![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
40 y.o. male w/ c/o HA, decreased libido, during workup found to have decreased testosterone, decreased LH/FSH, prolactin level is 800. on visual field exam has bitemporal hemianopia. what's the diagnosis? what test will you order? how do you treat it?
|
prolactinoma, order MRI, though can also use CT. treat w/ bromocriptine or cabergolin, two dopamine agonists which inhibit prolactinoma. if they can't tolerate either they go for surgery.
|
|
|
A pt w/ prolactinoma, taking bromocriptine or cabergolin became pregnant what do yo do?
|
stop the medications
|
|
|
how do you follow prolactinoma during pregnancy??
|
by regular visual exam, not by doing an MRI every month. can't measure prolactin levels b/c they're high in pregnancy anyway.
|
|
|
a young female comes in w/ complaint of milk discharge coming from the nipple. which of the following is important to ask in the history?
|
Ask about her medications
|
|
|
young female w/ c/o amenorrhea, weakness, galactorrhea, workup suggests pregnancy negative. prolactin level is 100. LH, FSH, and cortisol levels are normal. TSH is 25 (0.5-6 is normal), total T4 is 3 (5-15). how do you manage this patient?
|
patient has high prolactin levels because of hypothyroidism. start levothyroxine instead.
|
|
|
50 y.o. M c/o HA, arthritis, enlarging shoes and glove size, increased head size. O/E has prominent jaw, increased soft tissue in palm and sole. Large tongue. increased glucose level in the blood. what's the diagnosis? what's the best test to screen for this? how do you treat
|
acromegaly. screen with IGF-1 or oral glucose suppressant test if the findings of IGF-1 are equivocal. order an MRI afterwards to look for pituitary adenoma. treat w/ transphenoidal surgery.
|
|
|
A long distance runner came w/ amenorrhea, pregnancy test is negative, LH/FSH is decreased, prolactin level is normal. what do you do next??
|
tell the patient to stop running so much. no further study required.
|
|
|
pt w/ h/o peripartum hemorrhage, required multiple blood transfusions. since last pregnancy the patient never menstruated. c/o weakness easy fatiguability, has loss of axillary and pubic hair. what's the diagnosis?
|
Sheehan syndrome (post partum pituitary necrosis)
|
|
|
26 y.o. comes w/ c/o weakness, impotence, as a child has h/o ALL. treated w/ chemotherapy and intracranial brain radiation. in the lab TSH is normal, free T4 is low, cortisol is low, LH-FSH is normal. what's the diagnosis?
|
radiation induced hypopituitarism.
|
|
|
10 y.o. c/o HA, visual disturbance, poor sexual development, increased prolactin level, CT scan of head shows dense suprasellar calcifications. what's the diagnosis??
|
craniopharyngioma, (dense suprasellar calcification)
|
|
|
young pt w/ symptoms of pituitary adenoma has suprasellar calcifications. what's the diagnosis? how do you treat?
|
craniopharyngioma. treat w/ surgery.
|
|
|
pt on lithium has decreased free T4, increased TSH, what's the diagnosis? what do you do?
|
lithium induced hypothyroidsim? Continue lithium and start levothyroxine
|
|
|
a hypothroidism pt becomes pregnant, what do you do??
|
increase dose of levothyroxine and check TSH after 4 weeks
|
|
|
70 y.o. male brought to the emergency room as he was found in coma in the snow. the pt is having hypothermia, bradycardia, dry skin, hair loss, puffy eyes, what's the diagnosis? how do you treat this patient?
|
myexedema coma secondary to hypothyroidism. treat w/ IV hydrocortisione and IV levothyroxine
|
|
|
pt on propylthiouracil came w/ c/o fever, sore throat, cough, what next test will you like to order?
|
order CBC, b/c pt is on propylthiouracil and may develop agranulocytosis
|
|
|
pt presents w/ symptoms of thyrotoxicosis, atrial fibrillation, fever, delirium, tachycardia, diarrhea, what's the diagnosis? how do you treat?
|
thyroid storm (when delirious it is called thyroid storm). treat w/ propanolol, iodide, propylthiouracil, and hydrocortisone
|
|
|
pt w/ recent h/o URI comes w/ symptoms of thyrotoxicosis, has painful enlargement of thyroid. O/E thyroid is large and tender. what's the diagnosis? subacute thyoriditis. how do you confirm?
|
subacute thyoriditis. confirm w/ RAI the uptake will be low. treat w/ aspirin and propanolol.
|
|
|
pt w/ PNA, septic, intubated, on vasopressors, thyroid shows low T4, free T4 low, TSH is low. what's the diagnosis?
|
sick euthyroid syndrome
|
|
|
A pregnant pt, referred from obstetrician is found to have increased total T4. Free T4 is normal. TSH is normal. what's the diagnosis?
|
increased thyroid binding globulin is increased (same as for patients on oral contraceptives)
|
|
|
pt w/ papillary thyroid ca is status post-thyroidectomy on levothyroxine 100 mg/day. has TSH level of 0.2 (0.5-0.6). will you continue the same dose?
|
yes, because we want the TSH to be low to prevent stimulation of the remaining thyroid ca cells.
|
|
|
pt w/ hypothyroid on levothyroxine comes for f/u. TSH is 0.2 (0.5-6). what do you do next?
|
decrease the levothyroxine dose
|
|
|
pt has developped diabetic nephropathy what is the most important thing to do to prevent progression of the disease?
|
tight blood pressure control <130/80! not glucose control. most important once diabetic nephropathy develops.
|
|
|
pt w/ DKA, blood sugar is 800, ketones are strongly positive. started on IV insulin and normal saline. blood glucose is 150. what do you do next?
|
change IV fluid to D5W or D5W normal saline and continue insulin drip.
|
|
|
pt w/ DKA on IV fluild plus IV insulin. after acidosis improves, serum ketones became negative insulin drip was discontinued. pt started on sliding scale for insulin. after 3 hours finger stick is again high and serum ketones are positive. what went wrong in the management?
|
they did not give subcutaneous insulin before discontinuing IV insulin. ketogenesis will start again in absence of insulin.
|
|
|
a type 2 diabetic pt c/o change mental status while in the ED develops seizures. In the lab blood sugar is 900. serum ketones are negative. BUN/Cr is high. what's the diagnosis? how do you treat?
|
non-ketotic hyperosmolar syndrome. BUN is high because of dehydration. treat w/ IV fluid normal saline and IV insulin.
|
|
|
a diabetic patient comes to the ED w/ change in mental status, diaphoresis, tachycardia, what do you do next?
|
fingerstick, if glucose is low give 50% dextrose 50 cc IV, if IV access is not available give them glucagon 1 mg IM or subcutaneous and then search for IV line.
|
|
|
young female came to ED w/ change in mental status, blood sugar is 35. after D50 she is asymptomatic. what do you do next?
|
check C-peptide level, she is taking insulin from the outside. factitious hypoglycemia
|
|
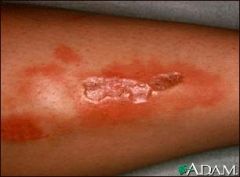
identify this abnormality? it is a sign of what disease
|
necrobiosis lipoidica a complication of diabetes
|
|
|
pt w/ weakness, central obesity, easy bruisability, increased 24 hour urine for free cortisol, decrease ACTH, what next test would you like to order?
|
order CT scan of abdomen to look for adrenal adenoma because the ACTH is low and cortisol is high.
|
|
|
alcohol abuser has nausea, vomiting, muscle spasm, potassium is 2.9, calcium is 6.5, potassium and calcium being supplemented but is not corrected. what to do next?
|
check magnesium level as it is hard to correct in hypomagnesium
|
|
|
20 y.o. man has short stature, comes to you w/ h/o muscle cramps, calcium is low, phosphorous is high, PTH is high, what's the likely diagnosis?
|
pseudohypoparathyroidsims
|
|
|
pt w/ bony pain has increased head size, deafness, calcium is normal, phosphorous is normal, alk phos is high. what's the diagnosis? what investigation?
|
paget's disease? bone scan.
|
|
|
pt w/ hirsutism has increased testosterone, increase DHEA, normal 17-OH progesterone. wha do you order next?
|
abdominal CT to look for adrenal tumor.
|
|
|
pt w/ hirsutism has increased testosterone, normal DHEA, normal 17-OH progesterone. wha do you order next?
|
pelvic ultrasound for ovarian tumor
|
|
|
35 y.o. male who is a long distance runner, married to miss america, came for workup of fertility. on examination a muscular man w/ gynecomastia testicular atrophy, decreased sperm count. which of the following questions would you like to know in the history??
|
is he using anabolic steroids
|
|
|
male pt came for workup of fertility, on examination a tall man w/ gynecomastia, small testes, azospermia, what's the diagnosis?
|
klinefelter's syndrome
|
|
|
young girl w/ short stature, web necked, amenorrhea, high LH-FSH, wide spaced nipples. what's the diagnosis?
|
turner's syndrome
|
|
|
male pt w/ infertility has anosmia. what's the diagnosis?
|
kallman's syndrome.
|
|
|
what are the most common types of thyroid nodules???
|
1. colloid nodule and follicular adenoma
|

