![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the fitness of a strong, healthy long living individual who does not reproduce? |
zero |
|
|
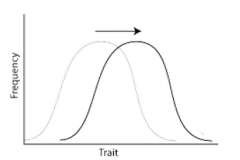
directional selection |
|
|
directional selection |
select traits for one extreme ex: tall trees in canopy |
|
|
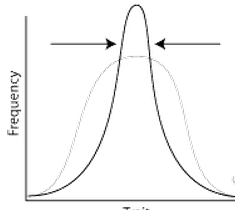
stabilizing selection |
|
|
stabilizing selection |
1. selects for a trait that is moderate 2. selects against the extremes ex: birth weight |
|
|
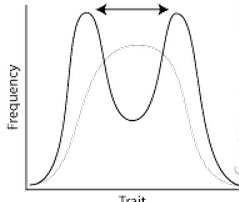
disruptive selection |
|
|
disruptive selection |
selects for extremes ex: birds in two distinct niches |
|
|
group selection |
1. natural selection acting on the group, not the individual 2. explains altruism |
|
|
altruism |
1. sacrifice fitness of individual 2. benefit to group that shares similar genes |
|
|
conditions for a species |
1. interbreed 2. produce fertile, viable offspring 3. does this naturally |
|
|
polymorphism |
different forms of alleles/traits |
|
|
adaption |
1. genetic change in a population caused by natural selection 2. Darwin's natural selection ex: Giraffe's neck |
|
|
specializiation |
adaptation of traits to better fill a niche |
|
|
competition |
1. occurs when niches overlap 2. controls population growth 3. increases with resource scarcity 4. drives speciation |
|
|
inbreeding |
1. mating between relatives 2. increases the frequency of homozygotes 3. decreases heterzygotes 4. decreases genetic diversity |
|
|
bottleneck |
1. severe reduction in population size 2. increase effects of genetic drift 3. ex: natural disaster |
|
|
genetic drift |
1. random changes in allele frequencies 2. increases as population size decreases |
|
|
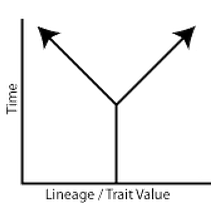
divergent evolution |
1. same lineage (common ancestor) 2. evolving apart to be more different 3. ex: bats and horses (mammals) 4. produces homologous structures |
|
|
divergent evolution |
|
|
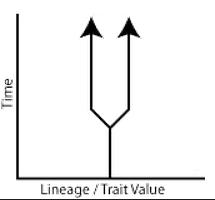
parallel evolution |
1. same lineage (common ancestor) 2. evolving closer together to be similar 3. using similar mechanisms 4. ex: feeding structure in crustaceans |
|
|
parallel evolution |
|
|
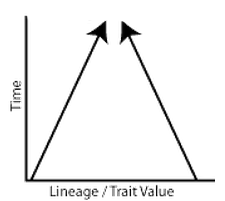
convergent evolution |
1. different lineage (no common ancestor) 2. evolving closer together to be similar 3. using different mechanisms 4. ex: bats and butterfly wings 5. analogous structures |
|
|
convergent evolution |
|
|
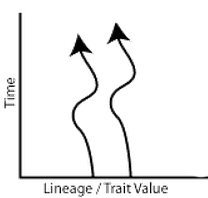
coevolution |
1. Two species evolve in response to each other 2. ex: predator/prey OR host/parasite 3. not to be confused with parallel evolution 4. no common ancestor |
|
|
coevolution |
|
|
parasitism |
Relationship where one benefits (parasite), and the other is harmed (host) ex: worm in an animal |
|
|
Commensalism |
* Relationship where one benefits, and other is not affected
* ex: plant seeds stick to animal fur |
|
|
Mutualism |
* Relationship where both species benefit
* ex: fungi and algae |
|
|
ontogeny |
development through the life of an organism |
|
|
phylogeny |
development through evolutionary time of lineages/species |
|
|
similar features shared by vertebrates during early development |
1. gill slits 2. notochord 3. segementation 4. paddle-like limbs |
|
|
random genetic mutations |
1. drift 2. not acted on by natural selection 3. occur at constant rate |
|
|
Urey-Miller experiment |
* origin of life
* atmospheric gases: H2O, CH4, NH3, H2, * lightning * heat from ocean * can create amino acids |
|
|
RNA world hypothesis |
* organic molecules formed from RNA polymers
* self replicate * enzymatic activity * template |
|
|
protocells |
1. aggregates of RNA 2. proteins inside lipid envelopes |
|
|
prokaryotic evolution |
anaerobic heterotrops --> anaerobic autotrophs, aerobics |
|
|
eukaryotic evolution |
endosymbiosis: hetertrophs engulfed mitochondria autotrophs engulfed chloroplasts |
|
|
cordate |
1. notochord --> bones (vertebrates) 2. embryonic gill slits --> head and neck 3. dorsal nerve cord --> NS --> CNS |
|
|
vertebrate phylogeny |
1. fish 2. jawaless fish (agnatha) 3. cartilagenous fish and bony fish 4. amphibians and reptiles 5. mammals and birds |

