![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
69 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Energy waves of particle displacement, both compression (more dense) and rarefaction (less dense) within an elastic medium; triggers sensation of hearing
|
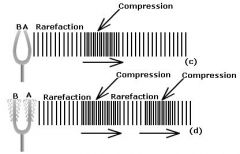
Sound
|
|
|
Extent of vibratory movement from rest to furthest point from rest in compression and rarefaction phases of energy waves
|
Amplitude of sound
|
|
|
Amount of sound energy through an area per time. Refers to sound strength or magnitude. Psychoacoustic correlate is loudness.
|
Intensity of sound
|
|
|
Sound force (related to acceleration) over a surface per unit time.
|
Sound pressure
|
|
|
Unit to express intensity of sound. More specifically the logarithm of the ratio of two sound intensities. One-tenth of a Bel (named for Alexander Graham Bell)
|
Decibel (dB)
|
|
|
Number of cycles (complete oscillations) of a vibrating medium per unit of time. Psychoacoustic correlate is pitch. Time of one cycle is period.
|
Frequency
|
|
|
Unit to express frequency
|
Hertz (Hz)
|
|
|
Human ear is capable of hearing in which frequency range?
|
20 to 20,000 Hz
|
|
|
1) The single-frequency sound rarely occurs in nature.
2) Sound comprising more than one frequency |
Pure tone
Complex sound |
|
|
Aperiodic complex sound
|
Noise
|
|
|
What are the differences between the following noise:
1) White noise 2) Narrow-band noise 3) Speech noise |
1) White noise - contains all frequencies in the audible spectrum at average equal amplitudes
2) Narrow-band noise - white noise with frequencies above and below a center frequency filtered out or reduced. 3) Speech noise - white noise with frequencies above 3000 and below 300 Hz reduced by a filter. |
|
|
Frequency at which a mass vibrates with least amount of force and greater amplitude
|
Resonant frequency - determined by elasticity, mass, in fractional characteristics of the medium.
|
|
|
What are the natural resonant frequencies of the following structures?
External auditory canal Middle ear Tympanic mmbrane Ossicular chain |
External auditory canal - 3000 Hz
Middle ear - 800 - 5000 Hz (mostly 1000-2000 Hz) Tympanic membrane - 800 - 1600 Hz Ossicular chain - 500 - 2000 Hz So the ear has gratest sensitivity at those frequencies most important to understand speech (~300 - 3500 Hz) |
|
|
Is the decibel scale linear or nonlinear?
|
Nonlinear - eg, the energy increase from 5-7 dB is far greater than the increased from 1 - 3 dB)
|
|
|
Does 0 dB indicate the absence of sound?
|
No, it's a relative measure. 0 dB is the threshold of hearing.
|
|
|
What is the most common measure of sound strength?
|
Sound Pressure Level (SPL)
|
|
|
What is the scale which takes into account differences in human sensitivity for the various frequencies?
|
dB Hearing Level (HL) - 0 dB HL at any frequency is the average lowest intensity perceived by normal ears 50% of the time.
Human ears are not equally sensitive to all frequencies. Ie, we can't perceive 0 dB SPL at 250 Hz...rather, a 250 Hz sound must be raised to 26.5 dB SPL before it is heard. This level is assigned the value 0 dB HL. |
|
|
What is the difference between dB Hearing Level (HL) and dB Sensation Level (SL)?
|
dB Hearing Level (HL) - hearing ability and threshold is based on an average lower intensity perceived by normal ears 50% of the time. Takes into account an entire population of test subjects.
dB Sensation Level (SL) - hearing ability and threshold is based on an individual subject. 0 dB SL is the level of intensity at which an INDIVIDUAL can just perceive a sound 50% of the time. |
|
|
Long exposure at >____ dB SPL may eventually harm hearing
|
>90
|
|
|
Noise >____ dB SPL may cause pain
|
>140
|
|
|
What's the length, diameter and volume of an average external auditory canal?
|
~1in (2.5cm) long, 1/4 in diameter, and 2cm3 volume
|
|
|
What's the volume of the middle ear space?
|
1-2 cm3
|
|
|
What is the area of the adult TM?
What is the area of the stapes footplate? |
Adult TM - 85-90 mm^2
Stapes footplate - 3.2 mm^2 Thus, the ratio of the vibrating portion of the TM to that of the stapes footplate results in a 17:1 increase in sound energy by concentrating it into a smaller area. |
|
|
What is the phase difference in dB between the oval window and the round window?
|
~ 4dB
|
|
|
Which two membranes are moved by a wave created when the stapes moves in and out of the oval window?
|
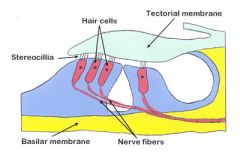
basilar and tectorial membranes
|
|
|
Which sound frequencies, low or high, travel to the apex of the cochlea?
|
low frequencies
|
|
|
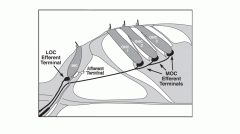
95% of afferent sensory receptors innervate which hair cells (inner or outer)?
Efferent sensory nerves synapse on which hair cells |
Inner hair cells
Outer hair cells - are active and help to amplify the sound |
|
|
How many rows of outer hair cells are there?
How many rows of inner hair cells are there? |
Three outer rows
One inner row |
|
|
Trace the central auditory pathway from the cochlea to the cortex
|
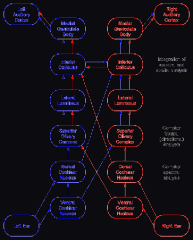
Cochlea --> spiral ganglion which forms the cochlear part of CN 8 --> cochlear nucleus in the brain stem --> superior olivary complex --> lateral lemniscus pathway --> inferior colliulus in the midbrain --> medial geniculate body in the thalamus --> auditory cortex
Mnemonic is "E COLI" (eight cranial nerve, cochlear nucleus, olivary complex (superior), lateral lemniscus, inferior colliculus) |
|
|
A positive Rinne test is when the pt perceives the sound as louder when the tuning fork is on (the mastoid OR outside of the ear canal)
|
Outside of the ear canal
(negative Rinne test is with conductive hearing loss, when the tuning fork is louder on the mastoid) |
|
|
Describe the Bing test
(what does it examine; process, positive and negative tests) |
Examines the occlusion effect
Tuning fork is placed on the mastoid process while the tester alternatively opens and closes the pt's ear canal with a finger. Positive Bing - pt's with normal hearing or SNHL will report a pulsating tone. Negative Bing - pt's with a conductive HL will notice no change in the tone |
|
|
Describe the Schwabach test
(what does it examine; process, normal, diminished and prolonged tests) |
Compares the pt's bone conduction hearing to that of a normal listener (examiner)
Tuning fork is alternatively placed on the mastoid process of the pt and the examiner. When the pt no longer hears the sound, the examiner listens to see if he can still perceive the sound. Normal Schwabach test - pt with normal hearing will stop hearing the sound at about the same time as examiner Diminished Schwabach test - pt's with SNHL will stop hearing the sound BEFORE the examiner Prolonged Schwabach test - pt's with CHLwill hear the sound longer than examiner |
|
|
Describe the Gelle test
(what does it examine; process, normal, diminished and prolonged tests) |
Used to determine if TM and ossicular chain are mobile and intact
Tuning fork is placed on the mastoid. Assesses the loudness of the sound heard by the patient while varying amounts of pressure are applied to the TM via an insufflation bulb Mobile/Intact ossicular chain - pt's will report a DECREASE in loudness of bone-conducted sound as the pressure against the TM increases Ossicular discontinuity or fixation - no decrease in loudness of bone-conducted sound as pressure against the TM increases |
|
|
The lowest level, in decibels, at which a pt can repeat spondaic words (spondees) in 50% of presentations
What is a spondee? Why do this test? |
Speech Recognition Threshold (SRT)
Spondee is a two-syllable compound word that is pronounced with equal stress on both syllables (eg. railroad, sidwalk, eardrum) SRT is measured primarily to confirm pure tone thresholds. SRT should be within 10 dB of the pure tone average (PTA.,.which is the average of AC thresholds at 500, 1000, and 2000 Hz). |
|
|
The lowest level in decibels at which an individual responds to the presence of speech.
Why do this test? |
Speech Awareness/Detection Threshold (SAT/SDT)
It is sometimes used when assessing small children, persons with physical or mental disabilities, or those with a language barrier or any time an SRT can't be obtained. |
|
|
This test reflects how clearly a pt can hear speech
|
Word Recognition Score (previously called speech discrimination)
It is the percentage of phoentically balanced words that a pt repeats correctly Speech stimuli are usually presented at 30-40 dB SL in order to obtain individual's maximum score. |
|
|
What is the level in decibels of the average conversation?
|
50-60 dB HL
|
|
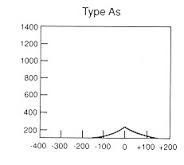
What are three causes of a Type As tympanogram curve?
|
1) Otosclerosis
2) Scarred TM 3) Fixation of the malleus |
|
|
What is the acoustic reflex testing?
|
Objective measure of the lowest stimulus level that elicits the stapedial reflex
|
|
|
In the acoustic reflex decay test, if there is inability to maintain the contraction of the stapedius at 10 dB above the acoustic reflex threshold for 10 seconds, it is considered positive for what?
|
Retrocochlear involvement
|
|
|
Summarize the glycerol test for Meniere's dz.
|
Pt drinks a mixture of glucose and water. Prior to and 3 hrs after ingestion, pure tone thresholds are measured. In Meniere's dz, there is a temporary improvement in hearing due to a diuretic effect of the glycerol.
|
|
|
What test is used to assess the auditory system from the eighth nerve up through the level of the brain stem?
|
Auditory brain stem response
|
|
|
What is the most sensitive audiologic test to detect the presence of retrocochlear pathology?
|
Auditory brain stem response
|
|
|
List some variables that affect ABR's
|
1) Age (incomplete at birth, with only a few waves observed)
2) Gender (females have shorter latencies) 3) Temperature 4) Medication and drugs (affected by numbers of drugs and acute/chronic alcohol intoxication) 5) Attention and state of arousal (ie. being asleep yields better results) 6) Hearing Loss (type, degree and configuration of HL must be taken into account before presuming retrocochlear involvement) |
|
|
Typical ABR's have how many waves?
Which auditory structure is each wave believed to be caused by? (there is a mnemonic..) |
Waves I - V
Mnemonic is "E COLI" Wave I - Eight cranial nerve Wave II - Cochlear nucleus Wave III - Olivary complex (superior/auditory) Wave IV - Lateral lemniscus Wave V - Inferior colliculus Another theory: Wave I - Distal eighth cranial nerve Wave II - Proximal eighth cranial nerve Wave III - Cochlear nucleus Wave IV - Superior Olivary complex Wave V - Inferior colliculus |
|
|
What are otoacostic emissions testing?
|
measuring the acoustic signals generated by cochlear outer hair cells, which are transmitted through the middle ear and to the ear canal, where they are recorded by a sensitive microphone.
|
|
|
What are the two types of otoacoustic emissions?
|
Evoked (EOAE)
Spontaneous (SOAE) |
|
|
Trace the pathway of energy transfer in OAE starting with the cochlea
|
OHC in cochlea --> basilar membrane --> cochlear fluids --> oval window --> ossicles --> TM (acts like a loudspeaker to the external ear canal)
|
|
|
Present OAE's indicate intact OHC function, but do absent OAE's necessarily indicate OHC malfunction? Why or why not.
|
Not necessarily, unless normal middle ear status is confirmed.
- the sound has to pass through the middle ear to be picked up in the EAC by a microphone, so if fluid in the middle ear, then will likely have absent OAE |
|
|
What are the three types of clinically recorder OAE's
|
1) Spontaneous OAE (SOAE) - only 35-60% of population have these
2) Transient OAE (TOAE) - occurs in response to transient signals such as clicks or very brief tone burst 3) Distortion product OAE (DPOAE) - occurs in response to two simultaneous brief pure tones of different frequencies (F1 and F2). F1 and F2 are typically separated by a ratio of 1.2 (so F2/F1 = 1.2). The new DP tone will be found at 2F1-F2 (ie..2(1000 Hz) - 1200 Hz = 800 Hz) |
|
|
A pt has 50db HL and an OAE are normal. Where is the site of the lesion most likely?
|
CN VIII. If OAE is normal, then the outer hair cells in the cochlea are working properly.
Remember that if OAE are low, the cause may also be an acoustic neuroma which is affecting cochlear blood flow. |
|
|
What are the three most common behavioral techniques for eliciting auditory responses in children?
|
1) Behavioral observation audiometry (BOA)
2) Visual reinforcement audiometry (VRA) 3) Conditioned play audiometry (CPA) |
|
|
What's the audiogram symbol for unmasked air conduction of the left and right ears?
|
Left - X
Right - O |
|
|
What's the audiogram symbol for masked air conduction of the left and right ears?
|
Left - ☐
Right - Δ |
|
|
What's the audiogram symbol for unmasked bone conduction of the left and right ears?
|
Left - >
Right - |
|
|
What's the audiogram symbol for masked bone conduction of the left and right ears?
|
Left - ]
Right - [ |
|
|
What is the name of the mandate targeted at catching hearing loss in newborns?
By which age does this need to occur? If hearing loss is present on screening, by which age does further testing need to be completed? If permanent hearing loss is confirmed, by which age must intervention take place? |
Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI)
Birth - 1 month 3 months of age 6 months of age |
|
|
What is the term used to describe either hearing behaviors discrepant with audiologic test results, inconsistent/invalid test results, or an alleged loss of hearing sensitivity in the abscence of organic pathology.
|
Pseudohypoacusis
It can be deliberate, unconscious or a mix of both. ("functional" and "nonorganic" have been used synonymously with PHA) |
|
|
What the the typical age among children with pseudohypoacusis? Male or female is more common?
|
Typical age is 11 yo
Twice as common in females |
|
|
What is the most common audiologic testing disparity in pseudohypoacusis?
|
Disparity between pure tone averages and speech recognition threshold (>10 dB).
|
|
|
What is the Stenger test used in pseudohypoacusis?
|
A test for detecting simulation of unilateral hearing impairment, in which a tone below the admitted threshold is presented to the test ear and a tone of lesser intensity is presented to the other ear. If the subject is feigning a hearing loss, the lesser tone cannot be appreciated.
|
|
|
For patient's receiving ototoxic medications, is low or high frequency testing performed along with pure tone thresholds in the conventional freq range?
|
High-frequency (10,000-20,000 Hz)
Detecting threshold changes in the high-freq range provides the physician the opportunity to change the medication protocol before the hearing loss affects the conventional frequency range and the pt's communication. |
|
|
What are the general criteria for ototoxic change on audiometry?
|
1) Threshold shift of 20 dB or greater at any one test frequency
2) Threshold shifts of 10 dB or greater at any two adjacent frequencies 3) Loss of response at any three consecutive frequencies where thresholds were previously obtained |
|
|
What are the five types of hearing aids?
|
1) Body aid
2) Behind the ear (BTE) 3) In the ear (ITE) 4) In the canal (ITC) 5) Completely in canal (CIC) |
|
|
Which hearing air is able to pick up the signal on the poor side and route it to the normal hearing ear. Used in unilateral, unaidable hearing losses.
|
Contralateral routing of signal (CROS)
|
|
|
What are some examples as to when you would use a BAHA as apposed to an AC hearing aid?
|
Atresia of the ear canal
Chronic purulent otitis media or externa |
|
|
What device can help patients with tinnitis?
|
A tinnitus masker. Some hearing aids combine a tinnitus masker
|
|
|
At any age, the single most important element in hearing (re)habilitation is proper __________.
|
amplification
|
|
|
What does hearing loss from noise looks like on an audiogram?
|
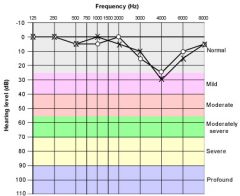
Begins in a notch pattern in the 3000-6000 Hz region, but as time broadens to the other frequency regions with a less steep slope.
|

