![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Epithelial tissue |
A sheet of cells that cover a body surface or lines a body cavity |
|
|
|
Covering and lining epithelium |
Forms outer layer of skin. dips into and lines the open cavities of urogenital, digestive and respiratory system. covers and the walls and organs of the closed ventral body cavity |
|
|
|
Glandular epithelium |
Fashions the glands of the body |
|
|
|
Apical surface |
An upper free surface exposed to the body exterior or the cavity of an internal organ |
|
|
|
Basal surface |
Lower attached surface to all epithelia |
|
|
|
Microvilli |
Finger like extensions of the plasma membrane, increase exposed surface area |
|
|
|
Cilia |
Tiny hairlike projections that propel substances along free surfaces |
|
|
|
Basal lamina |
Adjacent to the basal surface; noncellular adhesive sheet acts as elective filter, determines which molecules diffusing are allowed to enter epithelium |
|
|
|
Reticular lamina |
Layer of extracellular material containing a fine network of collagen protein fibers that belong to underlying conncetive tissue |
|
|
|
Basement membrane |
Reinforces the epithelial sheet, helps it resist stretching and tearing, defines epithelial boundary |
|
|
|
Simple epithelia |
Consist of single cell layer, found where absorption, secretion, and filtration occur |
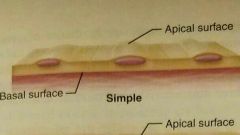
|
|
|
Stratified epithelia |
Composed of two or more cell layers, skin surface and lining of mouth |
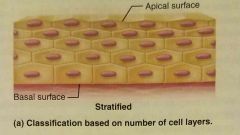
|
|
|
Squamous cells |
Flattened and scale like |

|
|
|
Cuboidal cells |
Boxlike, as tall as wide |

|
|
|
Columnar cells |
Are tall column shaped |
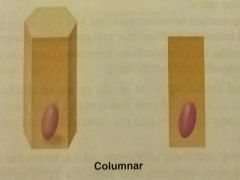
|
|
|
Simple squamous epithelium |
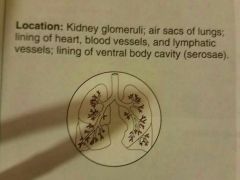
Allows materials to pass by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important, secretes lubricating substances in serosae |
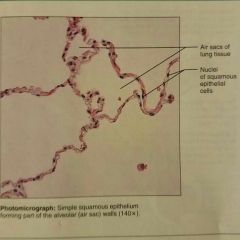
|
|
|
Simple cuboidal epithelium |
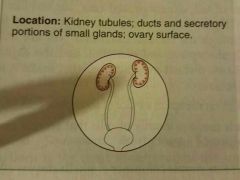
Secretion and absorption |
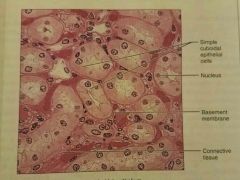
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium |
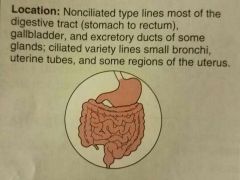
Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances |
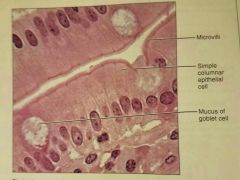
|
|
|
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
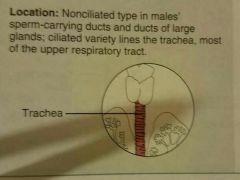
Secrete substances |
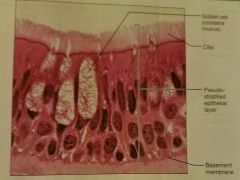
|
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium |
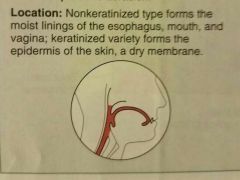
Protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion |
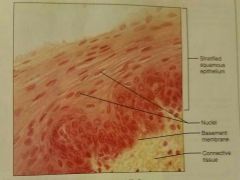
|
|
|
Transitional epithelium |
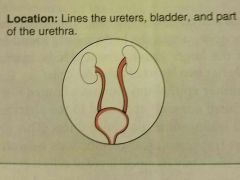
Stretches readily, permits stored urine to distend urinary organ |
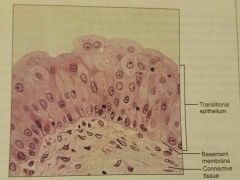
|

