![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
7 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|
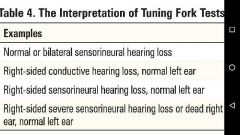
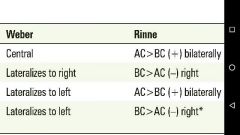
Conductive Hearing Loss
• conduction of sound to the cochlea is impaired • can be caused by external and middle ear disease |
Sensorineural Hearing Loss • due to a defect in the conversion of sound into neural signals or in the transmission of those signals to the cortex • can be caused by disease of the inner ear (cochlea), acoustic nerve (CN VIII), brainstem, or cortex |
|
|
|
|
|
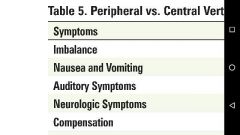
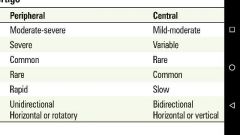
Differential Diagnosis of Vertigo Based on History Differential Diagnosis of Vertigo Based on Time Course |

|
|
|
Retropharingeal abscess |
-- Neck pain, fever, limited neck mobility -- Trismus (innability to open mouth normally) -- Due to local trauma * CT of the neck ** Treatment: IV anibiotics and urgent grainage |
|
|
Herpangina |
-- Coxsackie A virus -- vesicles on the tonsils and soft palate -- Tipically in children -- Sore throad, fever, and pain with swallowing |
|
|
Malignant Otitis Externa |
-- Severe pseudomonal infection -- Granulation tissue -- Eldery, with poor controled diabetis -- Severe ear pain, drainage and fever -- Osteomyelitis of the skull base or temporomandibular joint can develop ** Systemic therapy with anti-pseudomonal antibiotics --> ciprofloxacin |

