![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
71 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What occurs with DM on a histological level of the spinal cord? |
demylenation axonal degeneration (loss of neurons) astrocytosis of the white matter (what transmits the movement/sensory info from limbs to brain) |
|
|
Etiology of Degenerative Myelopathy |
unknown possible inheritance |
|
|
Gender prediliction for DM? |
males MC |
|
|
How long are dogs with DM until they are nonambulatory |
several months to 1 year after diagnosis of DM |
|
|
What neurological functions are still intact with DM |
cutaneous and deep pain perception |
|
|
TX for DM? |
No effective TX has been reported vitamin supplementation epsilon-aminocaproic acid N acetylcysteine exercise |
|
|
What dose DISH stand for |
diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis |
|
|
signalment for DISH lesions |
young dogs - large and giant breeds |
|
|
What criteria must be met to be diagnosed with DISH lesions |
Must meet 4 of the 5: 1 ventral ossification along 3 continual vetebral bodies 2 preservation of disk space 3 periarticular osteophytes surrounding vetebral joints 4 formation of pseudoarthrosis between spinous processes 5 enthesophytes |
|
|
C/S of DISH |
minimal |
|
|
Etiology of discospondylititis |
bacteria or fungi from migrating plant awns hematongenous spread extension of paravetebral infection penetrating wound previous disk SX
|
|
|
Where vetebral bodies do plant awns affect with discospondylitis |
L2-L4 |
|
|
What is the most common cause of discospondylitis |
hematogenous spread |
|
|
Causes of discospondylitis |
Brucella canis Staphlococcus |
|
|
Signalment for discospondylitis |
large and giant breed dogs |
|
|
MC location for discospondylitis |
Occur anywhere T3-L3 MC L2-L4 - grass awn |
|
|
Radiographic findings of discospondyltitis |
destruction of the bony endplates collapse of IVD space +/- new bone formation |
|
|
What diagnostics should be performed for discospondylitis? |
aerobic/aneaerobic and fungal cultures B. canis evaluation |
|
|
TX of discospondylitis |
long term ab: cephalosporins or B lactamase resistant penicillins TX for 6 weeks - 6 months monitor rads q 2-3 weeks Should respond w/in 2 weeks |
|
|
What are dural ossification |
formation of bony plaques on the inner surface of the dura matter |
|
|
C/S with dural ossification |
rarely causes spinal pain |
|
|
This is a chronic, slowly progressive (several months) encephalomyelitis of unknown etiology in immature and mature cats
Aka |
feline polioencephalomyelitis
Borna virus |
|
|
This is an inhertied lysosomal storage disease that results from a deficiency of galactocerbrosidase activity |
globoid cell leukodystrophy (Krabbe-type Leukodystrophy) |
|
|
What breed of dog get Globoid cell leukodystrohy |
Westies |
|
|
What occurs histologically with globoid cell lekodystrophy |
demylenation of the white matter everywhere |
|
|
What age is globoid cell leukodystrophy seen |
2-6 months of age and are progressive |
|
|
DX of globoid cell leukodystrophy |
DNA test |
|
|
Inhertited progressive, generalized ataxia has been reported in these breeds |
fox terriers jack russels |
|
|
Age of onset for heredity ataxia |
2-6 months of age |
|
|
Feeding what causes hypervitaminosis A of cats |
liver |
|
|
Most common areas affected with hypervitaminosis A |
C1-C3 |
|
|
What occurs with Type 1 disk disease |
degenertion and rupture of the dorsal anulus fibrosus and extruxion of the nucleus pulposus into the spinal canal. chondroid degeneration - increase collagen content of the disk, aleration of glycosaminoglycan concentration of the nucleus pulposus and decreased water concentration of the disk |
|
|
What occurs with Type 2 disk disease |
Bulging of the intervetebral disk without complete rupture of the anulus fibrosus
fibroid disk degenration - fibrous metaplasia of the nucleus pulposus |
|
|
Where are the MC disk extrusion sites |
T11-L3 |
|
|
What type of disk disease do cats have? |
Type II |
|
|
What is FCE |
fibrocartilaginous embolism causing ischemic myelopathy |
|
|
What happens anatomically with FCE |
iscemic necosis of the spinal cord gray and white matter associated with fibrocartilaginous emboli that occlude arteries/veins of the leptomaninges and spinal cord. The fibrocartilaginous substance possibly originate from the nucleus pulposus of an intervertebral disk. |
|
|
How dose FCE present |
acute onset of neurological deficits and is generally nonprogressive after several hours |
|
|
Signalment for FCE |
large/giant breed dogs C/S not progressive over 12 hours Not painful |
|
|
DX of FCE |
signalment non-painful tend to be asymmetrical R/O other diseases |
|
|
TX for FCE |
good nursing care can take weeks to Months for return to function LMN can persist |
|
|
Prognosis for FCE |
if retain pain and tail perception regain function (can take a long time) loss of pain for 24 hours have a poor prognosis |
|
|
WHt happens with leukoencephalomyelopathy of Rottweilers |
demylinating disorder of the brain and spinal cord |
|
|
What occurs clinically with leukoencephalomyelopathy of Rots signalment TX |
progressive tetraparesis and hypermetria of the thoracic limbs 18-42 months No TX |
|
|
What nerve roots make up cauda equina (Name of nerves) |
sciatic pudendal caudal and pelvic nerves |
|
|
What is the instability or ventral displacement of the sacrum with respect to L7 called |
retrolisthesis |
|
|
TX for LS disease |
confinement for 4-6 weeks SX for those with severe effects and urinary/fecal incontience |
|
|
This is a group of diseases that results from a defect in the metabolism of gulcosaminoglycans |
mycopolysaccharidosis |
|
|
What are the 2 subclasses of mucopolysaccharidosis? |
MPS VI MPS I |
|
|
What breed is MPS associated with |
Siamese |
|
|
What are the clinical findings of MPS VI |
small head flat boad face widely spaced eyes corneal clouding small ears depressed bridge of nose large forepaws |
|

|
MPS VI |
|

|
MPS VI |
|
|
This describes a number of malformations of the spinal cord believed to result from incomplete closure or development of the neural tube |
myelodysplasia |
|
|
Myelodysplasia is considered an inherited condition in the ____ |
Weimaraner |
|
|
C/S of myelodysplasia - lesion localization - gait abnormality |
T3-L3 symmetrical bunny hopping |
|
|
This disease causes accumulation of axonal spheroids throughout the neruoaxis |
neuroaxonal dystrophy of rottweilers |
|
|
C/S of neuroaxonal dystrophy of Rottweilers |
progressive ataxia and severe hypermetria esp. of the front limbs |
|
|
What is osteochondromatosis |
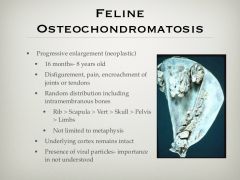
|
|
|
What are pilonodal sinus? anatomically |
invagination of the skin dorsal to the spine that extends below the skin to variable depths and in some cases to the dura mater when it may communicate with the subarachnoid space |
|
|
Why do pilonodal sinuses form |
failure of complete separation of the neural groove from the epidermal during embryonic development. |
|
|
Other names for pilonidal sinus |
epidermoid cyst dermoid cyst |
|
|
What causes myelomalacia? |
acute severe spinal cord injury that results in progressive ascending and descending infarction and hemorrhagic necrosis of the spinal cord parenchyma. Following explosive IVDD |
|
|
C/S of myelomalacia generaly lesion localization |
T3-L3 severe neurological deficits peracture onset (several hours) extreeme pain, anxious and have increased temperature |
|
|
How is a clinical DX of myelomalacia made? |
progressive clinical signs acute onset of paraplegia T3-L3 that shows LMN in pelvic and thoracic limbs should be syspected of having more than one lesion or PHM.
|
|
|
Prognosis of progressive hemorrhagic myelomalacia |
fatal in 24-48 hours No TX euthanasia |
|
|
Clinical signs of this disease consist of dogs under a year of age, progressive paralysis, and rigid extension of both pelivic limbs. |
T. Gondi Neosopora |
|
|
What type of organism is T. Gondii
Definitive host |
Obligate Intracellular Coccidian
Cats |
|
|
What is spina bifida |
Failure of fusion of the vetebral arches with or without protrusion of the spinal cord meninges |
|
|
Signalment for spina bifida
Tx |
English bulldogs Mc in lumbar spine C/s when start walking
No tx |
|
|
Signalment for spina bifida
Tx |
English bulldogs Mc in lumbar spine C/s when start walking
No tx |

