![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hormones of the thyroid gland |
Thyroxine T3 Triiodothyronine T4 |
|
|
Synthesis and secreation of thyroid hormone |
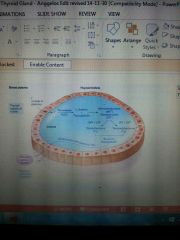
Iodine found in food and water combines with tyrosine and form thyroxine and triiodothyronine Iodide trap- iodine from food and drinks is reduce to iodide in the GIT and is concentrated in the thyroide gland by the iodide pump stimulated by TSH Transport bind to pendrin Iodide oxidation- peroxidase and hydrogen peroxide oxidase iodide to iodine Thyroglobulin synthesis- takes place in the follicular cells Exocytosis Iodination- free iodine attaches to position 3 of tyrosyl molecule to form MIT and position 5 to form DIT coupling- 2 molecule of DIT form thyroxine and 1 MIT and DIT form trioidothyronine Pinocytosis Proteolysis Secreation |
|
|
Transport of thyroid hormones |
T3 - albumine T4- globulin |
|
|
Levels of thyroid hormones in plasma |
T4 - 8 T3- 0.15
|
|
|
Half life of thyroid hormes |
T4 - 6-7days T3- 1-2days |
|
|
T3 |
Increase activity and synthesis of Na/k ATPase pump Increase protein synthesis |
|
|
Hyper and hypo thyroidism |
Hyper increase metabolism Hypo decrease metabolism |
|
|
Hormones of pancreas |
Alpha- glucagon increase blood glucose Beta- insulin decrease blood glucose Delta- somatostatin inhibition of glucagon insulin and PP F cells- pancreatic polypeptide |
|
|
Insulin |
Contain 2 alpha and 2 beta subunit linked by disulfide bonds Alpha subunit lies outside the cell Beta subunit have tyrosine kinase activity |
|
|
Mechanism of action of insulin |
Bind to insulin subunit activate tyrosine kinase activity on beta subunit causing autophosphorylation of beta subunit |
|
|
Action of insulin |
It increase uptake of glucose except from the brain RBC kidney and GI Convert excess glucose to triglycerides |
|
|
Regulation of insulin secretion |
Arginine and lysine increase insulin secreation Anti-natriuretic effect Increase potassium in cells Increase uptake of phosphates |
|
|
Glucagon |
Increase glycogenolysis Increase gluconeogenesis Inhibit storage of triglycerides Activating adipose cell lipase and makes fatty acids available for energy |
|
|
Hyperinsulinism |
Excess insulin in blood Brain starvation leads to death Stimulate epinephrine |
|
|
Parathyroid gland hormones |
Chief cells- Bones- increase osteclast bone remodeling GI- increase formation of vitD Kidney- increase calcium reabsorption Oxyphil |
|
|
Disorders of parathyroid glands |
Hypo- muscle spasm twitch Hyper- otitis fibrosa cystica |
|
|
Anterior pituitary |
Six protein hormones Adrrnocorticotropic hormones regulate the synthesis and secreation of glucocorticoids and androgens from adrenal cortex CHR regulate ACTH increases when stressed Thyroid stimulating hormones- increase in morning decrease at night Growth hormone- increase at night Decrease with age Regulate growth and metabolism Obesity decrease GH FSH spermatogenesis LH estrogens Progesterone Testosterone |
|
|
Hormones |
Way in which cells communicate with each other |
|
|
Autocoids |
Prostaglandin Bradykinin Serotonin |
|
|
Location of hormones receptor |
Steriods- cytoplasm Thyroid- nucleus Amines and peptides- cell membrane |
|
|
Posterior pituitary |
ADH- release when increase osmolarity of the blood and low blood volume Oxytocin- stimulate the nipples during breast feeding cervical dialatation |
|
|
Adrenal cortex |
Zona glomerulosa- aldosterone Zona fasciculata- glucocortucoid Zona reticularis- androgen |
|
|
Glucocorticoids |
Cortisol Bind to globulin Increase during street any type cortisol block inflammation and help in healing High in morning low at night |
|
|
Adrenal medulla |
Make 80%epinephrine and nor 20%epinephrine Formed in chromoffin cells from tyrosine Nor adrenaline more alpha caise in contraction on all blood vessels |
|
|
Hypoadrenalism addison's disease |
Atrophy autoimmunity or destruction of adrenal cortex |
|
|
Hyperadrenalism Cushing disease |
Increase cortisol |
|
|
Primary aldosteronism conn syndrome |
Tumor of the zona glomerulosa Hypokalemia Hypertension |
|
|
Growth hormone |
Causes growth in bone cartilage and soft tissue Too much causes giganitism in children Acromegaly in adult Too little dwarfism |
|
|
Prolactin |
Lactation Too much infertility and amenorrhea |
|
|
Sheehan's syndrome |
Necrosis of the pituitary with associated hypopituitarism resulting from postpartum hemorrhage |
|
|
Regulation pattern of hormones |
Chronic- thyroid Acute- adrenal Episodic- FSH LH |
|
|
One hormone multiple action |
Testosterone |
|
|
One action multiple hormone |
Glucogon |
|
|
Panhypopituitarism |
Deficiency of 2 or more pituitary hormones |
|
|
Vitamin D binds to |
Globulin |
|
|
Plasma total calcium and ionized |
2.5-2.7 1.1-1.4 |
|
|
Hormones that need cAMP |
FSH LH ADH TSH ACTH glucogon
|
|
|
Peptide hormons |
Glucogon Oxytocin ADH insulin |
|
|
Metabolic clearance rate |
the quantitative removal of hormone from plasma Kidney and liver |
|
|
Lipid soluble hormone |
Aldosteron Calcitriol Testosterone Estrogen Progesterone T3 T4 |
|
|
Prolactin stimulation |
Sleep Exercise Stress pregnancy Sucking |
|
|
Transport of oxytocin and ADH |
In Secretary granules which flows to nerve ending to the posterior p ituritory Short half life |
|
|
Storage of calcium |
Mitochondria ER |
|
|
Function of calcium |
Formation of bone and tissue Blood coagulation Muscle contraction Tissue excitability |
|
|
Function of phosphate |
Part of the glycolic compound Regulation of blood and urin pH Part of energy transfer compound Found in bone and teeth |
|
|
Control of secreation of parathyroid hormone |
Increase in phosphate Calcitonin Ca low than 7-11 |
|
|
Osteoporosis |
Adult Reduced bone mass Normal calcification |
|
|
Osteomalacia |
Children Normal bone mass Disease calcification |
|
|
Neurons in the satiety center |
Glucostats Send inhibition signal to the hunger center and suppress it |
|
|
Ghrelin |
Hunger hormone Decrease after a meal |
|
|
Leptin |
Fat Suppress hunger Affect the arcuate nuclei Inhibit neurologic Y neurons |
|
|
Pyy |
Suppress hunger |
|
|
Control of food intake |
Lipostatic hypothesis- inhibit Glucostatic hypothesis- inhibit Thermostat hypothesis- decrease temperature increase hunger increase temperature decrease hunger Gut peptide hypothesis- inhibit |
|
|
Degradiation of the cathecholamines |
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) Cathechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) |
|
|
GAS general adaptation syndrome |
Epinephren nor epinephrine |
|
|
Degradation of catecholamines |
Monoamine oxidase Cathechol O methytransferase |
|
|
Hormone synthesis |
Peptide- RER stored in vesicles and release by exocitosis Steroid- Smooth ER diffuse across the plasma into the blood |
|
|
ADH stimulation |
Sleep Stress Exercise Pain Morphin |
|
|
Amylin |
S ecreated from the bets cells in the islets of langerhan Inhibit the secreation of glucagon Slow the emptying of the stomach |
|
|
Storage and exocytosis of insulin |
Stored in granules complex with zinc Calcium dependent |

