![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
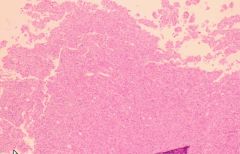
Pituitary Adenoma
|
sporadic, may be associated w/ Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome
May store/secrete any combination of hormones Micro<1cm Macro>1cm -->hyperfunction, visual changes, oculomotor palsy, hypothalamus invasion |
|
|
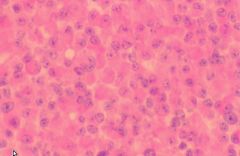
pituitary adenoma
|
sporadic, may be associated w/ Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome
May store/secrete any combination of hormones Micro<1cm Macro>1cm -->hyperfunction, visual changes, oculomotor palsy, hypothalamus invasion |
|
|
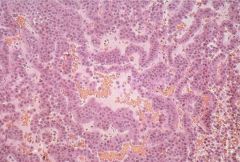
Pituitary Adenoma
|
sporadic, may be associated w/ Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome
May store/secrete any combination of hormones Micro<1cm Macro>1cm -->hyperfunction, visual changes, oculomotor palsy, hypothalamus invasion |
|
|
hypopituitarism
|
compression by tumor
Sheehan Syndrome - post partum pituitary infarct Pituitary Apoplexy - infarct of adenoma (presents w/ headache & visual changes) Trauma Inflammation Iron Deposition (hemochromatosis) Isolated Hormone Deficiencies GH (Kallmann Syndrome) End organ resistance (Laron Syndrome) Empty Sella syndrome (herniation) |
|
|
|
Lactotrope Adenoma (Prolactinoma)
|
Most common
may show amyloid and psammoma bodies (spherical calcified structures) females: amenorrhea, galactorrhea, infertility males: decreased libido, erectile dysfunction TX: Bromocriptine (DA agonist) shrinks tumor |
|
|
|
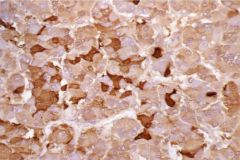
Somatotrope Adenoma (GH)
|
prior to epiphyseal closure - Gigantism
after epiphyseal closure - Acromegaly Acromegaly: course facies & hair, enlarged hands, feet, head, & organs, headache, musculoskeletal symptoms, peripheral neuropathy, DM, hypercalciuria, hyperprolactinemia TX: surgery, somatostatin (GH antagonist) |
|
|
Corticotroph Adenoma (ACTH)
|
increase proopiomelanocortin increases ACTH, lipocortin, MSH, endorphins (all cleaved from precursor)
Cushing's Disease Nelson's Syndrome - rapidly growing corticotroph adenoma following adrenalectomy for cushings |
|
|
|
Gonadotrope Adenoma (FSH & LH)
|
more common in men, causes testosterone suppression and hypogonadism
|
|
|
|
Thyrotropin Adenoms (TSH)
|
Least common, causes hyperthyroidism, goiter and/or pit mass lesions
|
|
|
|
nonfunctional adenomas
|
null cell, oncocytoma, silent
|
|
|
|
Central Diabetes Insipidus
|
ADH deficiency --> polydypsia, polyuria
caused by: sporadic mutations, familial, tumors, inflammatory processes (sarcoid) |
|
|
|
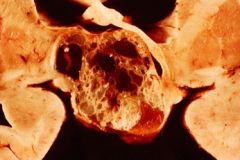
Craniopharyngioma
|
cystic supersellar mass
squamous cells from Rafke's pouch kids, men/women 50s-60s compression symptoms or variety of hormonal symptoms |
|
|
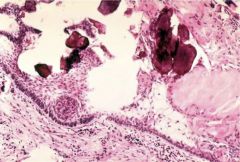
Craniopharyngioma
|
cystic supersellar mass
squamous cells from Rafke's pouch kids, men/women 50s-60s compression symptoms or variety of hormonal symptoms |
|
|
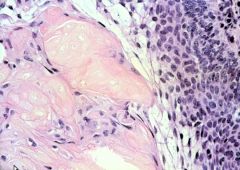
craniopharyngioma
|
cystic supersellar mass
squamous cells from Rafke's pouch kids, men/women 50s-60s compression symptoms or variety of hormonal symptoms |
|

|
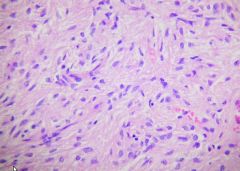
acromegaly
|
result of a somatotrope adenoma after epiphyseal closure
coarse facies, enlargement of hands, feet, head, internal organs headache, musculoskeletal symptoms, peripheral neuropathy, DM, hyperCa, Hyperprolactinemia Tx: surgery, somatostatin |
|
|
Posterior Pituitary
|
Neurohypophysis
from evagination of floor of the diencephalon axon terminals from paraventricular & supraoptic nuclei vasopressin & oxytocin |
|
|
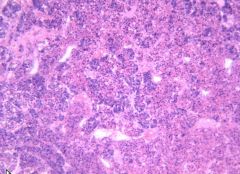
anterior pituitary
|
|
|
|
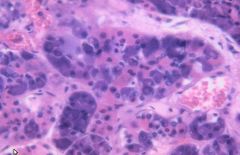
anterior pituitary
|
|
|
|
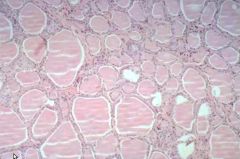
Thyroid
|
T4 - deiodinated in periphery
T3 - regulates gene transcription, increased thermogenesis, increased metabolic rate, increased gluconeogenesis, increased glycogenolysis |
|
|
Goiter
|
Nontoxic goiter
enlargement not associated w/ functional, inflammatory, or neoplastic alterations. may progress to toxic multinodular goiter TX: thyroid hormone, decrease TSH, radioactive iodine or surgery if compression |
|
|
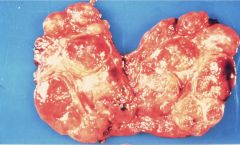
Nodular Goiter
|
more common >50y/o, female
toxic = functional, will cause hyperthyroid unresponsive to TH administration, presents similar to toxic adenoma, T3/T4 mildly elevated |
|
|
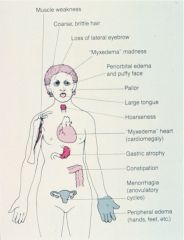
Hypothyroid
|
defective synthesis of thyroid hormone (compensatory goiter), iatrogenic, inadequate TSH or TRH
effects: myxedema, easy bruise, lethargy, confusion, agitation, decrease CO, dilated cardiomyopathy, increase PVR, constipation, anovulatory (female), erectile dysfunction & oligospermia (male) |
|
|
Nodular Goiter
|
more common >50y/o, female
toxic = functional, will cause hyperthyroid unresponsive to TH administration, presents similar to toxic adenoma, T3/T4 mildly elevated |
|
|
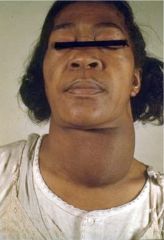
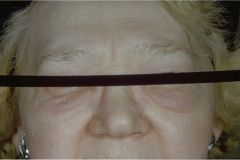
Hypothyroidism (periorbital edema)
|
defective synthesis of thyroid hormone (compensatory goiter), iatrogenic, inadequate TSH or TRH
effects: myxedema, easy bruise, lethargy, confusion, agitation, decrease CO, dilated cardiomyopathy, increase PVR, constipation, anovulatory (female), erectile dysfunction & oligospermia (male) |
|
|
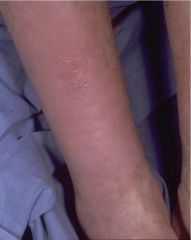
hypothyroid (myxedema)
|
defective synthesis of thyroid hormone (compensatory goiter), iatrogenic, inadequate TSH or TRH
effects: myxedema, easy bruise, lethargy, confusion, agitation, decrease CO, dilated cardiomyopathy, increase PVR, constipation, anovulatory (female), erectile dysfunction & oligospermia (male) |
|
|
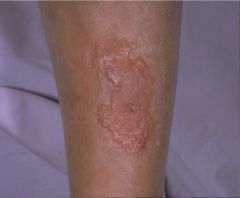
hypothyroid (myxedema)
|
defective synthesis of thyroid hormone (compensatory goiter), iatrogenic, inadequate TSH or TRH
effects: myxedema, easy bruise, lethargy, confusion, agitation, decrease CO, dilated cardiomyopathy, increase PVR, constipation, anovulatory (female), erectile dysfunction & oligospermia (male) |
|
|
Congenital Hypothyroidism (Cretinism)
|
endemic, sporadic, familial
within first weeks of life: apathy, lethargy, enlarged abdomen, decreased body temp, anemia, dilated heart, mental retardation, stunted growth TX: TH replacement (early can prevent) |
|
|
|
Primary Hypothyroidism
|
5th-6th decade, females, circulating thyroid antibodies
end stage autoimmune thyroiditis? |
|
|
|
Hyperthyroidism
|
increased TSH (rare), abnormal stimulation (Graves), ectopic thyroid tissue (rare), thyroiditis before progression to hypo, Goitrous
|
|
|
|
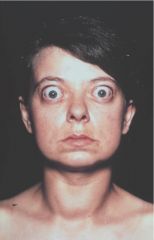
Graves Disease (Lid Lag)
|
Hyperthyroidism, diffuse goiter, exophthalmos
anti-TSH receptor antibodies (Yersinia Enterocolitica?) Histo: papillary projections of epithelium into follicles w/ scalloped borders, lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate Symptoms: nervous, tremor, weak, weight loss, heat intolerance, palpitations, exophthalmos, Graves dermopathy Dx: incresed Iodine uptake, elevated T3 & T4 Tx: antithyroid meds, radioactive I2, corticosteroids, adrenergic antagonists |
|
|
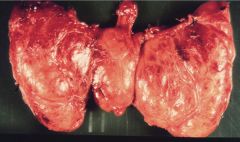
Graves (diffusely enlarged thyroid)
|
Hyperthyroidism, diffuse goiter, exophthalmos
anti-TSH receptor antibodies (Yersinia Enterocolitica?) Histo: papillary projections of epithelium into follicles w/ scalloped borders, lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate Symptoms: nervous, tremor, weak, weight loss, heat intolerance, palpitations, exophthalmos, Graves dermopathy Dx: incresed Iodine uptake, elevated T3 & T4 Tx: antithyroid meds, radioactive I2, corticosteroids, adrenergic antagonists |
|
|
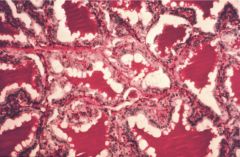
Graves (note scalloped borders of follicles)
|
Hyperthyroidism, diffuse goiter, exophthalmos
anti-TSH receptor antibodies (Yersinia Enterocolitica?) Histo: papillary projections of epithelium into follicles w/ scalloped borders, lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate Symptoms: nervous, tremor, weak, weight loss, heat intolerance, palpitations, exophthalmos, Graves dermopathy Dx: incresed Iodine uptake, elevated T3 & T4 Tx: antithyroid meds, radioactive I2, corticosteroids, adrenergic antagonists |
|
|
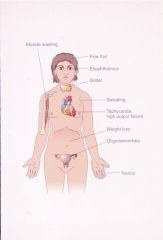
Graves
|
Hyperthyroidism, diffuse goiter, exophthalmos
anti-TSH receptor antibodies (Yersinia Enterocolitica?) Histo: papillary projections of epithelium into follicles w/ scalloped borders, lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate Symptoms: nervous, tremor, weak, weight loss, heat intolerance, palpitations, exophthalmos, Graves dermopathy Dx: incresed Iodine uptake, elevated T3 & T4 Tx: antithyroid meds, radioactive I2, corticosteroids, adrenergic antagonists |
|
|
Treated Graves
|
|
|
|
Toxic Adenoma
|
hyperfunctioning nodule
rare Tx w/ radioactive iodine and/or surgery |
|
|
|
Hypersecretion of TSH
|
thyrotropin adenoma (trophoblastic tumor)
|
|
|
|
Thyroiditis
|
Hashimoto's - cell mediated & humoral response against TSH receptors
Subacute (DeQuervian, Granulomatous, Giant Cell) - post URI Silent - post partum, anti-thyroid peroxidase antibodies, resolves in months Riedel - fibrosis |
|
|
|
Toxic Adenoma
|
hyperfunctioning nodule
rare Tx w/ radioactive iodine and/or surgery |
|
|
|
Hypersecretion of TSH
|
thyrotropin adenoma (trophoblastic tumor)
|
|
|
|
Thyroiditis
|
Hashimoto's - cell mediated & humoral response against TSH receptors
Subacute (DeQuervian, Granulomatous, Giant Cell) - post URI Silent - post partum Riedel - fibrosis |
|
|
|
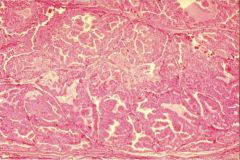
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
|
Cell mediated & humoral response against thyroid microsomal peroxidase, thyroglobulin, & TSH receptor, genetic predisposition
Gradual Goiter development Hypothyroid Hyperthyroid rare (Hashitoxicosis) elevated TSH, circulating antibodies Histo: lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, destruction of follicles, Hurthle (Askanazy) cell metaplasia Tx: Hormone Replacement |
|
|
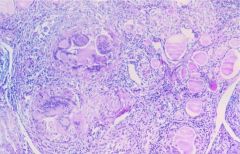
DeQuervain, Granulomatous, Giant Cell Thyroiditis (more names = more enjoyment garnered from studying)
|
following viral URI, granulomatous inflammation, transient hyperthyroidism w/ follicle destruction
|
|
|
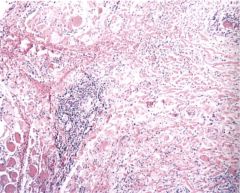
Riedel Thyroiditis
|
Dense fibrosis of thyroid
associated w/ extrathyroid fibrosis (retroperitoneum, medisatinum) histo: dense hylanized tissue w/ chronic inflammatory infiltrate |
|
|
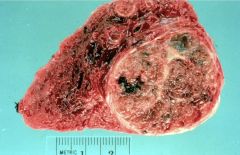
Follicular Adenoma
|
Most common thyroid tumor
Benign neoplasm, follicular differentiation, "cold", many histologic variants |
|
|
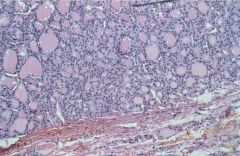
Follicular Adenoma
|
Most common thyroid tumor
Benign neoplasm, follicular differentiation, "cold", many histologic variants |
|
|
Thyroid Carcinoma
|
Most common malignant endocrine tumor
pathogenesis: Iodine excess, radiation |
|
|
|
|
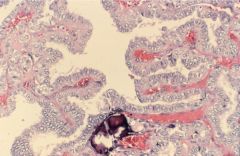
Papillary Carcinoma
|
most common variant
Histo: variable morphology, orphan annie nuclei, pseudonuclear inclusions, nuclear grooves, psammoma bodies lymphatic spread RET oncogene reasrrangement Excellent prognosis |
|
|
Thyroid Carcinoma
|
Most common malignant endocrine tumor
pathogenesis: Iodine excess, radiation |
|
|
|
Papillary Carcinoma
|
most common variant
Histo: variable morphology, orphan annie nuclei, pseudonuclear inclusions, nuclear grooves, psammoma bodies lymphatic spread RET oncogene reasrrangement Excellent prognosis |
|
|
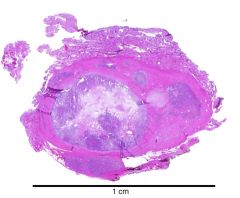
Follicular Carcinoma
|
purely follicular, resembles follicular adenoma but w/ CAPSULE INVASION
blood born mets prognosis dependent on invasiveness |
|
|
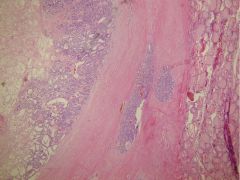
Follicular carcinoma (capsular invasion)
|
purely follicular, resembles follicular adenoma but w/ CAPSULE INVASION
blood born mets prognosis dependent on invasiveness |
|
|
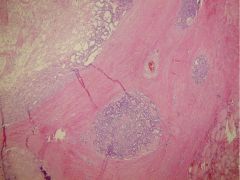
Follicular Carcinoma (Capsular invasion)
|
purely follicular, resembles follicular adenoma but w/ CAPSULE INVASION
blood born mets prognosis dependent on invasiveness |
|
|
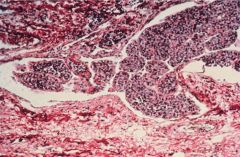
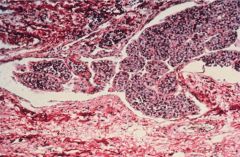
Follicular Carcinoma (bone metastasis)
|
purely follicular, resembles follicular adenoma but w/ CAPSULE INVASION
blood born mets prognosis dependent on invasiveness |
|
|
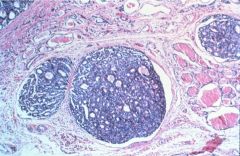
follicular carcinoma
|
purely follicular, resembles follicular adenoma but w/ CAPSULE INVASION
blood born mets prognosis dependent on invasiveness |
|
|
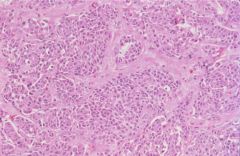
Follicular Carcinoma
|
|
|
|
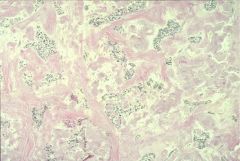
Medullary Carcinoma
|
derived from C cells (hyperplasia is precursor lesion)
20% familial (MEN 2), RET oncogene produces calcitonin (possible ACTH, glucagon, insulin, HCG, VIP, serotonin) histo: solid sheets of polygonal granular cells w/ amyloid |
|
|
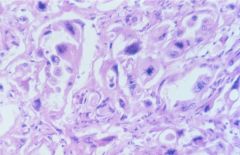
Medullary Carcinoma
|
derived from C cells (hyperplasia is precursor lesion)
20% familial (MEN 2), RET oncogene produces calcitonin (possible ACTH, glucagon, insulin, HCG, VIP, serotonin) histo: solid sheets of polygonal granular cells w/ amyloid |
|
|
Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma
|
Rapidly Fatal
50% have hx of longstanding goiter many had prior lower grade neoplasms histo: large pleomorphic cells not resembling thyroid |
|
|
Lymphoma
|
95% B cell tumors
arise in setting of chronic thyroiditis |
|
|
|
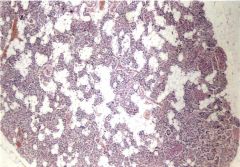
parathyroid
|
typically 4 glands
functionality shown by ratio of adipose to glandular tissue Chief cells - PTH clear cells - glycogen oxyphil cells - mitochondria |
|
|
Hypoparathyroidism
|
iatrogenic most common cause, idiopathic & familial forms
Hypocalcemia --> tingling, muscle cramps, convulsions Tx: Ca & Vit D PseudohypoPT - end organ resistance (Albright's Hereditary Osteodystrophy - short stature, obese, mental retardation, subcutaneous calcification, bone congenital abnormalities) PseudopseudohypoPT - similar to Albright's w/o abnormal cAMP response to PTH |
|
|
|
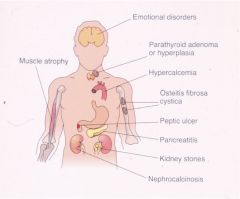
hyperparathyroidism
|
Increased serum Ca++, Osteitis fibrosa cystica, nephrocalcinosis (stones), polyuria, mental status change, muscle weak, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, HTN
PT Hyperplasia, PT Adenoma, PT Carcinoma Secondary (to renal failure) - increased PTH b/c Ca++ lost through kidneys Tertiary - Secondary continuing after renal transplant |
|
|
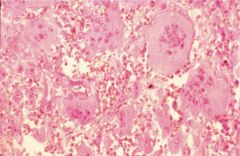
Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
|
following hyperparathyroidism
|
|
|
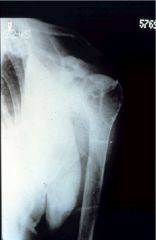
Osteitis Fibrosa Cystica
|
following hyperparathyroidism
|
|
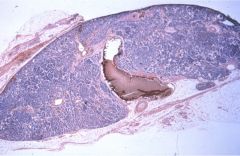
|
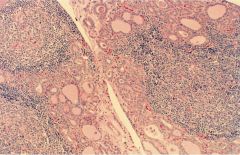
PT Hyperplasia (note decreased amount of adipose tissue)
|
1/3 MEN1 and 2A
1/3 show monoclonality lack of cellular pleomorphism symptoms: osteitis fibrosa cystica, neprocalcinosis, renal stones, polyuria, mental status changes, muscle weak, peptic ulcer, chronic pancreatitis, HTN |
|
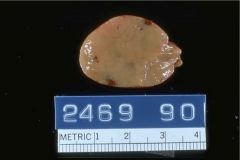
|
Parathyroid Adenoma
|
Sporadic or MEN1
histo: sheets of chief cells w/ rim of normal tissue other glands atrophic (this one doing all the work) |
|
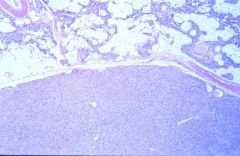
|
Parathyroid Adenoma
|
Sporadic or MEN1
histo: sheets of chief cells w/ rim of normal tissue other glands atrophic (this one doing all the work |
|
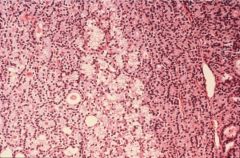
|
Parathyroid Adenoma
|
Sporadic or MEN1
histo: sheets of chief cells w/ rim of normal tissue other glands atrophic (this one doing all the work |
|
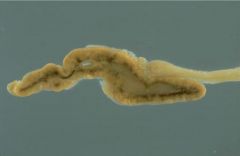
|
Normal Adrenal Gland
|
Cortex (outershell)
Zona Glomerulosa (aldosterone) Zona Fasiculata (cortisol) Zona Reticularis (androgens)(dark band) Medulla (neuroectoderm)(Epi, NE, DA) |
|
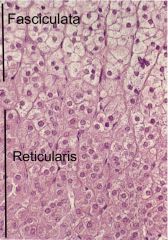
|
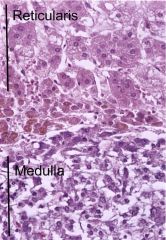
normal adrenal
|
Cortex (outershell)
Zona Glomerulosa (aldosterone) Zona Fasiculata (cortisol) Zona Reticularis (androgens)(dark band) Medulla (neuroectoderm)(Epi, NE, DA) |
|
|
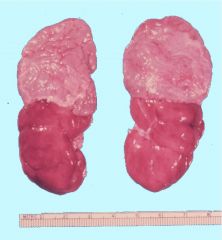
Normal Adrenal
|
Cortex (outershell)
Zona Glomerulosa (aldosterone) Zona Fasiculata (cortisol) Zona Reticularis (androgens)(dark band) Medulla (neuroectoderm)(Epi, NE, DA) |
|
|
Adrenal Hyperplasia
|
Congenital
21 Hydroxylase (90%) --> impaired cortisol production w/ excess androgens --> premature epiphyseal closure, virilization, salt wasting 11 beta Hydroxylase deficiency (5%) --> decreased cortisol w/ virilization, Na retention, HTN |
|
|
Acute Adrenal Insufficiency
|
abrupt withdrawal of corticosteroid therapy
stress Waterhouse-Fridrichsen symptoms: HOTN, shock, abd & back pain --> pituitary damage, corticotropin deficiency (autoimmune), hyperpigmentation |
|
|

|
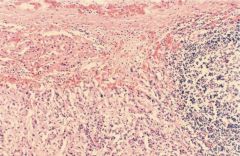
Adrenal Hyperplasia
|
Congenital
21 Hydroxylase (90%) --> impaired cortisol production w/ excess androgens --> premature epiphyseal closure, virilization, salt wasting 11 beta Hydroxylase deficiency (5%) --> decreased cortisol w/ virilization, Na retention, HTN |
|
|
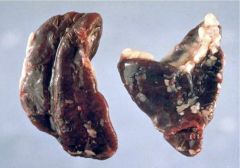
Addison's Disease
|
Primary Adrenal Cortical Insufficiency (#1 in US, TB #1 in world)
symptoms: weakness, anorexia, skin pigmentation, HOTN, GI, personality changes, low Na, high K, lymphocytosis, elevated eosinophils |
|
|
Waterhouse-Fridrichsen
|
meningococcal or pseudomonal septicemia w/ adrenal hemorrhage
|
|
|
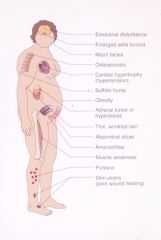
Cushing Syndrome
|
Hypercorticolism
most commonly iatrogenic Cushing Dz (pituitary adenoma realeasing ACTH) Other paraneoplastic causes symptoms: truncal obesity, atrophic skin, osteoposis, muscle weak, virilization, diabetes, personality changes, lymphopenia |
|
|
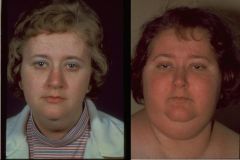
Cushings
|
Hypercorticolism
most commonly iatrogenic Cushing Dz (pituitary adenoma realeasing ACTH) Other paraneoplastic causes symptoms: truncal obesity, atrophic skin, osteoposis, muscle weak, virilization, diabetes, personality changes, lymphopenia |
|
|
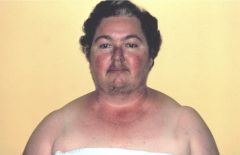
Cushings
|
Hypercorticolism
most commonly iatrogenic Cushing Dz (pituitary adenoma realeasing ACTH) Other paraneoplastic causes symptoms: truncal obesity, atrophic skin, osteoposis, muscle weak, virilization, diabetes, personality changes, lymphopenia |
|
|
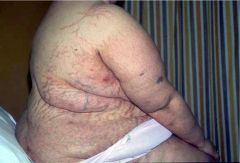
Cushings
|
Hypercorticolism
most commonly iatrogenic Cushing Dz (pituitary adenoma realeasing ACTH) Other paraneoplastic causes symptoms: truncal obesity, atrophic skin, osteoposis, muscle weak, virilization, diabetes, personality changes, lymphopenia |
|
|
Adrenal Tumors
|
hyperplasia doesn't lead to adenoma
adenomas hormonally active 80% adrenal cortical carcinomas functions poor prognosis |
|
|
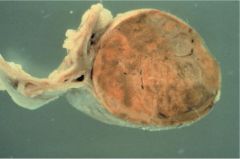
|
Adrenal Adenoma
|
|
|
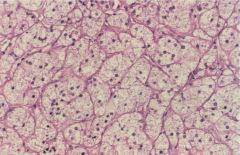
|
adrenal adenoma
|
|
|
|
Adrenal Tumors
|
hyperplasia doesn't lead to adenoma
adenomas hormonally active 80% adrenal cortical carcinomas functions poor prognosis |
|
|
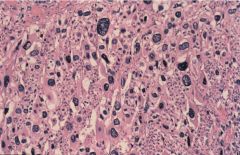
|
Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma
|
|
|
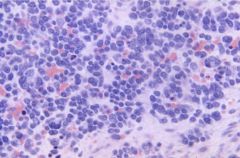
|
Adrenal Neuroblastoma
|
originates in adrenal medulla or SNS chain
10% childhood cancers, 15% childhood caner deaths HSR on chromosome 2 amplifies N-myc TRK, <2y/o, dissemination, extra adrenal origin = good prognosis |
|
|
Primary Aldosteronism (Conn Syndrome)
|
Aldosteronomas (90%) or hyperplastic adrenal
symptoms: hypoK, HTN, weak, polyuria, polydispsia, decreased renin Tx: surgery, Na restriction, spironolactone (aldosterone antagonist) |
|
|
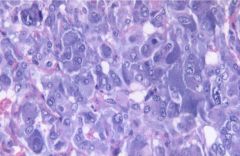
|
pheochromocytoma
|
sporadic or MEN2, NF1, vHL, etc --> need to rule out these etiologies in dx
histo: sheets, trabeculae, Zellballen pattern symptoms: HTN, anxiety, hypervent, convulsions, heat intolerance, increased urinary catecholamine metabolites Tx: surgery + adrenergic antagonists |
|
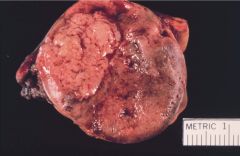
|
Pheochromocytoma
|
sporadic or MEN2, NF1, vHL, etc --> need to rule out these etiologies in dx
histo: sheets, trabeculae, Zellballen pattern symptoms: HTN, anxiety, hypervent, convulsions, heat intolerance, increased urinary catecholamine metabolites Tx: surgery + adrenergic antagonists |
|
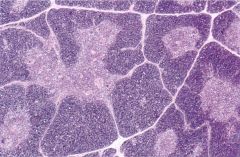
|
Thymus
*next slide name the developmental abnormalities |
developmental abnormalities --> immunodeficiency
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (bubble boy) - B & T cell dysfunction DiGeorge Syndrome - thymic, parathyroid agenesis + heart defects Wiscott-Aldrich Syndrome - X recessive, thymic hypoplasia, eczema, thrombocytopenia Ataxia Telangiectasia - AR, no Hassal's corpuscles or epithelial differentiation |
|
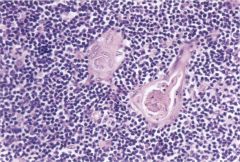
|
Thymus
*next slide name the developmental abnormalities |
developmental abnormalities --> immunodeficiency
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (bubble boy) - B & T cell dysfunction DiGeorge Syndrome - thymic, parathyroid agenesis + heart defects Wiscott-Aldrich Syndrome - X recessive, thymic hypoplasia, eczema, thrombocytopenia Ataxia Telangiectasia - AR, no Hassal's corpuscles or epithelial differentiation |
|
|
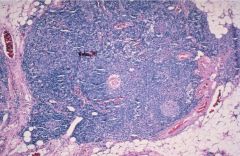
Thymic Hyperplasia
|
Lymphoid follicles in thymus
myasthenia gravis in 2/3 associated w/ other autoimmune disorders |
|
|
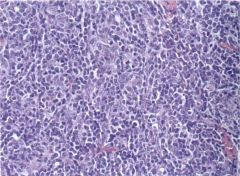
Thymoma
|
neoplasm of epithelial cells
10% of myasthenics other autoimmune disorders associated |
|
|
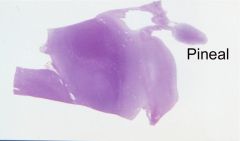
Pineal gland
|
melatonin major secretory product (secreted in darkness)
sleep & mating regulator? serotonin & other peptides released |
|
|
pineal
|
melatonin major secretory product (secreted in darkness)
sleep & mating regulator? serotonin & other peptides released |
|
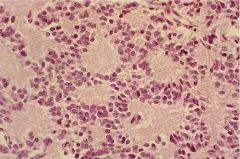
|
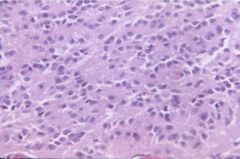
pineocytoma
|
|
|
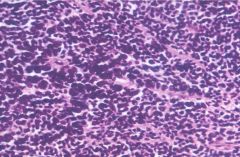
|
pineoblastoma
|
|
|
|
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
|
Autosomal Dominant
MEN 1 (Wermer's Syndrome) - pit adenoma, PT hyperplasia, pancreatic islet tumor MEN 2A (Sipple's Syndrome) - 95% MEN 2, medullary thyroid carcinoma, pheochromocytoma, PT hyperplasia & adenoma, other neural crest MEN 2B - similar to MEN2A except PT uncommon, ganglioneuromas Genetics: RET mutation |
|

