![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an enzyme? |
Protein which has a special/unique shape |
|
|
What are enzymes made of? |
Normally proteins |
|
|
What do enzymes do/control? |
Energy metabolism How cell functions How genetic info is used Obtain energy Build chemicals |
|
|
What are enzymatic properties? |
RNA |
|
|
What are the parts of an enzyme? |
Active site- where the substrate binds Substrate- the chemical that initiates a reaction |
|
|
What is the cycle of an enzyme? |
Affinity- when substrate binds to active site Catalysis- when substrate changes to product Product dissociating from enzyme |
|
|
What are the environmental factors which effect enzymes? |
Temperature and pH |
|
|
How does substrate availability effect the rate of a reaction? |
The higher the availability the more likely it will bump into an active site on an enzyme= faster rate of reaction; at some point it will reach a max speed and plateau |
|
|
What is a negative feedback loop? |
When the product of a reaction becomes the inhibitor Inhibitor prevents the enzyme from accepting substrate |
|
|
What are allosteric inhibitors and activators? |
Inhibitors- change the shape to block substrate Activators- change shape to fit substrate |
|
|
What is a post transcriptional modification? |
Modifies shape of an enzyme; can deactivate or activate enzyme |
|
|
What is kinase and phosphatase? |
Parts of phosphorylation; kinase + phosphate; phosphatase (-) phosphate |
|
|
How are reactions characterized? |
By how fast an enzyme work [S]/t
|
|
|
What is enzyme kinetics? |
What determines the timing of a reaction |
|
|
What are the two types of enzyme inhibitors? |
Competitive- interferes with active site affect affinity Noncompetitive- allosteric change active site affects catalysis |
|
|
Memorize the functional classes of enzymes |
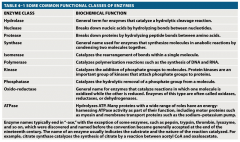
|

