![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
130 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Tillage |
Turning over the soil every season |
|
|
Pros of tillage: |
Helps deter weeds |
|
|
Cons of tillage: |
Organic matter needs to be on the surface to decompose |
|
|
Pros of no till: |
Cheaper Easier Reduces compaction Reduced CO2 released |
|
|
5 planting techniques: |
1. Terracing 2. Contour planting 3. Strip cropping/poly culture 4. Alley cropping/agro forestry 5. Wind breaks/hedge rows |
|
|
3 Ways to get more nutrients into the soil |
1. Organic fertilizer 2. Crop rotation (corn, soybean, wheat) 3. Commercial inorganic fertilizer |
|
|
Pros of commercial inorganic fertilizer: |
Easy to get, store, and use Depend on it for 40% of food |
|
|
Cons of commercial inorganic fertilizer: |
Not food for detritivores Only has PNK Excess N can become greenhouse gas Can pollute rivers |
|
|
Main ideas of sustainable agriculture: |
1. Low inputs + use efficiently 2. Soil conservation and restoration 3. Economic incentives |
|
|
How to prevent soil salinization: |
Reduce irrigation |
|
|
How to clean up soil salinization |
Flush soil, underground drainage system, salt tolerant crops |
|
|
Pest: |
Anything that is in the way of achieving a goal, an unwanted organism |
|
|
Pesticide: |
Kills or controls unwanted organisms |
|
|
History of pesticides: |
Before: crop rotation, vary planting times First generation: sulphur, lead, arsenic, plant's natural chemicals Second generation: synthetic organic compound, broad to narrow spectrum, persistence |
|
|
Pros of pesticides: |
Save lives (from diseases), increased food supply, health risks may be better than risks |
|
|
Cons of pesticides: |
Genetic resistance, kill non-target species, health threat |
|
|
Alternatives to pesticides |
Biological pest control (biomimicry) insect birth control, preditors Hot water Genetically resistant plants |
|
|
Biomimicry |
the design and production of materials, structures, and systems that are modeled on biological entities and processes |
|
|
Classifications of forests |
Old growth New growth Tree farm/plantation |
|
|
Ecological services of forests |
carbon sinks, erosion protection, landslide, wind, tsunami protection, water and air purification, climate regulation |
|
|
Economic services |
Food, shelter, medicine, lumber, paper, jobs, recreation, fuel |
|
|
Mangroves |
where rainforest meets ocean, protect from tsunamis |
|
|
Types of forests |
Tropical Temperate Boreal/Taiga |
|
|
Forest regions in Ontario |
Boreal (biggest) Taiga Carolinian (most threatened) Great Lakes St Lawrence |
|
|
Types of forest management |
1. Selective cutting 2. Shelterwood 3. Seed tree cutting 4. Clear cutting 5. Strip cutting |
|
|
What type of forest suffers the greatest loss? |
Rainforest |
|
|
Primary causes of deforestation |
Not valuing ecological significance Lack of policy Population growth Poverty |
|
|
Process of tropical rainforest destruction |
1. Roads are built 2. Selective cutting 3. Ranchers/slash and burn 4. Settles (subsistence farming) 5. Land is abandoned |
|
|
Solutions to deforestation |
Teach and subsidize sustainable methods Debt for nature swap Reduce poverty and population growth Reduce illegal cutting Use new equipment (Spider) |
|
|
Deforestation and climate change |
Reduction of carbon sinks Increased CO2 release Change in hydrologic cycle (decreased rainfall) Loss of NPP Albedo |
|
|
Mountain pine beetle |
British Columbia Bug eats trees, kills them, they rot, they release carbon, warmer temperatures, beetle can live longer, eat more trees |
|
|
Invasive species |
Take up resources and space, disrupt food chain |
|
|
Best defence against invasive species |
High biodiversity (more likely for there to be a predator, niche resources) |
|
|
Examples of invasive species |
European buckthorn, kudzu, emerald ash borer (kills ash trees), giant hogweed |
|
|
Levels of the atmosphere |
1. Thermosphere 2. Mesosphere 3. Stratosphere 4. Troposhere |
|
|
Good ozone: |
Where: Stratosphere What: o2 + sunlight |
|
|
Bad ozone: |
Where: troposphere What: VOCs + NO + sunlight |
|
|
Outdoor air pollution |
any chemical that is in the atmosphere and in high enough concentrations to cause harm |
|
|
3 sources of air pollution |
Mobile Stationary Natural |
|
|
Primary vs secondary air pollution |
Primary = the form they are emitted in Secondary = ground level ozone |
|
|
Types of smog |
1. Photochemical (reduce photosynthesis) 2. Industrial |
|
|
Natural factors that reduce air pollution |
Rain, snow, sea spray Wind |
|
|
Natural factors that increase air pollution |
Tall buildings/mountains High temperatures |
|
|
Grass hopper effect |
Chemicals in the air move from hot regions to colder regions (polar) because of prevailing winds |
|
|
How to prevent air pollution |
Burn low sulphur coal, remove sulphur, convert to liquid/gas Use less polluting fuels |
|
|
Clean up air pollution |
Smoke stacks, scrubbers, tax pollution |
|
|
Prevent motor vehicle air pollution |
Mass transport Loss polluting engines/fuels Improve fuel efficiency Remove old cars Tax breaks Restrictions in polluted areas |
|
|
Motor vehicle air pollution clean up |
Emission control devices Exhaust inspections Stricter emission standards |
|
|
Sources of acid deposition |
NO and SO2 from acid and salt |
|
|
Types of acid deposition |
Wet and dry |
|
|
Impacts |
Respiratory health, toxic metal leeching (kills fish), damage to buildings and structures, soil pH changes (less productive and more susceptible to diseases) |
|
|
Clean up |
Neutralize acid with lime or phosphate (but can lead to eutrophication) |
|
|
Greenhouse effect is... |
...naturally occurring and essential for life |
|
|
Green house gasses |
CO2, N2O, CH4 (methane) |
|
|
Albedo |
The amount of light or radiation that is reflected by a surface |
|
|
Nation that is the biggest offender in term of greenhouse effect |
United States |
|
|
Human actives that increase greenhouse effect |
Fossil fuel use Deforestation/grassland destruction Increased cattle raising Growing rice Inorganic fertilizer use (bacteria in soil release NO into the atmosphere) |
|
|
Ozone depleting chemical |
CFCs / chloroflurocarbons |
|
|
CFCs... |
Are human creates Last 11-20 years in the troposphere Last 65-110 years in stratosphere |
|
|
Process of CFCs breaking up ozone bonds |
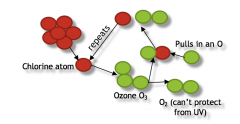
|
|
|
Ozone loss vs greenhouse effect |
Ozone loss is the loss of good zone in the stratosphere GH effect is heat trapped in the troposphere |
|
|
Connections |
CFCs are GHG GHGs cause stratosphere to cool (where good ozone is) |
|
|
Climate |
a measure oflong term conditions (average temperature and temperature) |
|
|
FactorsDetermining Climate: |
1.Uneven heatingof Earth’s surface (direct sun vs angled) 2.Seasonalchanges in temperature and precipitation (tilting of axis) 3.Convectioncurrents (sun evaporates ocean, becomes precipitation) Convection cells: 6 giant ones, distribute warmth and precipitation 4.Rotation ofearth on axis (turns faster at equator = prevailing winds) Coriolis effect: northern hemisphere = air moves right, southern =air moves left |
|
|
Globalwarming: |
averagetemperature increases in troposphere |
|
|
Global climate change |
Changes in any aspect of earth's climate |
|
|
How to study climate change |
1.Ice core takenfrom Antarctica (air bubbles analyzed for GHGs) 2.Sediment cores(pollen, fossils, plants, bottom of lakes) 3.Directmeasurement of troposphere 4.Air samplecollection |
|
|
Past climate change |
- Prolongedperiods of heating and cooling - Gradual toquick temperature changes |
|
|
Present climate change |
Interglacialfor 12,000 years Relativelystable global climate Regionalclimate changes More CO2 in atmosphere than last 90,000 years |
|
|
Drivers of climate change |
Rate ofchange: temperature changes happen quickly Volcaniceruptions Changes insolar radiation- active vs quiet Changes inEarth’s tilt- axis wobble Oceansmoderate temperature- El Nino brings warm water to coast every 7 years Oceans storeheat and CO2 Clouds andwater vapour (warmer temperature = more clouds) Increased CO2 (greenhousegasses and photosynthesis) Methaneemissions (melting ice, organic matter breaking down) |
|
|
Evidence of troposhere warming: |
1.20th century hottest in 1000 years 2.Temperature oftroposphere risen 0.74 degrees Celsius 3.Warmest yearssince 1850 4.Glaciers, seaice, and permafrost melting 5.Rising sealevel (thermal expansion + melting) |
|
|
Should CO2 be classified as an air pollutant? |
•Industry says: Highconcentration is bad for any chemical•Scientistssay: Changes wereprecipitation happens and food grows Rising sealevels Harmorganisms/ ecosystems |
|
|
Effects of climate change |
Decreasedwater quality More draughtand flooding Environmentalrefugees Habitat lossand extinction Changes indemands and yields |
|
|
Disagreements |
Cost of reducing GHGs vs economic benefits Who is responsible |
|
|
Options |
1.Do nothing 2.Do moreresearch 3.Act now: -Precautionaryprinciple -Improve energyefficiency and reduce fossil fuels (renewable energy) -Changeagriculture and food choices -Politicalpressure -Economicchanges |
|
|
Transpiration |
the process by which moisture is carried through plants from roots to small pores on the underside of leaves, where it changes to vapor and is released to the atmosphere |
|
|
Evapotranspiration |
the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from the Earth's land and ocean surface to the atmosphere |
|
|
Percolation |
Water slowly moving through the soil |
|
|
What does latitude have to do with water? |
Dry spots at 30 degrees North and South |
|
|
Types of water |
Surface water- precipitation that doesn't infiltrate, Drains into watershed or drainage basin Ground water Aquifers |
|
|
Reliable run off |
Amount of water that can be counted on each year until |
|
|
What is above and below the water table? |
Area of aeration Area of saturation |
|
|
What are the 3 types of aquifers |
Unconfined (precipitation can get to it) Confined (rock above and below) Fossil |
|
|
Two types of water use |
Withdrawal- removed and returned Consumptive- removed and not returned |
|
|
Biggest global water uses |
1. Agriculture 2. Industry 3. Domestic/cities |
|
|
What does Canada use the most water for? |
Power plant cooling |
|
|
Problems with water distribution in Canada |
-Population pressure and over burden -Rivers flow north -Soil salinization and aquifer depletion |
|
|
Contributors to water scarcity |
Dry climate Drought (less precipitation) Dry Soil Demand |
|
|
Types of water scarcity |
Physical- reduced input + too much demand Economic- don't have money to get to it |
|
|
Political conflict related to water scarcity |
Aral Sea dried up because input river was diverted for agriculture |
|
|
Ways to increase water supply |
1. Store it 2. Transport it 3. Groundwater withdrawal 4. Desalination 5. Reduce water waste 6. Other options (deep aquifer mining, cloud seeding, towing icebergs, biomimicry) |
|
|
Pros and cons of dams and reservoirs |
Pros: increased volume and access, recreation, electricity, agriculture Cons: more evaporation, habitat destruction |
|
|
Cons of transporting it |
Displaces people and habitats |
|
|
James Bay Project |
600 Dams in northern Quebec, used to collect hydro electricity but displaced aboriginal people |
|
|
Pros and cons of ground water withdrawal |
Pros: cheap and easy, no evaporation issueCons: depletionand pollution, subsidence (groundsinking) |
|
|
Ways to desalinate |
Distillation- Boil water and collect vapour Reverse osmosis- filter out salt (what to do with salt??) |
|
|
Ways to reduce water waste |
subsidies, precision irrigation, xeriscaping, use greywater |
|
|
Cloud seeding |
Putting silver oxide into the air to force precipitation) |
|
|
Water pollution |
Any chemical,biological, or physical change to water that is harmful |
|
|
Types of water pollution |
Biological and Chemical |
|
|
Indicator organisms |
Fish fly = clean leech - dirty |
|
|
Major sources of water pollution |
Agriculture Industry Mining |
|
|
Water types |
Stream/River (runoff, poverty) Freshwater Lake (more vulnerable bc less mixing) Groundwater (landfill leakage, wells) Ocean (plastic waste, dredge spoils, oil spills) |
|
|
Biomagnification |
Concentration of toxins as they move up the food chain |
|
|
Bioconcentration |
Concentration of toxins through generations |
|
|
4 Characteristics of groundwater |
1. Low flow/recharge 2. Low oxygen 3. Few bacteria 4. Cold temperatures |
|
|
Process of algae blooms |
1. Block Sunlight 2. Aerobic bacteria(use up the dissolved oxygen)3. Anaerobic bacteria(create methane + sulfide) 4. Dead zones |
|
|
Prevention/clean up of algae blooms |
Prevention: less runoff, fertilizers, phosphates in detergents Cleanup: weeding, algaecides, add oxygen |
|
|
General solutions |
Nonpoint: focus on agriculture run-off Point:focus on legislation Personal:waste and drugs down drain |
|
|
What is the anthropocene era? |
Humans have changed earth's climate so much that its a new geological era |
|
|
A gallon of gasoline = |
8-10 weeks of hard human labour |
|
|
What type of living arrangement was created based on the dependence on cheap oil? |
Suburbs |
|
|
What is peak oil? |
May 2005, demand became greater than supply |
|
|
Why no other countries want to adapt western culture? |
Seen in media as being good Improves wellbeing and happiness |
|
|
Why shouldn't they adapt western culture? |
Use many resources because of huge population |
|
|
What is the latest crisis we should be concerned about? |
The fresh water crisis (access and supply) |
|
|
What human activity accounts for 70% of water use? |
Irrigated agriculture |
|
|
What is fossil water? |
Aquifer, from long ago, used for irrigation but not easy to replace |
|
|
What is the source and use of the Ogallala aquifer? |
Millions of years old, used to grow corn for energy |
|
|
Why is the speed of climate change the greatest problem for humanity? |
People depend on water for agriculture, floods destroy homes, economies depend on climate |
|
|
Bark beetles |
warmer climate = more beetles = more dead trees |
|
|
Glaciers in Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau melt |
Himalayas- feed major rivers (Ganges) Tibet- supply rivers that grow crops for the world Rising sea levels |
|
|
Ecosystem services |
Provisioning (food, water) Cultural (recreation, education) Supporting (photosynthesis, biodiversity) Regulating (store carbon, purify water) |
|
|
Effect of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere on ocean life |
Oceans absorb CO2, increases acidity, inhibits shell formation |
|
|
Dead zones |
Caused by excessive nutrient pollution, low oxygen levels in lakes and oceans Occur near inhabited coastlines with lots of aquatic life |
|
|
Chacoan/Anasazi people |
Took advantage of rainfall and created market economy for corn Population grew too much, drought caused wars so people left |
|
|
Why are failing states a concern? |
All systems and states are interconnected, it is a sign of failing civilization |
|
|
Ways to reduce resource depletion |
Reduce consumption (oil, minerals) Use less energy Steady state + sustainable economy Change throw-away economy |
|
|
Greatest challenges |
Getting over transition Rethink and change lifestyle |
|
|
GPI and GDP |
GPI= Genuine progress Indicator Measures people's satisfaction with their lives, deeper than GDP, environmental, economic, and social calculations |

