![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The ship on which Darwin sailed |
The Beagle |
|
|
Published "The Origin of Species" |
Charles Darwin |
|
|
Phylogenetic trees |
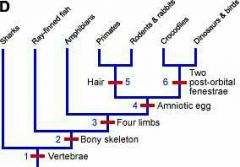
Show the relation between different species |
|
|
The process by which new species are formed. |
Speciation |
|
|
Fossil |
Preserved remains of an organism |
|
|
Also known as "Survival of the Fittest" |
Natural Selection |
|
|
Population |
The individuals of a species which live in the same place. |
|
|
Evolution |
The theory that species change over long periods of time. Proposed by Charles Darwin. |
|
|
Vestigial structures |
Organs that once served a purpose, but no longer do. Eg. The appendix |
|
|
Homologous structures |
Structures that develop from the same embryonic tissue but have different uses. |
|
|
Genetic equilibrium |
When the gene pool does not change or evolve. |
|
|
Diversifying equilibrium |
When the individuals at the extremes of the curve have a higher fitness than those in the middle. |
|
|
Adaptations |
The inherited traits that improve the chances of survival and reproduction. |
|
|
Selective breeding |
The breeding of certain plants or animals with prefered traits. |
|
|
The islands Darwin visited when he devopled the theory of Evolution |
Galapagos islands |
|
|
Fitness |
An orgamisms ability to survive and reproduce in their environment. |
|
|
Convergent evolution |
Two species in different areas adapting to become more similar to eachother. |
|
|
Divergent Evolution |
A species adapting to an environment and creating two different species. |

