![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
53 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Matter |
Anything that has mass and volume (takes up space) |
|
|
Atom |
The smallest part of an element |
|
|
Element |
Matter that is only made of one type of atom |
|
|
Proton |
Has a positive charge, located in the nucleus |
|
|
Nucleus |
Center of the atom, holds the protons and neutrons |
|
|
Electron |
Has a negative charge, flies around the nuclues |
|
|
Neutron |
Has no charge, located in the nucleus |
|
|
Mixture |
Is made of elements or compounds that are NOT chemically combined |
|
|
Heterogeneous |
Has parts you CAN see |
|
|
Homogenous |
Looks the same throughout |
|
|
Compound |
A substance whose smallest unit is made up of atoms of more than one element |
|
|
Why do we have seasons? |
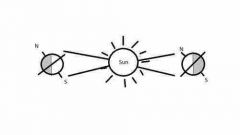
We have seasons because the Earth is tilted. The northern hemisphere is tilted to get more sunlight in summer (long days short night) |
|
|
Layers of the atmosphere |
Troposphere Stratosphere Mesosphere Thermosphere Exosphere |
|
|
Conduction |
Heat transfer through direct contact |
|
|
Convection |
Heat transfer from flowing/moving liquid or gas |
|
|
Radiation |
The Suns rays heat whatever surface it touches |
|
|
Cirrus |
Wispy, feathery clouds high up in the sky
Pleasant weather |
|
|
Cumulus |
Puffy cottonballs with flat bases
Good weather |
|
|
What causes land and sea breezes? |
Land heats up and cools down faster than water. |
|
|
Transpiration |
Water vapor that is released into the atmosphere by living things |
|
|
Condensation |
Water vapor changing into a liquid |
|
|
Evaporation |
Water changing into a vapor form |
|
|
Precipitation |
Water that falls from the atmosphere to the Earth |
|
|
Infiltration |
Water seeps through the rocks to become ground water |
|
|
Prokaryotic |
No nucleus of membrane covered organelles
Bacteria |
|
|
Eukaryotic |
Has a nucleus and membrane covered organelles
Plants, Animals, Fungus |
|
|
Osmosis |
Movement of water from a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to low concentration |
|
|
Diffusion |
Movement of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from an area of high concentration to low concentration |
|
|
Equilibrium |
When the concentrations are the same |
|
|
Fermentation in yeast |
Glucose is taken in and a small amount of ATP, alcohol, and carbon dioxide is produced |
|
|
Fermentation in muscles |
Glucose is taken in and a small amount of ATP and lactic acid are produced, in many cases, carbon dioxide is also produced |
|
|
Organ |
A group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job |
|
|
Tissue |
A group of cells that work together to perform a specific job |
|
|
Organism |
Anything that can sustain life on its own |
|
|
Organ system |
A group of organs that work together to perform a specific job |
|
|
Natural Gas |
Cleanest burning fossil fuel |
|
|
Inherited traits |
Characteristic that are passed from parents to offspring that are controlled by DNA |
|
|
Acquired Traits |
Characteristics that are NOT controlled by your DNA |
|
|
Mitosis |
Cell division for all body cells
Result: 46 chromosomes per cell, two identical cells |
|
|
Meiosis |
Cel division for sex cells (egg and sperm)
Result: 23 chromosomes, 4 non-identical cells |
|
|
Mutation |
An error on a gene |
|
|
Active transport |
the movement of molecules across a semi-permeable membrane from low concentration to high concentration by using ENERGY |
|
|
Five characteristics of life |
Responds to stimuli Reproduce Uses energy Made of 1 or more cells Grows and develops |
|
|
Asexual reproduction |
One parent makes an identical copy of itself |
|
|
Sexual reproduction |
Two parents produce offspring with DNA from both parents |
|
|
Homeostasis |
An organisms ability to keep a stable internal environment |
|
|
Complex carbohydrates |
Chains of sugar that are used for long lasting energy |
|
|
Lipids |
Fats and oils used as stored energy when an organism has used up its carbohydrates, they can not mix with water |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Contains instructions for making proteins |
|
|
Protein |
Make up most of your cells (used to make more of you) |
|
|
Simple carbohydrates |
Single rings of sugar used for quick energy |
|
|
Starch |
Complex carbohydrates from plants |
|
|
Cells |
The smallest part of a living thing that can carry out all the necessary functions of life |

