![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is the function of epithelial cells ? |
Their function is to line any surface that it is in contact with the external environment. They also line the surface of internal organs eg lungs. |
|
|
|
What the two types of epithelial tissue in the lungs. |
Squamous epithelial and the columnar epithelial. |
|
|
|
Where are columnar epithelial cells situated? |
They are situated in the upper airway ( trachea and bronchi). It is lined with cilliated cells. |
|
|
|
What are ciliated cells and what do they do? |
The ciliated cells are hair like structures design to move mucus away from the lungs,preventing any inhaled particles causing infection. |
|
|
|
What cells produce mucus? |
Goblet cells |
|
|
|
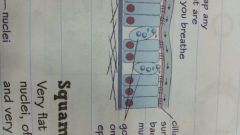
Where do goblet cells release mucus? |
They release sticky mucus onto the outer surface of the epithelium. |
|
|
|
How is mucus removed in the lungs? |
The mucus is removed in the lungs by tiny hairs on the outer surface of epithelial cells. They waft back and forth to move surface mucus out of lungs. |
|
|
|
Why does the top later of the columnar epithelial cell contain mucus? |
The layer mucus helps trap any unwanted particles that are present in the air that you breath. |
|
|
|
What are properties of squamous epithelial cell. |
They are very flat and thin with egg-shaped nuclei,often only one cell thick and very good for surfaces where diffusion occurs as in the lungs. |
|
|
|
What is COPD |
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease includes several conditions and is more common in smokers.because substances in smoke damage the lungs. |
|
|
|
What is the effect of cigarette smoke on cilia of columnar epithelial cell? |
The smoke causes the ciliated cells to slow and stop beating and eventually die off so mucus builds up. This blocks the airways and causes more coughing that ruptures the thin aveolar epithelial cells destroying the, by reducing the surface area of gas exchange. This provide a good environment for pathogens to grow. |
|

