![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Auricular hematoma:
1) more common name? 2) Tx |
1) cauliflower ear
2) Evaculate hematoma, repair incision, place bolster |
|
|
Random systemic disease which can cause epistaxis?
|
Osler-Weber-Rendau
|
|
|
Common systemis disease which can predispose to epistaxis
|
hypertension
|
|
|
Drugs which predispose to epistaxis
|
coumadin, plavix, apsirin
|
|
|
Local cause of epistaxis
|
trauma: digital, fracture
|
|
|
Epistaxis is an emergency ONLY of a person:
|
cannot manage their airway
|
|
|
1)most common site of epistaxis
2) ant or post? |
Keiselbachs plexus, anterior
|
|
|
Keisselbachs plexus gets blood supply from:
|
both internal and external carotid (opthalmic and, facial, lingual)
|
|
|
Tx for epistaxis
|
compress for 20 minutes
|
|
|
Mot common treatment for a persistent nose bleed, and what is done if that doesnt work
|
1) anterior nasal pack
2)and and posterior nasal pack |
|
|
Surgical treatment of epistaxis
|
IR ligation of the sphnopalatine, and anterior ethmoidal artery
|
|
|
Most common bacterial causes of acute sinusitis
|
S. pneumo, H. flu
|
|
|
What is the mode of spread of acute sinusitis?
|
hematogenous through the valve-less veins of the mid-face and intra-cranial cavity.
|
|
|
complications of acute sinusitis
|
orbital infections, intracranial abscess, meningitis and cavernous sinus thrombosis.
|
|
|
Indications for urget surgery for sinusitis complications
|
Intracranial involvement
Near total opthalmoplegia Worsening visual acuity or ocular exam while on medical treatment Failure to improve within 48 hours of medical treatment |
|
|
Seatelt injuries can cause:
|
Fracture of laryngeal cartilage
|
|
|
NECK ZONE 1
1) define 2) Mode of evaluation for penetrating injury |
1) below clavicle
2) ANGIOGRAM |
|
|
NECK ZONE 2
1) define 2) Mode of evaluation for penetrating injury |
1) mandible to clavicle
2) exploration |
|
|
NECK ZONE 3
1) define 2) Mode of evaluation for penetrating injury |
1) ABOVE mandible
2) ANGIOGRAM |
|
|
Which two neck zone require angiogram?
|
1 and 3 ( ANYTHING above mandible or below clavicle)
|
|
|
Know the three zones of the neck
|
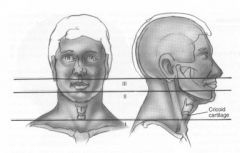
|
|
|
Inspiratory stridor is due to obstruction
|
Extrathoracic: Tupraglottic
|
|
|
Expiratory stridor is due to obstruction:
|
Intrathoracic: trachea/lungs
|
|
|
Biphasic stridor is due to obstruction:
|
Subglottis
|
|
|
At barnes who adresses a peds airway?
|
an ENT AND a Anesthesiologist
|
|
|
Drooling is a sign of?
|
Airway obstruction
|
|
|
Steeple sign on plain film indicates?
|
Croup
|
|
|
Presentation of a retropharyngeal abcess
|
High WBC, fever, ring enhancing lesion which may compress airway
|
|
|
Floor of mouth Abcess is called?
|
Ludwigs Angina?
|
|
|
Describe Ludwigs angina
|
floor of mouth abcess that is ROCK HARD, this abcess raises the tongue to touch the top of the mouth.
|
|
|
What is the probable cause of ludwigs angina?
|
Odontogenic
|
|
|
Why do cric instead of a trach in emergency situation?
|
cricothyroid membrane is thing and close to skin
|
|
|
What can one do if there is dificulty getting an airway in a non-obstucted pt.?
|
Bag the patient
|
|
|
Danger of tracheostomy?
|
false passage into space behind sternum
|
|
|
1) Position of head best for manipulation of neck and airway
2) caution? |
1) extended
2) spine trauma |
|
|
Location of cricothyroid membrane?
|
between thyroid cartilage and cricoid cartilage
|

