![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a. In 4 words, describe the Endocrine System - Endocrine Glands control activities which require __(b)__, not __(c)__ d. Give 5 functions of the Endocrine System |
a. Long Distance Regulatory System b. Duration c. Speed d. - Controls Reproduction - Regulates Red Blood Cell production - Supports Smooth, Sequential Growth + Development - Homeostasis (Electrolyte/Water/Metabolic Nutrient balance) - Adaptive changes to help the body withstand stressful situations |
|
|
a. Name the 3 Endocrine glands b. Name 4 Peripheral Exocrine glands c. Which 4 glands have a SOLELY Endocrine function? |
a. - Pineal gland - Hypothalamus - Pituitary Gland b. - Thyroid - Parathyroid - Pancreas - Adrenal c. - Pituitary glands (x2) - Thyroid - Parathyroid - Adrenal glands (x2) |
|
|
a. Give the definition of a Hormone |
a. - a long-distance Chemical Mediator - secreted by an Endocrine Gland - into the Blood, where it is transported to Target Cell |
|
|
- Hormones are __(a)__ to their __(b)__ - Target Cell Receptor Proteins include __(c)__ and __(d)__ - Hormones direct their effect by __(e)__ |
a. Specific b. Target cells c. Transmembrane receptors d. Intracellular receptors e. Altering Intracellular Proteins |
|
|
Hormone Classification is based on either of which two things? |
Solubility or Biochemical Structure |
|
|
a. In relation to Hormone Solubility, hormones can be either of which 2 things? b. Give examples |
a. Hydrophilic or Hydrophobic/Lipophilic b. Hydrophilic: - Peptides - Indoleamines - Catecholamines Hydrophobic: - Steroids - Thyroid hormones |
|
|
a. Where are Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic hormones found? b. What kind of hormones are the most abundant? + example c. What are Amine hormones |
a. Hydrophilic: Dissolved in Plasma Hydrophobic: Bound to carrier Proteins b. Peptide/Protein (amino acids) c. Derivatives of Amino Acids |
|
|
What are the 3 types of Amine Hormones? |
1. Indoleamines 2. Thyroid 3. Catecholamines |
|
|
a. What are Steroids (hormone)? b. What are they derived from? c. Give 2 examples of Steroid hormones |
a. Neutral LIPIDS b. Cholesterol c. - Cortisol - Sex hormones |
|
|
a. Describe the interaction with a Hydrophobic Hormone with its target cell b. Describe the interaction with a Hydrophilic Hormone with its target cell |
a. - Hormone/ligand binds to transmembrane receptor - This activates the Secondary Messenger - This alters the activity of Pre-existing IC proteins b. - Hormone/ligand with receptor INSIDE target cell - This activates specific Genes - Formation of new IC proteins |
|
|
Name the 3 ways in which hormones can be regulated |
1. Negative feedback 2. Neuroendocrine reflexes 3. Diurnal Variation |
|
|
a. Define Negative Feedback (hormones) b. What does Negative Feedback ensure? |
a. Effect of a Hormones actions can inhibit its own secretion b. Ensures things are TURNED OFF |
|
|
a. Give an example of a hormone which undergoes Negative Feedback + classify it b. Give 2 important functions of this hormone |
a. Thyroid Hormone (Amine hormone + Hydrophobic) b. - Important role in setting Metabolic Rate - Thermoregulation (chemical induced thermogenesis) |
|
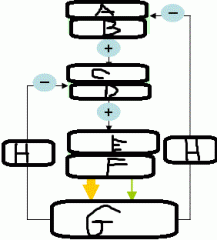
|
a. Hypothalamus b. TRH c. Pituitary gland d. TSH gland e. Thyroid gland f. T3 + T4 g. Target cells h. T3 +T4 |
|
|
In a negative feedback loop involving Thyroid hormone, what causes negative feedback on what? |
- T3 + T4 - Cause Negative Feedback on Hypothalamus and Pituitary gland - Therefore, Pituitary gland does not induce Thyroid gland to produce Thyroid Hormone |
|
|
a. What are the 2 components of a Neuroendocrine reflex? b. Describe what a Neuroendocrine reflex is |
a. Neural and Hormonal components b. - A rapid increase in Hormone Secretion - In response to Stimuli |
|
|
a. Describe what Diurnal Variation is b. What is secretion related to? + example |
a. Variation in amount of hormone produced throughout Day/Month b. In Diurnal Variation, secretion is related to EXTERNAL CUES e.g. Light/Dark |
|
|
What are the 2 functions of a TROPIC hormone? |
- Stimulate the release of another hormone - Maintain and Stimulate Endocrine Target Tissue |
|
|
a. Give 2 examples of Tropic Hormones b. State where they are secreted from + their functions |
a. TSH ans TRH b. TSH: - Secreted from Anterior Pituitary gland - Stimulates Thyroid gland to release Thyroid hormones (T3 + T4) TRH: - Secreted from Hypothalamus - Stimulates Anterior Pituitary gland to secrete TSH |
|
|
a. How do Tropic Hormones from the Hypothalamus get to the Anterior Pituitary gland? b. Describe 3 Tropic Hormone pathways |
a. Via the Hypothalamus-Pituitary PORTAL VEIN b. 1.) TRH (h) ---> TSH (ap) ---> Thyroid (Thyroid G) 2.) CRH (h) ---> ACTH (ap) ---> Cortisol (Adrenal C) 3.) GnRH (h) ---> LH/FSH (ap) ---> (Gonads) - Female: Estrogens + Progesterone - Male: Androgens |

