![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
45 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
4 types of thyroididis.
|
1. acute thyroiditis
2. subacute grannulomatous thyroiditis (DeQuervain's) 3. Hashimoto's thyroditis 4. fibrous (Riedel) thyroiditis |
|
|
What type of thyroiditis is this?
- begins as headache and myalgia - painful neck that raidiates to the jaw - biopsy: giant cells, damaged/collapsed follicles |
subacute granulomatous thyroiditis (DeQuervains)
- viral or postviral process |
|
|
What is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in US adults?
|
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
|
|
|
Pathogenesis of Hashimoto's thyroiditis.
|
1. CD4 T cell sensitization to thyroid antigen
2. helper T cells 3. CD8 toxicity through Fas-L 3. CD4 Th1 -> INF -> macrophage 3. plasma cell -> antibodies to TG, TSHR, thyroid peroxidase -> Fc receptor of NK cells - |
|
|
What is this disease?
- enlarged nodular thyroid - geminal centers, lymphocytic infiltration, Hurthle cells in atrophic follicles - hypothyroid |
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
|
|
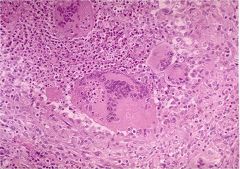
What type of thyroiditis is this?
|
Subacute granulomatous thyroiditis
- giant cells - collapsed follicles - surrounding macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells |
|
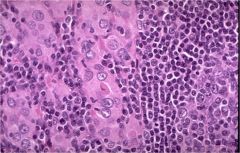
What type of thyroiditis is this?
|
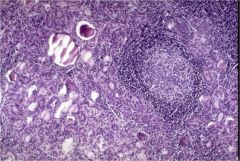
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- hurthle cell: metaplasia - germinal center - atrophic follicles - lymphocytic infiltration |
|
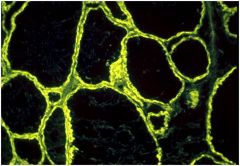
What is this disease?
- anti-TPO stain |
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
- diagnostic test of choice - other test: anti-TG stain |
|
|
Compare Hashimoto's and Riedel thyroiditis.
|
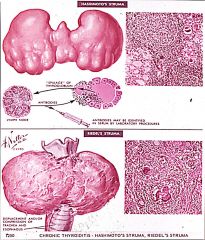
|
|
|
What type of thyroiditis is this?
- rock hard fixed mass - hypothyroid - fibrosis |
Reidel thyroiditis
|
|
|
In which type of thyoiditis would you see increased incidence of papillary carcinoma and B cell malignant lymphoma?
|
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
|
|
|
What is Hashimoto's toxicosis?
|
initial hyperthyroidism due to inflammation
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- hyperfunctioning, hyperplastic goiter - exophthalmos - pre-tibial, ankle edema - micro: papillary hyperplasia/infoldings |
Grave's disease
- IgG to TSHR and mimics the action of TSH (increase cAMP) |
|
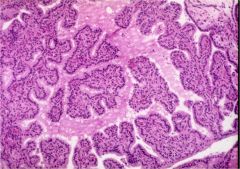
What is this disease?
- gross: diffusely enlarged ithyroid - symptoms: goiter, exophthalmos, ankle edema |
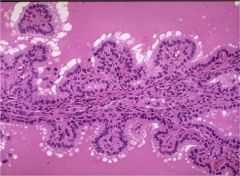
Graves disease
- IgG against TSHR - papillary infoldings, hyperplasia |
|
|
What is the most common cause of this?
- diffuse nontoxic goiter |
iodine deficiency
- high TSH -> follicular cell hyperplasia and hypertrophy - goitrogens: cabbage, brussel sprouts, cassava |
|
|
Mechanism of action of goitrogens such as cabbage, brussel sprouts, cassava.
|
inhibit iodide transport within thyroid
|
|
|
What is the most common type of goiter in the US?
|
diffuse nodular goiter
|
|
|
What % thyroid nodules are neoplastic?
|
low
if neoplastic, 90% are adenomas |
|
|
Benign or malignant?
- "hot" nodules on scintiscan |
- most likely benign
- likely to be malignant in young people |
|
|
A thyroid nodule in a male is more likely to be ____ (benign/neoplastic).
|
neoplastic
|
|
|
Low dose therapeutic radiation has risk for what type of thyroid diseases?
|
- nodular goiter
- adenomas (single nodular or enlarged multinodular) - chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis - papillary carcinoma (more multicentric and bilateral) |
|
|
What type of goiter is this?
- euthyroid - colloid rich - micro: areas of hemosiderin, cystic degeneration, calcifications, fibrosis |
nodular goiter (adenomatous)
|
|
|
What is the initial step in diagnosing thyroid nodules?
|
fine needle aspiration
- 25 or 27 gauge needle - 4-6 samples |
|
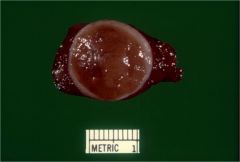
What is this disease? What would you see on histologic section?
|
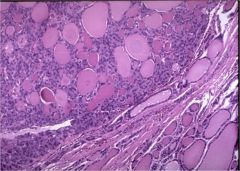
follicular adenoma
- gross: solitary, discrete, well circumscribed, connective tissue capsule - micro: hurthle cells. Do not transgress the capsule, do not invade blood vessels. |
|
|
Pathogenesis of follicular adenomas.
|
- gain of function on TSHR or alpha subunit of Gs cause excess cAMP
|
|
|
Name the four malignant thyroid tumors. Which is the most common?
|
- papillary carcinoma (most common)
- follicular carcinoma - medullary carcinoma - anaplastic carcinoma (worst prognosis) |
|
|
Pathogenesis of papillary carcinoma.
|
- reciprocal translocation between chromosome 10 and 17 which creates ret/PTC oncogene
- consequence of irradiation during first 2 decades of life |
|
|
Is high dose I131 tumorogenic?
|
No. Only therapeutic radiation is tumorogenic.
|
|
|
Which malignant papillary carcinoma?
- gross: gray-white, firm, calcifications - micro: orphan annie nuclei, psammoma bodies - invading lymphatics |
papillary carcinoma
- lots of occult cyts, so treatment is to remove all thyroid tissue. |
|
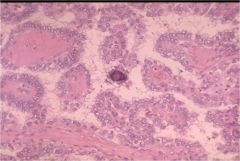
What is this thyroid tumor?
|
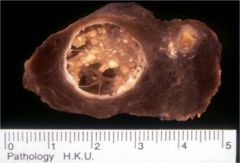
papillary carcinoma
- gross: gray-white, firm, often with calcifications, cystic change - micro: orphan annie nuclei, psommoma bodies. - lymphatic spread |
|
|
What is the prognosis of papillary carcinoma?
|
90% survival at 20 yrs
favorable factors - female - under age 20 - confinement to thyroid gland |
|
|
Pathogenesis of follicular carcinoma.
|
fusion gene PAX8-PPAR-gamma1
|
|
|
What thyroid condition may develop into follicular carcinoma?
|
- multinodular goiters
- but most are de novo |
|
|
What is this thyroid tumor?
- capsular, vascular invasion - sometimes "warm" - tend to metastasize by hematogenous route to lungs and bones |
follicular carcinoma
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of follicular carcinoma?
|
- good prognosis when it is well circumscribed
|
|
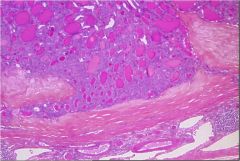
What is this thyroid tumor?
|
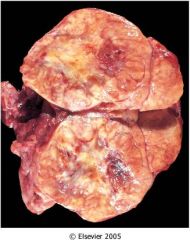
follicular carcinoma
- neoplastic cells invading fibrous capsule - vascular invasion |
|
|
Pathogenesis of medullary carcinoma.
|
- cancer of parafollicular C cells: secrete calcitonin
- 20% associated with MEN syndromes IIa and IIb |
|
|
What is this thyroid tumor?
micro - round to polygonal cells in sheets with amyloid stroma |
medullary carcinoma
|
|
|
What is the prognosis of medullary carcinoma?
|
- familial medullary carcinoma: fairly indolent
- poorer prognosis if associated with MEN IIb. |
|
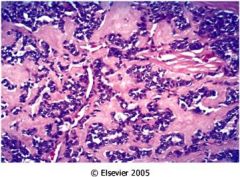
What is this thyroid tumor?
|
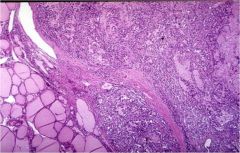
medullary carcinoma
- abundant amyloid stroma between neoplastic cells - neoplastic cells form sheets |
|
|
What is this?
- mucosal neuromas - pheochromocytoma - medullary carcinoma of thyroid |
MEN type IIB
|
|
|
What is this?
- parathyroid hyperplasia - pheochromocytoma - medullary carcinoma of thyroid |
MEN type IIA
|
|
|
What is this disease?
- neuromas in lips, tongue, buccal mucosa - enlarged bubbery lips - weakness, HTN, diarrhea - lump in the neck |
MEN type IIB
- mucosal neuromas: plexiform - pheochromocytoma (bilateral): weakness, HTN, diarrhea - medullary carcinoma of thyroid: lump in the neck |
|
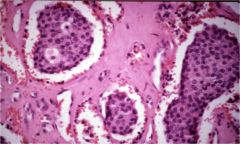
What is this disease?
- mucosal neuroma - diarrhea, HTN - lump in the neck |
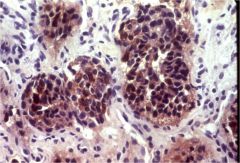
MEN type IIB
- mucosal neuroma - pheochromacytoma: diarrhea, HTN - medullary carcinoma: lump in the neck. scerete calcitonin (see figure) |
|
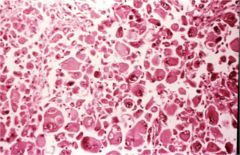
What is this disease?
|
anaplastic carcinoma of thyroid
- fatal within 1 year |

