![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
46 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Enviromental science |
a field of research used to understand the natural world and the interactions with it |
|
|
Applied Science |
discipline of science that applies existing scientific knowledge to developing things like technology or inventions |
|
|
Empirical Science |
a science based on evidence with a working hypothesis that can be tested using observations and experiments |
|
|
Environmental Science Scientific Method |
Observations --> Questions --> Hypothesis --> Experiment --> Data/Analyze --> Conclusion --> Results support hypothesis/ Results do not support hypothesis --> observation and experiment again |
|
|
experimental study vs. observational study |
-experimental study- control group and experimental group -observational study- no control over the variables, simply collect data based on what is seen, heard, and inferred based on the data collected |
|
|
What is the relationship between evidence, certainty, hypotheses, theories, and absolute proof? |
Evidence- serves to support or counter against a scientific theory or hypothesis Certainty- the state of being or feeling certain about something Hypotheses- a set of propositions set as an explanation for the basis of reasoning, without any assumption of it's truth Theories- well proved explanation based on a body of facts that have been repeatedly confirmed through observation and experiement absolute proof- always valid, regardless of context |
|
|
Uncertainty vs variability in the context of measurements in environmental science, How can they be quantified? |
Uncertainty is a situation involving imperfect/ unknown information in measurements while variability is the measure of the spread of a data set. They can be quantified by the standard/percent error using charts and graphs. |
|
|
precautionary principle, What is it's relationship to the uncertainty of science? How can we reduce uncertainty? |
precautionary principle- states that if an action or policy has a risk of causing harm to the public or the environment, then the product should not be used or the action should not be taken. This relates to uncertainty of science because when there are uncertainties, there are many risks that will occur. To reduce uncertainty, something should be tested many many times to note all the consequences and variables. |
|
|
What's the difference between a correlation and cause- effect relationship? |
A correlation is a statistical measure of how two or more variables fluctuate together, while a cause and effect relationship is a relationship between events or things, where one is the result of the other or others. |
|
|
What is the difference between primary and secondary sources? |
A primary source provides direct and firsthand evidence about an event, object, person, or work of art. A secondary source is created later by someone who did not experience the events or conditions first hand. |
|
|
What is the process of peer review? |
-scientists study something - scientists write about their results - journal editors receives an article and sends it out for peer review - editors may send comments to the scientists, then revise and resubmit the article for further review, or it may be rejected. - peer reviewers read the article and provide feedback to the editor - If an article meets editorial and peer standards, it is published in a journal, but if not, then it is sent back for to the editor and to the scientists |
|
|
How do chlorofluorocarbons affect ozone in the atmosphere? |
Chlorofluorocarbons slowly gets pulled into the stratosphere where they are broken up by ultraviolet radiation, releasing the chlorine that destroys the ozone. |
|
|
What is the potential harm to people if ozone concentration in the atmosphere is low? |
If ozone concentration in the atmosphere is low, then more harmful UV rays will touch people's skin and can lead to skin cancer and cataracts. |
|
|
What are the issues and root causes of issues at Plumb beach? |
The issues that Plumb beach faces are that the Belt Parkway is built right through it, so erosion is always going to effect it. |
|
|
How effective was the recent Army Corps of Engineers restoration project, and how is the beach responding? |
The recent restoration project was pretty effective because the sand that was placed before a hurricane, most of it stayed put and prevented a worse erosion that could have happened. The beach is in good size and shape right now. However, the restoration project would have to be done at least once-twice every two years. |
|
|
What are the factors that affect the exposure of energy of a shoreline? |
- Night and day - grain size (sands) - wind (direction & speed) - high/low tide -human interaction - vegetation near a shoreline |
|
|
How do waves affect beach dynamics (ex: erosion, seasonal changes)? |
High tide can push an entire beach backwards, and over time can cause erosion through the waves coming in and out, carrying sand with it. Waves can affect seasonal changes through the wind/jet streams and ocean currents, causing certain temperatures in certain areas. Seasonal changes in currents and wave action produce a cycle of erosion |
|
|
How do storms affect beach dynamics (What is storm surge)? |
Storms contribute to erosion, loss of sand (change in beach face, berm), forming summer and winter beaches -Storm surge- the rising of the sea as a result of atmospheric pressure changes and wind associated with a storm |
|
|
What are the methods used to stabilize the shoreline to protect infrastructure and property? What are the potential adverse consequences of each method? |
The methods used to protect property near the shoreline are groins, vegetation near shorelines, jetties/piers, keeping the slope gentle, gradual, and natural, stone rip rap -jetties- structure that projects from the land out onto the water (walkway) -Consequences: - groins: causes a sand deficit and erosion on the down drift side, - vegetation: not tough enough (can be trampled/eaten) - jetties: gentle shoreline: erodes over time, only softens the blow of waves - stone rip rap: rocks can come loose, habitat destruction for animals that live near the shoreline |
|
|
What are some of the components of Earth's radiation budget and what are their corresponding timescales? (Milankovitch cycles, sunspots, volcanic aerosols, greenhouse gases, albedo, clouds, ozone) |
- Earth's radiation budget- the balance between incoming energy from the sun and the outgoing longwave (thermal) and reflected shortwave energy from the Earth. - Milankovitch cycles: occurs every 100,000 years, plays a role in influencing climate change events - sunspots: when hot gas deep within the sun boil up the surface and release energy (takes a couple of years) - volcanic aerosols: Following an eruption, large amounts of sulphur dioxide (SO2), hydrochloric acid (HCL) and ash are spewed into Earth's stratosphere. HCL, in most cases, condenses with water vapor and is rained out of the volcanic cloud formation - greenhouse gases: as earth's surface warms, it emits radiation but traps long wave radiation and earth stays warm - albedo: the amount of reflection a surface on earth can have - ozone: (O3) layer in the stratosphere,prevents dangerous radiation from the Sun from reaching the surface of the Earth |
|
|
What is the difference between weather and climate? |
-Weather- conditions of the atmosphere (troposphere) over a sort period of time -Climate- the average daily weather for an extended period of time at a certain location |
|
|
Why can regional and local climate changes be different than global climate? (think about global radiation budget vs redistribution of heat by oceans and atmosphere) |
Regional/local climates are different than global climate because of how radiation and energy (sunlight) are distributed differently due to the earth's rotation, the different biomes, latitude and longitude with how intense the sun hits on each, average weather for each region, and the redistribution of heat by oceans and atmosphere) |
|
|
How does possible climate change over the next 80 years compare with climate change since the last glacial maximum 18,000 years ago? |
Climate change over the next 80 will rapidly increase by than over the last 18,000 year. |
|
|
How is New York City's climate expected to change over the next century? (temperature, rainfall, storms, and heatwaves) |
New York City's climate is expected to: - temperature: +4.2F, +12.1F - rainfall: -6, +25% - storms: -heatwaves: 5-9 inches |
|
|
How much sea level change is expected in New York City over the next century? |
Sea level is expected to rise 2 meters/ 6 ft over the next century. |
|
|
Biosphere |
The parts of the land, sea, and atmosphere in which organisms are able to live |
|
|
Biome |
a specific environment that's home to living things suited for that place and climate ex: forest, grassland, tundra, desert, tropical rainforest |
|
|
Ecosystem |
complex set of relationships among the living resources, habitats, and residents of an area. Ex: plants, trees, animals, fish, birds, micro- organisms, water, soil, and people |
|
|
Community |
A group of organisms or populations living and interacting with one another in a particular environment. The organisms in a community affect each other's abundance, distribution, and evolutionary adaptation. |
|
|
Population |
the number of all the organisms of the same group or species, which live in a particular geographical area, and have the capability of interbreeding. |
|
|
Individual |
a single person/animal/plant/member |
|
|
Habitat |
the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism/ a person's usual or preferred surroundings |
|
|
Niche |
The function or position of a species within an ecological community/ a scientific term used to describe the relationships between a species and the elements in its ecosystem |
|
|
What is the ultimate source of energy for the biosphere? How do ecosystems capture this energy and make it available? |
Sunlight, primary producers capture this energy through photosynthesis |
|
|
What is primary production? |
- primary production- the production/forming of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide, occurs through the process of photosynthesis and chemosynthesis - chemosynthesis- uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy - Gross Primary production (GPP)- the amount of chemical energy as biomass that primary producers create in a given length of time - Net Primary production (NPP)- the rate at which all the plants in an ecosystem produce net useful chemical energy -biomass- the total mass of organisms in a given area or volume NPP = GPP - respiration [by plants] |
|
|
How does net production of salt marshes and estuaries compare with rain forests, oceans, farmland and other ecosystems on a square meter basis? How about on a global basis? Why are they different? |
On a square meter basis, the net production of marshes and estuaries are greater than rain forests, oceans, and farmland, while on a global basis, it would be the opposite. They are different because in a small area, a lot is still done for marshes and estuaries, while for oceans, if it's talking about the whole ocean, the ocean does more according to production. |
|
|
What is a range of tolerance and zone of optimum range? How might climate change affect ranges of tolerance for populations and how might populations respond? |
The range of tolerance is the limit to which an organism can survive on the basis of light, water, salinity, and nitrogen. Climate change will severely affect population's range of tolerance by taking away many of what organisms need to be able to survive in that environment, forcing organisms to either adapt, leave, or die out. |
|
|
How and why is grain size important to organisms living on a beach? |
Grain size is important because many organisms depend on fine grain sand to quickly escape under the sand for (coolness, habitat, escape from predators, and laying eggs) and when eggs hatch, the animals need to quickly break through. |
|
|
What are ecosystem services? What are the three main categories and what are three examples of each? Which is the most valuable ecosystem service? |
Ecosystem services are the needs and wants that the ecosystem provides to us. The four main categories are provisional services (things ecosystem provides: food, timber, fuel, medicine), regulating services (climate regulation, waste decomposition and detoxification, water & air purification, and pest and disease control), cultural services (aesthetics, education, recreation, spiritual), and supporting services (nutrient recycling, primary production and soil formation) The most valuable is provisional services. |
|
|
How are grain size and beach populations related? How might changing the grain size on a beach change the species richness and abundance of organisms? |
The finer the grain size, the more the beach population increases for reasons before. |
|
|
How might sea level rise effect marsh ecosystems ? (use Plumb beach as an example.) |
Sea level rise will drown out marsh ecosystems, ruining the organisms and habitats in the area and critical fisheries, as well as water quality and erosion control services. |
|
|
What is biodiversity? What is species richness? What is species evenness? |
- biodiversity-the variety of life in the world or in a particular habitat or ecosystem. - species richness- the abundance of species in an area - species evenness- how balanced species are distributed throughout an area |
|
|
How do you measure and calculate elevations and slope gradients? |
ON PHONE |
|
|
What is the difference between variability and uncertainty? How are each expressed? Can you reduce variability? Can you reduce uncertainty? |
- variability-measure of the spread of a data set ex: range, mean, variance and standard deviation - uncertainty-margin of error of a measurement, when explicitly stated, is given by a range of values likely to enclose the true value (standard error) Yes variability can be reduced and uncertainty can be reduced but not rid of |
|
|
What are some advantages to using UTM coordinates over latitude and longitude? |
UTM coordinates are even more precise than latitude and longitude and more constant, no more minutes and seconds to convert and it's already in the metric units |
|
|
Sketch and explain how the breakwater and groins have affected Plumb beach. Draw a typical cross section of a beach profile and label it. |
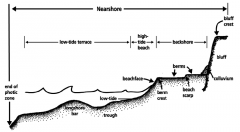
- breakwater- a barrier built out into a body of water to protect a coast or harbor from the force of waves - cross section of a beach profile- side view of a beach profile |

