![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Energy |
Capacity to do work |
|
|
Kinetic energy |
Energy due to motion |
|
|
Potential Energy |
Energy due to position or composition |
|
|
System (chemistry) |
Usually a closed container of a substance or a chemical reaction |
|
|
Surroundings |
Everything else that is part of the system |
|
|
Heat |
AKA thermal energy • Energy transferred as a result of a temperature difference between system and surroundings |
|
|
Work |
All other forms of energy transfer when an object is being moved by a force |
|
|
q |
Heat |
|
|
w |
Work |
|
|
∆E |
Change in energy |
|
|
q + w = |
∆E |
|
|
(+) heat |
Heat absorbed |
|
|
(-) heat |
Heat released |
|
|
(+) work |
Work done on |
|
|
(-) work |
Work done by |
|
|
(+) ∆E |
Internal energy increases |
|
|
(-) ∆E |
Internal energy decreases |
|
|
State functions |
Anything with ∆ in front of it |
|
|
∆E |
Only depends on final and initial state ∆E= E(final) - E(initial) |
|
|
P |
Pressure |
|
|
P = |
Force/Area |
|
|
Units: atm |
Atmospheres |
|
|
P(ext) |
(constant) external pressure |
|
|
∆V |
Change in volume |
|
|
1 atm • 1L = |
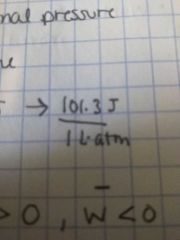
101.3 J
101.3 J ----------- 1L•1atm |
|
|
w = |

-P(ext)•∆V |
|
|
V final > V initial |
Gas expands
∆V is (+) W is (-) work done BY system |
|
|
V final < V initial |
Gas compressed ∆V is (-)W is (+) work done ON system |
|
|
H |
Enthalpy |
|
|
∆H |
Change in enthalpy Heat measured at constant P |
|
|
∆H = |
qp = ∆E + P•∆V |
|
|
1) Reactions NOT involving gases |
Very small volume changes P∆V ~ 0 ∆H~∆E |
|
|
2) Reactions where moles of gas DOES NOT change |
Ex: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) = 2HCl (g) P∆V = 0 P∆V = 0∆H = ∆E ∆H = ∆E |
|
|
3) Reactions where mole of gas DOES change |
2CO (g) + O2 (g) = 2CO2 (g)
P∆V not equal 0 P∆V <<< q•p ∆E not equal to ∆H ∆H~∆E
|
|
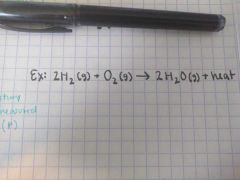
Exothermic |
qp = ∆H < 0 Heat is released as a "product" Temperature of surroundings increases |
|
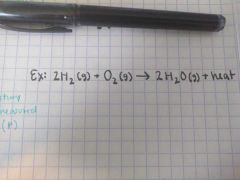
Exothermic |
qp = ∆H < 0 Heat is released as a "product" Temperature of surroundings increases |
|
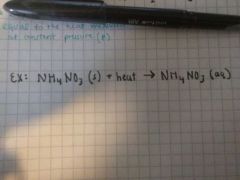
Endothermic |
qp = ∆H < 0 Heat is absorbed, can be shown as "reactant" Temperature of surroundings decreases |
|
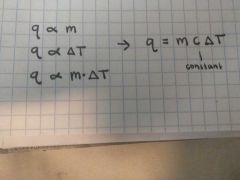
q α [heat is proportional to] |
m [mass] ∆T [change in temperature] C [constant]
|
|
|
Specific heat capacity |
C: amount of heat needed to raise the temp. of 1g of substance by 1°(1k) |
|
|
Molar Heat capacity (C) |
The amount of heat needed to raise temp. Of 1 mole of substance by 1K (°C)
|
|
|
Specific Heat capacity of water 💧 |
C= 4.184 J/gK |
|
|
Molar heat capacity of water 💧 |
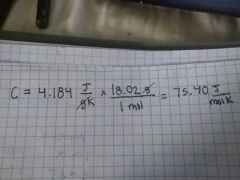
C |
|
|
Mass of H2O with 50 mL |
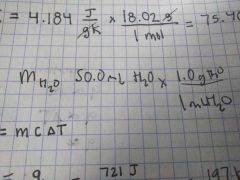
50 mL • 1 g H2O ------------- 1mL H2O |
|
|
Oz. to g |
M= 1.00 oz • 28.35 g ----------. = 28.35 g 1 oz |
|
|
Celsius to Kelvin |
+ 273.15 |

