are added or deleted |
|
|
Frameshift mutation |
The deletion of insertion of (1,2,4,5,7, etc) nucleotides affects all downstream codons. More harmful than an in-frame mutation. |
|
|
Polyploidy |
A cell or nucleus containing more than two homologous sets of chromosomes; replication of the entire genome |
|
|
Allopolyploidy |
Polyploidy through meiotic error and hybridization |
|
|
In non-eukaryotes, as the genome size increases, the mutation rate... |
Decreases |
|
|
In eukaryotes, as the genome size increases, the mutation rate... |
Increases |
|
|
Discrete traits are... |
Binomal (clockwise aloe spiral or counterclockwise) |
|
|
Continuous traits are... |
On a spectrum (skin color) |
|
|
5 assumptions of Hardy-Weinberg |
-No Chance Events AKA No Genetic Drift -No Mutation -Random Mating AKA Panmixia -No Selection -No Migration |
|
|
Fixation |
When all but one allele is eliminated from a population |
|
|
Overdominance |
When a heterozygote has a higher fitness than either homozygote |
|
|
Underdominance |
When the heterozygote has a lower fitness than either homozygote. The resulting fitness trajectory leads to fixation of one allele or the other |
|
|
P = |
Equilibrium frequency |
|
|
Positive frequency-dependent selection |
The more frequently a phenotype is found in a population, the higher its fitness |
|
|
Negative frequency-dependent selection |
The rarer a phenotype, the higher its fitness |
|
|
Adenomatous polyposis |
Polyps form in the colon; is not eliminated from the population because it is not deadly until you've passed the age of producting offspring |
|
|
Assortative Mating |
Like mates with like |
|
|
Disassortative Mating |
Individuals mate with phenotypes different from their own |
|
|
Identical by descent |
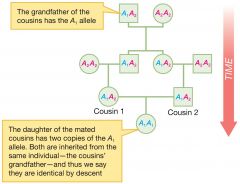
Two copies of a gene that were been inherited from a recent common ancestor |
|
|
Reproduction by selfing |
The extreme version of inbreeding; eventually the population will be dominated by homozygotes |
|
|
Wright's F |
The frequency of the inbred pool; allows you to make predictions of how a population would be affected by inbreeding |
|
|
Extinction Vortex |
A situation where a population gets so small that, without some type of influx of genetic variability, the population will continue to spiral into extinction |

